Leucopelargonidin
Leucopelargonidin is a colorless chemical compound related to leucoanthocyanins. It can be found in Albizia lebbeck (East Indian walnut), in the fruit of Anacardium occidentale (Cashew), in the fruit of Areca catechu (Areca nut), in the fruit of Hydnocarpus wightiana (Hindi Chaulmoogra), in the rhizome of Rumex hymenosepalus (Arizona dock), in Zea mays (Corn) and in Ziziphus jujuba (Chinese date).[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
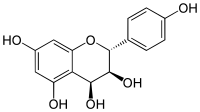
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S)-Flavan-3,4,4′,5,7-pentol | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4S)-2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-3,4,5,7-tetrol | |
| Other names
(+)-Leucopelargonidin cis-3,4-Leucopelargonidin Leucopelargonidine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O6 | |
| Molar mass | 290.271 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
(+)-Leucopelargonidin can be synthesized from (+)-aromadendrin by sodium borohydride reduction.[2]
Metabolism
Dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase uses cis-3,4-leucopelargonidin and NADP+ to produce (+)-aromadendrin, NADPH, and H+.
Leucoanthocyanidin reductase transforms cis-3,4-leucopelargonidin into afzelechin.
References
- Leucopelargonidin on liberherbarum.com
- Heller, Werner; Britsch, Lothar; Forkmann, Gert; Grisebach, Hans (1985). "Leucoanthocyanidins as intermediates in anthocyanidin biosynthesis in flowers of Matthiola incana R. Br". Planta. 163 (2): 191–196. doi:10.1007/BF00393505. PMID 24249337. S2CID 20854538.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.