Languages of Namibia
Namibia, despite its scant population, is home to a wide diversity of languages, from multiple language families: Germanic, Bantu, and the various Khoisan families. When Namibia was administered by South Africa, Afrikaans, German, and English enjoyed an equal status as official languages. Upon Namibian independence in 1990, English was enshrined as the nation's sole official language in the constitution of Namibia. German and Afrikaans were stigmatised as relics of the colonial past,[1] while the rising of Mandela's Youth League and the 1951 Defiance Campaign spread English among the masses as the language of the campaign against apartheid.[2]
| Languages of Namibia | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Official | English |
| National | Afrikaans, German, Otjiherero, Khoekhoegowab, Oshiwambo, RuKwangali, Setswana, siLozi |
| Recognised | !Kung, Gciriku, Thimbukushu |
| Vernacular | Namlish |
| Minority | Fwe, Kuhane, Mbukushu, Yeyi, Naro, ǃXóõ ǂKxʼauǁʼein |
| Signed | Namibian Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | |
Language demographics
.jpg.webp)
The most widely spoken languages used in households are Oshiwambo dialects, by 49% of the population; Khoekhoegowab by 11%; Afrikaans by 10%; RuKwangali by 9%; and Otjiherero by 9%.[3] Other native languages include the Bantu languages Setswana, Gciriku, Fwe, Kuhane, Mbukushu, Yeyi; and the Khoisan Naro, ǃXóõ, Kung-Ekoka, ǂKxʼauǁʼein and Kxoe.[4] English, the official language, is spoken by 3% of people as their native language. Portuguese was spoken by 4–5% of the total population, i.e. 100,000 people, made up mostly of the Angolan community in 2014.[5] The number of Angolans in Namibia declined from 2014 to 2015, affected by the neighbouring country's economic crisis.[6] Among the white population, 60% speak Afrikaans, 32% German, 7% English, and 1% Portuguese.
Indigenous languages are included in the school syllabus at primary level. From secondary level English is the medium of instruction. English is the main lingua franca in the north and Afrikaans in the south. English and Afrikaans are both widely spoken in Windhoek.[7]
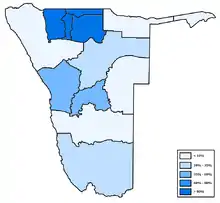 Distribution of Oshiwambo
Distribution of Oshiwambo_in_Namibia.png.webp) Distribution of Khoekhoegowab (also known as Nama or Damara)
Distribution of Khoekhoegowab (also known as Nama or Damara)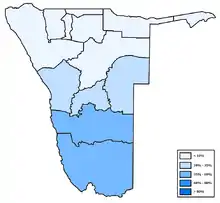 Distribution of Afrikaans
Distribution of Afrikaans
 Distribution of Otjiherero
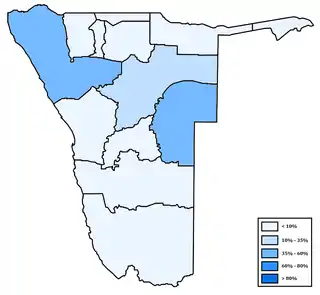
Distribution of Otjiherero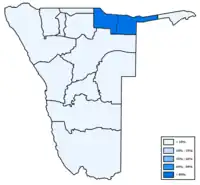 Distribution of Kavango languages
Distribution of Kavango languages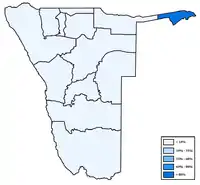 Distribution of Zambezi[8] languages
Distribution of Zambezi[8] languages
Languages most often spoken in Namibian households
| Main language | 2001 | 2011 |
|---|---|---|
| Oshiwambo | 48.5 | 48.9 |
| Khoekhoegowab | 11.5 | 11.3 |
| Afrikaans | 11.4 | 10.4 |
| Otjiherero | 7.9 | 8.6 |
| RuKwangali | 9.7 | 8.5 |
| siLozi | 5.0 | 4.8 |
| English | 1.9 | 3.4 |
| German | 1.1 | 0.9 |
| San | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Other | 1.8 | 2.4 |
References
- "Namibia Travel Guide". Retrieved 8 July 2010.
- Brutt-Griffler, J. (2002). World English: a study of its development. Multilingual Matters, p.165. ISBN 1853595772
- "Languages Spoken - GRN Portal". www.gov.na. Archived from the original on 2017-03-06. Retrieved 2018-04-22.
- Lewis, M. Paul, ed. (2009). Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Sixteenth edition. SIL International.
- "Portuguese to be introduced in schools". The Namibian. Archived from the original on 24 February 2014. Retrieved 19 February 2014.
- Marketing, Intouch Interactive. "Angolan tourists on the decline - Tourism - Namibian Sun". Retrieved 2018-04-22.
- Discrimination through language in Africa?: perspectives on the Namibian experience. Walter de Gruyter, p. 315. ISBN 311014817X
- "Zambezi Region | Caprivi Strip | Namibia". www.namibian.org. Retrieved 2018-04-22.
- "2001 Census" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on Sep 3, 2014.
- "2011 Census" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on Oct 2, 2013.
