Juanacatlán
Juanacatlán (Spanish pronunciation: [xwanakaˈtlan]) is a town and municipio (municipality) in the central region of the Mexican state of Jalisco.[2]
Juanacatlán
Xonacatlan | |
|---|---|
municipality | |
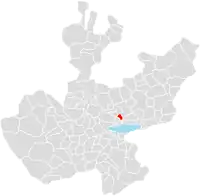 | |
 Juanacatlán | |
| Coordinates: 20°30′N 103°10′W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Government | |
| • Municipal president | Francisco de la Cerda Suárez PAN |
| Area | |
| • Total | 138.1 km2 (53.3 sq mi) |
| • Town | 3.01 km2 (1.16 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • Total | 30,855 |
| • Density | 220/km2 (580/sq mi) |
| • Town | 9,626 |
| • Town density | 3,200/km2 (8,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central Standard Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (Central Daylight Time) |
| Website | |
Origin of name
Juanacatlán gets its name from the Nahuatl word "Xonacatlan", which means place abundant in onions or onion place (from "Xonaca" for onions and "Tlan" for place).[3]
The hieroglyph of Juanacatlán includes the symbol of the Tlaxcala, representing the battles and the places where the Tlaxcaltecans went with the Nuño de Guzmán expedition, after the conquest of Mexico.
Seal
The seal of Juanacatlán is based on the region's economic activities and history, and is divided into four parts:
- In the center: Nahuatl ideogram of Tlaxcala, which signifies “Xonacatlan” in the indigenous vocabulary, from which is derived the name of the population.
- Upper left: This section includes symbols of the principal economic activity of the region, agriculture, and presents the basic products produced: wheat and corn, against a base of stone, and the image of Papantón hill, a monumental figure from the countryside that dominates the municipio.
- Upper right: at the base are the arches of the first public building of the area, that of the Municipal President, and in front, the Cross of Cantera, monument upon whose rectangular faces are inscribed the date of the foundation of the region's population.
- Lower part: As a memory of the past, the celebrated waterfall of El Salto de Juanacatlán, today almost gone, but once a monument that gave the region national recognition.
The leaves that surround the seal are identical to those in the seal of Jalisco, whose people Juanacatlán joins as a national entity. The seal was approved by H. Cabildo de Juanacatlán in 1993. Its creation was the responsibility of the teacher María de Lourdes Torres Alaniz, from the Municipality of Juanacatlán.
History
Although "place of onions" has been claimed to be a necessarily inappropriate translation of the indigenous name (as the onions were brought by the conquistadors), the origin of the name was in fact a different, native, plant- a type of jicama or cebollita as is commonly known in the region. The Jalisco writer Juan José Arreola translates the name as "place of the good onions".
In prehispanic times, the Xonacatlan region was part of the Tololotlán kingdom, which was itself part of the feudal Tonalá kingdom, one of four kingdoms that composed the Chimalhuacana federation.
In 1529, Nuño de Guzmán arrived in the area, while conquering the kingdoms of Tonalá and Xalisco. Later, the people of Coyula, Juanacatlán, Tatepozco and Tololotlán (because their populations were so small) were defeated. On March 25, 1530, Nuño de Guzmán took formal possession of the territory in the name of the Spanish monarch.
Beginning in 1531, the natives of the Xonacatlán region were converted and evangelized in the Christian faith by the religious order of San Francisco: Friar Antonio de Segovia, Fray Juan de Padilla, Fray Andrés de Córdova and Juan de Badillo. That same year, Father Segovia founded the convent of Our Lady of the Assumption in Tetlán, near modern-day Guadalajara.[3]
Geography
The municipio of Juanacatlán in the east-central part of the state, between 20º24’00’’ and 20º32’15’’ northern latitude and between 103º03’10’’ and 103º15’00’’ west latitude, at an altitude of 1,530m.
It is bordered to the north by Tonalá and Zapotlanejo, to the south by Chapala and Poncitlán; to the east by Zapotlán del Rey, and to the west by Ixtlahuacán de los Membrillos, El Salto, and Tlajomulco de Zuñiga.
Climate
The climate of the municipio is semi-dry in winter, with dry summers, and somewhat hot without a defined winter pattern. The average annual temperature is 20.1 °C, and the average annual precipitation is 819.1 mm, with a rainy season from June to August.
The dominant winds are from the east, west, and south. There's an average of 12 freezing days per year.
Hydrography
The region's hydrography includes the Santiago River, which surrounds much of the town, and the streams that flow in the rainy season: the Colorado, Buenavista Los Corteses, La Cruz, la Tinaja, El Gallo, El Puerto, Hondo, Miseria, Chiquito, Lomelines, and Limoncillo.
There is also the Santiago River Channel and the irrigation channel deriving from the Corona Dam.
The municipio's water resources belong to the town Lerma-Chapala-Santiago basin and the Verde-Atotonilco sub-basin. Since companies appearing in the industrial corridor of El Salto have polluted the waters, the waterfall that once attracted hundreds of visitors is now a hotbed of infection, with a terrible odor, worse in times of heat. This has led to the appearance of respiratory diseases, various cancers, and heart disease. The Rio Lerma and Rio Santiago have become the most serious threats among the populations of El Salto and Juanacatlán.[4]
Many people of Jalisco blame former President Vicente Fox's completed project, The El Cajón Dam, a hydroelectric dam on the Río Grande de Santiago in the Mexican state of Nayarit.[5]
Natural resources
The region benefits from a natural wealth including a 933 ha forest with species such as oak, oak, ash and Tabachines, mainly.
Its main mineral resources are sandbars. Among the species of fauna are mountain lions, rabbits, squirrels, skunks, foxes, snakes, coyotes and armadillos. The soils belong to the dominant type "Vertisol pélico" and "Regosol eútrico" and the associated soil type "Feozem háplico".
In the forested region are species such as oak, giant oak, Tabachines and ash. There are also minor species such as: guamúchil, bell, captain, tepamé, mesquite, nopal, huizache, and a variety of fruit trees.
Localities
| Name | Population (2020)[1] |
|---|---|
| La Aurora | 16,635 |
| Juanacatlán | 9,626 |
| San Antonio Juanacaxtle | 1,564 |
| Ex-Hacienda de Zapotlanejo | 967 |
| Miraflores | 449 |
| Casa de Teja | 353 |
| Rancho Nuevo (Estancia de Guadalupe) | 336 |
Economy
The region's key local crops are maize and sorghum. It breeds cattle, producing meat and milk, and breeds pigs, sheep, goats, horses, poultry meat and postura and colmenas. The main branch of industry is manufacturing.
Fishing in the Rio Santiago produces species such as catfish, lobina, carp and frog on a small scale for local consumption.
The Juanacatlán Lagoon offers a landscape worthy of admiration, for the transparency of its water and vegetation, with a surrounding forest of conifers.
The municipal seat provides financial, professional, technical, communal, social, personal and maintenance services.
Government
Municipal presidents
| Municipal president | Term | Political party | Notes |
| J. Santos Plascencia[6] | 1898 | ||
| Carlos Loza | 1901 | ||
| Cayetano Rodríguez | 1902 | ||
| J. Santos Plascencia | 1903 | ||
| Juan Bravo y Juárez | 1912 | ||
| Pedro J. Lomelí | 1913 | ||
| José Ma. Parraga | 1914 | ||
| José Ma. Parraga | 1915 | ||
| Severiano Beltrán | 1915 | ||
| Donacio Briseño | 1915 | ||
| Genaro Carrillo | 1915 | ||
| Carlos Maldonado | 1916 | ||
| Domingo Velázquez | 1916 | ||
| Domingo Velázquez | 1917 | ||
| Blas Arias | 1918 | ||
| Carlos Maldonado | 1918 | ||
| Severiano Beltrán | 1919 | ||
| Eusebio Arriaga | 1919 | ||
| Conrado Arias | 1919 | ||
| Lucio Casillas | 1920 | ||
| Domingo Velázquez | 1920 | ||
| José María Vázquez | 1920 | ||
| Francisco Vega | 1921 | ||
| José Velazco | 1921 | ||
| José Rodríguez | 1921 | ||
| Francisco Vega | 1921 | ||
| Francisco Vega | 1922 | ||
| Manuel Martínez | 1922 | ||
| Conrado Arias | 1923 | ||
| Leonardo Barba | 1923 | ||
| Leonardo Barba | 1924 | ||
| Eusebio Arriaga | 1924 | ||
| Ramón M. Torres | 1925 | ||
| Blas Casillas | 1925 | ||
| Bruno Casillas | 1925 | ||
| Alfredo A. Ibarra | 1925 | ||
| Miguel Avilés | 1927 | ||
| Blas Arias | 1927 | ||
| Alfredo A. Ibarra | 1928 | ||
| Lucio Casillas | 1930 | PNR |
|
| Lucio Casillas | 1931 | PNR |
|
| M. L. Gallardo | 1932 | PNR |
|
| José Cadena | 1933 | PNR |
|
| Catarino Barba | 1934 | PNR |
|
| Catarino Barba | 1935 | PNR |
|
| Pedro Arámbula | 1935 | PNR |
|
| Salvador Martínez | 1935 | PNR |
|
| Enrique Briseño | 1937 | PNR |
|
| Enrique Briseño | 1938 | PNR |
|
| Manuel Torres | 1938 | PRM |
|
| O.D.O.C. | 1940 | PRM |
|
| Enrique Briseño | 1940 | PRM |
|
| Ramón González Zamora | 1941 | PRM |
|
| Ramón González Zamora | 1942 | PRM |
|
| Rufino Zaragoza | 1943 | PRM |
|
| J. Jesús Morales | 1944 | PRM |
|
| Enrique Briseño Plascencia | 1945 | PRM |
|
| Enrique Briseño Plascencia | 1946 | PRI |
|
| Sebastián Valenzuela | 1947 | PRI |
|
| J. Guadalupe Pérez | 1947 | PRI |
|
| A. Cortés | 1947 | PRI |
|
| Sebastián Valenzuela | 1948 | PRI |
|
| A. Cortés | 1949 | PRI |
|
| José Zavala A. | 1949 | PRI |
|
| José Zavala A. | 1950 | PRI |
|
| José Zavala A. | 1951 | PRI |
|
| José Zavala A. | 1952 | PRI |
|
| Ramón F. Rivera | 1956 | PRI |
|
| Pedro Villalpando | 1958 | PRI |
|
| Antonio Orozco | 01-01-1959–31-12-1961 | PRI |
|
| Aurelio Franco Torres | 01-01-1962–31-12-1964 | PRI |
|
| Julián Casillas | 01-01-1965–31-12-1967 | PRI |
|
| J. Guadalupe Maldonado Hernández | 01-01-1968–31-12-1970 | PRI |
|
| J. Jesús Briseño García | 01-01-1971–31-12-1973 | PRI |
|
| Fermín García | 01-01-1974–31-12-1976 | PRI |
|
| Casiano Coronado | 01-01-1977–31-12-1979 | PRI |
|
| J. Jesús García Briseño | 01-01-1980–31-12-1982 | PRI |
|
| Esthela Cervantes de Parra[7] | 01-01-1983–31-12-1985 | PRI |
|
| Rigoberto Franco Palos | 01-01-1986–31-12-1988 | PRI |
|
| Pedro Cárdenas López[8] | 01-01-1989–1992 | PRI |
|
| Mario Venegas Vizcarra[9] | 1992–1995 | PAN |
|
| Juan Olmos Flores[10] | 1995–1997 | PAN |
|
| Alfredo Torres Ibarra[11] | 01-01-1998–31-12-2000 | PRI |
|
| Raymundo Orozco Ramírez[12] | 01-01-2001–31-12-2003 | PAN |
|
| Socorro Ramírez Márquez[13] | 01-01-2004–31-12-2006 | PAN |
|
| Ramiro Tapia Ornelas[14][15] | 01-01-2007–31-12-2009 | PRI |
|
| Lucio Carrero García[16] | 01-01-2010–30-09-2012 | PRI Panal |
Coalition "Alliance for Jalisco" |
| José Pastor Martínez Torres[17] | 01-10-2012–30-09-2015 | PRI PVEM |
Coalition "Compromise for Jalisco" |
| J. Refugio Velázquez Vallín[18] | 01-10-2015–30-09-2018 | MC |
|
| Adriana Cortés González[19] | 01-10-2018–30-09-2021 | MC |
|
| Francisco de la Cerda Suárez[20] | 01-10-2021– | PAN |
Notable people
- Saúl "Canelo" Álvarez – Mexican Boxer, Middleweight champion.
- Rigoberto Álvarez – Mexican Boxer, a contender in the Middleweight division.
References
- Citypopulation.de
- "Juanacatlán Gobierno Municipal". juanacatlan.gob.mx.
- "Gobierno municipal de Juanacatlan - Pleno del Ayuntamiento". Archived from the original on 2018-04-23. Retrieved 2018-03-19.
- "Pollution turned this Mexican river into a toxic hell".
- "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2018-03-20. Retrieved 2018-03-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "Enciclopedia de los Municipios y Delegaciones de México. Jalisco. Juanacatlán" (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Cómputo del Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco en las Elecciones de munícipes, 1982. Juanacatlán. PRI: 945 votos. Partido Demócrata Mexicano (PDM): 611 votos. Partido Socialista Unificado de México (PSUM): 319 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Resultados de la elección de munícipes, 1988. Juanacatlán. PRI: 990 votos. Partido Demócrata Mexicano (PDM): 246 votos. Coalición Cardenista Jalisciense (CCJ): 243 votos. PAN: 208 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Elección de munícipes, 1992. Juanacatlán. PAN: 1798 votos. PRI: 1709 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Elección de munícipes, 1995. Juanacatlán. PAN: 2390 votos. PRI: 1728 votos. Partido del Trabajo (PT) 416 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Resultados de la elección de munícipes, 1997. Juanacatlán. PRI: 2078 votos. PAN: 1509 votos. PRD: 852 votos. Partido Demócrata Mexicano (PDM): 300 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Resultados de la elección de munícipes del 12 de noviembre de 2000. Juanacatlán. PAN: 1994 votos. PRI: 1698 votos. PRD: 597 votos. Partido Alianza Social (PAS): 97 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Integración de votos correspondientes a cada partido por municipio, elecciones del año 2003. Juanacatlán. PAN: 1986 votos. PRI: 1651 votos. PRD: 752 votos. PVEM: 212 votos. Partido Alianza Social (PAS): 165 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Listado de presidentes municipales electos, Jalisco" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Consejo Electoral del Estado de Jalisco. CEEJ. Resultado de los cómputos municipales, 5 de julio de 2006. Juanacatlán. PRI: 2482 votos. PAN: 1894 votos. PRD-PT: 1135 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Instituto Electoral y de Participación Ciudadana del Estado de Jalisco. IEPC Jalisco. Proceso electoral 2009. Ayuntamiento de Juanacatlán. PRI-Partido Nueva Alianza (Panal): 1708 votos. Convergencia: 1592 votos. PAN: 1575 votos. PVEM: 947 votos. PRD: 188 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Instituto Electoral y de Participación Ciudadana del Estado de Jalisco. IEPC Jalisco. Integración ayuntamientos 2012. Anexo V. Juanacatlán. PRI-PVEM: 2521 votos. PAN: 1982 votos. PT-MC: 1568 votos. Partido Nueva Alianza (Panal): 389 votos. PRD: 346 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Instituto Electoral y de Participación Ciudadana del Estado de Jalisco. IEPC Jalisco. Resultados de la elección de munícipes. Proceso electoral local ordinario 2015. Integración de ayuntamientos 2015. Juanacatlán. MC: 2763 votos. PRI: 2092 votos. PAN: 1399 votos. PRD: 237 votos. Morena: 167 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Instituto Electoral y de Participación Ciudadana del Estado de Jalisco. IEPC Jalisco. Integración de ayuntamientos, 2018. Anexo 4. Juanacatlán. MC: 2778 votos. PAN: 2197 votos. PRI: 1657 votos. PT-Morena-PES: 878 votos. PVEM: 827 votos. Partido Nueva Alianza (Panal): 58 votos" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.
- "Alternativa Consultores. Resultados Electorales Jalisco 2021. Alternancia partidista por municipio: Juanacatlán: MC → PAN" (PDF) (in Spanish). Retrieved 9 December 2021.