Irritation fibroma
Irritation fibroma is a type of fibroma that occurs on the mucosa of the oral cavity.[2] Irritation fibromas are common benign tumors that are asymptomatic and resemble scarring. They are caused by prolonged irritation in the mouth, such as cheek or lip biting, rubbing from teeth, and dental prostheses.
| Irritation fibroma | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Oral fibroma, traumatic fibroma, focal intraoral fibrous hyperplasia, fibrous nodule, oral polyp |
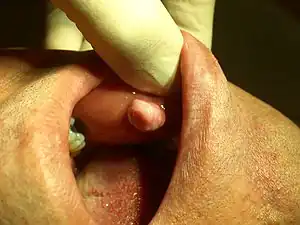 | |
| Irritation fibroma on the left cheek of a 40-year-old man. | |
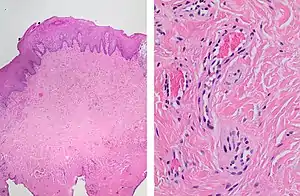 | |
| Histopathology of irritation fibroma. Low magnification (left) characteristically[1] shows a nonencapsulated nodular mass. High magnification (right) shows fibrous connective tissue with collagen bundles, and some blood vessels and fibroblasts. | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology |
| Symptoms | Palpable nodule |
| Frequency | 1–2% of adults[2] |
The fibromas are firm, smooth, and fibrous with a color usually identical to the oral mucosa but can be paler. If wounded, it may be darker. They are usually solitary and do not develop into oral cancer.
Pathophysiology
The epidermis of irritation fibromas typically exhibits enlargement (hyperplasia) and thickening of the stratum corneum (hyperkeratosis).[3] They grow outward from the surface (exophytic) and often have a distinct boundary. The base is either sessile or pedunculated.[4] Their growth is painless and slow, taking months or years, and rarely exceeding a diameter of one and a half centimeters. They are not true neoplasms, but are instead a focal increase in the amount of connective tissue. The histology of the fibromas shows dense collagen fibers, and the proliferation of mature fibroblasts and blood vessels which are dilated within the dermis of the nodule. There is slight or no infiltration of inflammatory cells.
Diagnosis
Irritation fibromas are surmised based on their clinical features[1] but a histopathological examination (such as a biopsy[2]) can be done.
Treatment
Surgical excision is available as a treatment for irritation fibromas. Though its reoccurrence is rare, it can happen if the cause of irritation continues.[4] Therefore, managing the cause is essential.[2] Irritation fibromas do not go away on their own if left untreated.
Epidemiology
Irritation fibromas can occur at any age but are most common in older individuals,[2] particularly in their fifties and sixties.[1] They are twice as common in females. One to two percent of adults have this condition.
References
- Smith MS. "Oral cavity & oropharynx - Soft tissue tumors & proliferations - Irritation fibroma". pathology Outlines. Topic Completed: 26 October 2020. Minor changes: 26 October 2020
- Dyall-Smith D (2010). "Oral (irritated) fibroma". DermNet. Retrieved 2023-08-18.
- Jiang M, Bu W, Chen X, Gu H (February 2019). "A case of irritation fibroma". Postepy Dermatologii I Alergologii. 36 (1): 125–126. doi:10.5114/ada.2019.82834. PMC 6409883. PMID 30858793.
- Lalchandani, Chahita M.; Tandon, Sandeep; Rai, Tripti S.; Mathur, Rinku; Kajal, Anupama (2020). "Recurrent Irritation Fibroma-"What Lies Beneath": A Multidisciplinary Treatment Approach". International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry. 13 (3): 306–309. doi:10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1769. ISSN 0974-7052. PMC 7450199. PMID 32904090.