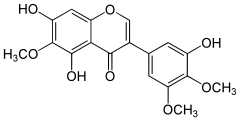
Irigenin
Irigenin is an O-methylated isoflavone, a type of flavonoid. It can be isolated from the rhizomes of the leopard lily (Belamcanda chinensis),[1] and Iris kemaonensis.[2][3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
3′,5,7-Trihydroxy-4′,5′,6-trimethoxyisoflavone | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
5,7-Dihydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.145 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H16O8 | |
| Molar mass | 360.31 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Inhibitory effects of Irigenin from the rhizomes of Belamcanda chinensis on nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 production in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Kwang Seok Ahn, Eun Jung Noh, Kwang-Hyun Cha, Yeong Shik Kim, Soon Sung Lim, Kuk Hyun Shin and Sang Hoon Jung, 2005
- Mahmooda, Umar; Kaula, Vijay K.; Jirovetzb, Leopold (December 2002). "Alkylated benzoquinones from Iris kumaonensis". Phytochemistry. 61 (8): 923–926. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00474-0. PMID 12453518.
- Jiaju Zhou, Guirong Xie and Xinjian Yan Encyclopedia of Traditional Chinese Medicines - Molecular Structures, Pharmalogical Activities, Natural sources and Applications, p. 214, at Google Books
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.