Hurricane Enrique (2021)
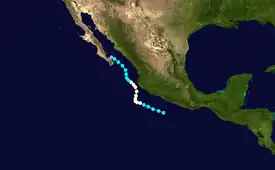
Hurricane Enrique was a Category 1 Pacific hurricane that brought heavy rainfall and flooding to much of western Mexico in late June 2021. The fifth named storm and first hurricane of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season, Enrique developed from a tropical wave the entered the Pacific Ocean off the coast of Nicaragua on June 22. In an environment conducive for intensification, the disturbance moved west-northwestward and developed into a tropical storm by 6:00 UTC on June 25, as it was already producing winds of 40 mph (65 km/h), and received the name Enrique. Enrique strengthened steadily within an environment of warm waters and low-to-moderate wind shear while continuing its northwestward motion. By 12:00 UTC on June 26, Enrique had intensified into a Category 1 hurricane as the storm turned more northwestward. Nearing the coast of Mexico, Enrique reached its peak intensity around 6:00 UTC the following day, with maximum sustained winds of 90 mph (150 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 972 mbar (28.7 inHg). Enrique, passing closely offshore west-central Mexico, maintained its intensity for another 24 hours as it turned northward toward the Gulf of California. Turning back to the northwest on June 28, increasing wind shear and dry air caused the hurricane to weaken. Enrique dropped to tropical storm status at 18:00 UTC that day, and further weakened to a tropical depression on June 30 just to the northeast of Baja California. The depression was absorbed into a larger low pressure area to the southeast later that day.
 Enrique at peak intensity on June 27, 2021. | |
| Meteorological history | |
|---|---|
| Formed | June 25, 2021 |
| Dissipated | June 30, 2021 |
| Category 1 hurricane | |
| 1-minute sustained (SSHWS/NWS) | |
| Highest winds | 90 mph (150 km/h) |
| Lowest pressure | 972 mbar (hPa); 28.70 inHg |
| Overall effects | |
| Fatalities | 2 |
| Damage | $50 million |
| Areas affected | Western Mexico |
| IBTrACS / [1] | |
Part of the 2021 Pacific hurricane season | |
Although the storm never made landfall, Enrique's path just offshore the Mexican coastline caused significant flooding, high surf, and rip currents across western Mexico. Two direct deaths resulted from the stormy conditions created by the cyclone in Guerrero. Over 115,000 electricity customers lost power in Jalisco. Some areas were inundated in over 4 feet of floodwater. Overall, Enrique was responsible for $50 million (2021 USD) worth of damage.
Meteorological history
Tropical storm (39–73 mph, 63–118 km/h)
Category 1 (74–95 mph, 119–153 km/h)
Category 2 (96–110 mph, 154–177 km/h)
Category 3 (111–129 mph, 178–208 km/h)
Category 4 (130–156 mph, 209–251 km/h)
Category 5 (≥157 mph, ≥252 km/h)
Unknown
On June 20, NHC noted a possible formation of a low-pressure area near the south of Guatemala and Gulf of Tehuantepec.[2] On June 22, an area of disturbed weather was tracking over Central America with satellite imagery indicating disorganized showers and thunderstorms.[3] With conductive environmental conditions, the system gradually organized and on June 25 at 09:00 UTC, the NHC assessed the system as a tropical storm, assigning the name Enrique.[4] Satellite imagery also revealed that the storm had developed a low-level circulation, with a scatterometer pass over the storm also showing that it was producing tropical storm-force winds to the southeast of the center.[5][4] The storm's structure had further improved six hours later, with prominent banding features to the south and east.[6] Later, a large convective burst developed over the storm.[7] Enrique continued to intensify throughout the day, with the NHC assessing the system to have strengthened into a category 1 hurricane by 09:00 UTC on June 26, after which the system possessed a well-defined central dense overcast and alongside persistent area of cold cloud tops.[8] An area of overshooting cloud tops signaled that the eyewall was developing.[9] However, its structure degraded shortly afterward due to dry air.[10] Enrique's structure improved later, though dry air still was being entrained into the storm's northern side.[11] Around this time, the storm obtained its peak intensity of 90 mph (150 km/h). Slight additional intensification was forecast,[12] but this did not occur. On June 28, at 15:00 UTC the convective structure of Enrique had been eroded with the inner core becoming increasingly ragged due to dry air, causing the hurricane to weaken.[13] On the same day at 21:00 UTC the NHC downgraded Enrique to a high end tropical storm as the structure continued to deteriorate and had a partially exposed center.[14] On June 30, at 12:00 UTC, the NHC further downgraded Enrique to a tropical depression as its thunderstorms shrunk to a small area of deep convection.[15] On 21:00 UTC that day, Enrique degenerated into a remnant low in the Gulf of California as all of its convection had dissipated.[16]
Preparations and impact
At 15:00 UTC on June 25, a Tropical Storm Watch was issued by the Government of Mexico from Punta San Telmo, Michoacán to Cabo Corrientes, Jalisco.[17]
At least two people drowned at a beach in Pie de la Cuesta, Guerrero due to rip currents between June 25–26.[18] At least 207 homes were damaged by landslides and winds caused by Enrique in Guerrero.[19] Heavy rain impacted areas of Manzanillo, while winds caused minor damage to homes.[20] In Lazaro Cardenas, areas were inundated by more than 50 cm (19 in) of floodwater.[21] A total of 115,904 customers lost power across the state of Jalisco, although power was restored to 96% within a couple of hours later.[22] Enrique left damage in parts of Nayarit, with trees being uprooted and falling onto homes and power lines being knocked down, leading to a citywide power outage in Tepic.[23] Nationwide, damage from the storm was estimated to be approximately US$50 million.[24][1]
See also
References
- Andy Latto (November 2, 2021). Tropical Cyclone Report: Hurricane Enrique (PDF) (Report). Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved December 25, 2021.
- Stacy R. Stewart (June 20, 2021). "Five-Day Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Robbie Berg (June 22, 2021). "Five-Day Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Jack Beven (June 25, 2021). "Five-Day Graphical Tropical Weather Outlook". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Jack Beven (June 25, 2021). "Tropical Storm Enrique Discussion Number 1". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; John Cangialosi (June 25, 2021). "Tropical Storm Enrique Discussion Number 2". nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; John Cangialosi (June 25, 2021). "Tropical Storm Enrique Discussion Number 3". nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 25, 2021.
- Jack Beven (June 26, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Forecast Discussion Number 5". nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; Stacy Stewart (June 26, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Discussion Number 6". nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; Jack Beven (June 26, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Discussion Number 7". nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 26, 2021.
- Andrew Latto; Stacy R. Stewart (June 27, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Discussion Number 10". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- Andrew Latto; Stacy R. Stewart (June 27, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Discussion Number 10". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; Stacy Stewart (June 28, 2021). "Hurricane Enrique Discussion Number 14". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 28, 2021.
- Philippe Papin; Stacy Stewart (June 28, 2021). "Tropical Storm Enrique Discussion Number 15". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 28, 2021.
- Richard Pasch (June 30, 2021). "Tropical Storm Enrique Discussion Number 21". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- Reinhart, Amanda; Brown, Daniel (June 30, 2021). "Remnants of ENRIQUE Advisory Number 23". www.nhc.noaa.gov. Miami, Florida: National Hurricane Center. Retrieved June 30, 2021.
- "Tropical Storm Enrique Forecast/Advisory Number 2". National Hurricane Center. June 25, 2021. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- Hugo Valencia (June 26, 2021). "Huracán 'Enrique' causa 2 muertos en las costas de Guerrero". Noticieros Televisa. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- "Huracán Enrique dañó 207 casas y causó 28 derrumbes a su paso por Guerrero". López-Dóriga Digital (in Mexican Spanish). June 27, 2021. Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- Demos, Editorial; corresponsal, Juan Carlos Flores. "La Jornada - Huracán 'Enrique' deja daños a negocios y viviendas en Colima". La Jornada (in Spanish). Retrieved June 28, 2021.
- Demos, Editorial; corresponsal, Ernesto Martínez Elorriaga. "Huracán 'Enrique' provoca inundaciones en Lázaro Cárdenas, Michoacán". La Jornada (in Spanish). Retrieved June 28, 2021.
- Staff, Forbes (June 26, 2021). "CFE restablece suministro eléctrico al 96% de usuarios afectados en Jalisco por tormenta 'Enrique'". Forbes México (in Mexican Spanish). Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- Demos, Editorial; corresponsal, Myriam Navarro (June 21, 2021). "Huracán 'Enrique' deja inundaciones y daños materiales en Tepic". La Jornada (in Spanish). Retrieved June 27, 2021.
- Global Catastrophe Recap: August 2021 (PDF) (Report). AON. 10 September 2021. Retrieved 18 September 2021.
External links
- The National Hurricane Center's advisory archive on Hurricane Enrique