Hoorn Islands
The Hoorn Islands (also Futuna Islands) are one of the two island groups of which the French overseas collectivity (collectivité d'outre-mer, or COM) of Wallis and Futuna is geographically composed. The aggregate area is 115 km2, and the population 4,873 (census of 2003).
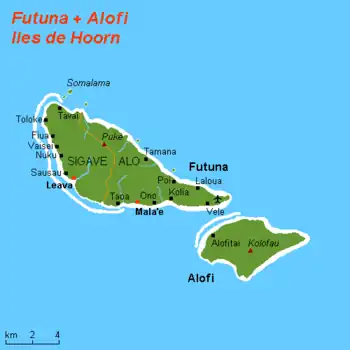
with Futuna Island in the northwest
History
The archipelago was named by the Dutch navigators Willem Schouten and Jacob Le Maire, who, in 1616, became the first Europeans to visit the islands. They named it after the Dutch city of Hoorn, from which their expedition had started. They had previously rounded and named Cape Horn on the same voyage; Schouten had been born in Hoorn.
Geography
Geographically, there are two islands:
- Futuna Island (in the northwest) (83 km2, pop. 4871)
- Alofi Island (in the southeast) (32 km2, pop. 2)
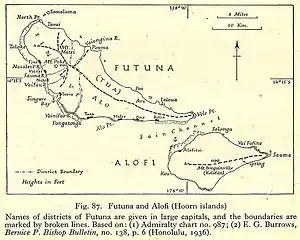
Administratively, the Hoorn Islands encompass two of Wallis and Futuna's three royal chiefdoms, namely:
- Tu`a (Alo), which comprises Alofi Island and the eastern part of Futuna Island (area 85 km2, pop. 2993)
- Sigave (Singave), which comprises the western third of Futuna Island (area 30 km2, pop. 1880)
(The third royal chiefdom is Uvea.)
See also
- Wallis Island (Uvea)
