Hezuo
Hezuo city (Chinese: 合作市), also known as Zö from its Tibetan name (Tibetan: གཙོས་གྲོང་ཁྱིར།), is the administrative seat of the Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (TAP) in southern Gansu province in Northwestern China. It is home to the Gêndên Qöling (Zö Gönba) and its Milaraiba Tower, the Langshangmaio Temple, and a mosque. There is a breed of pig, the Zoi Swine (a.k.a. Silverweed Pig), from here and the whole Gannan TAP also.
Hezuo
合作市 · གཙོས་གྲོང་ཁྱེར། Zö | |
|---|---|
 "Tso Monastery" in Hezuo | |
.png.webp) Hezuo City (red) within Gannan Prefecture (yellow) and Gansu | |
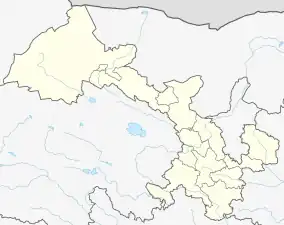 Hezuo Location in Gansu  Hezuo Hezuo (China) | |
| Coordinates (Hezhou municipal government): 35°00′01″N 102°54′37″E | |
| Country | China |
| Province | Gansu |
| Autonomous prefecture | Gannan |
| Municipal seat | Gyamkar Subdistrict |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,670 km2 (1,030 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 2,883 m (9,459 ft) |
| Population (2020)[1] | |
| • Total | 112,173 |
| • Density | 42/km2 (110/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 747000 |
| Area code | (0)941 |
| Website | www |
| Hezuo | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese name | |||||||
| Chinese | 合作市 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Tibetan name | |||||||
| Tibetan | གཙོས་གྲོང་ཁྱིར། | ||||||
| |||||||
Name
The Tibetan name "Zö" གཙོས། is pronounced Dzoi in Standard Tibetan and pronounced Hdzoi/Hdzu in local dialect.
The Chinese name before the 1950s was "Heicuo" (黑错), a transliteration of the Tibetan name. In 1956, the name was changed to the similar-sounding "Hezuo" (合作), meaning "cooperation", which reflected the desire to bring unity and harmony to Hezuo.
History
Originally a rare populated wetland, mass city-construction began in the 1950s.
During 1953, the Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture was created, and the town of Hezuo (not yet a city) was part of it.
In May 1956, Hezuo was named by a provincial government employee.
During June 1996, the government announced the establishment of Hezuo, and on January 1, 1998, the city was officially established.[2]
Population
The total population of Hezuo city in 2010 was 81,000. The rural population was 35,000, about for 43% of the total population, and the 57% of the urban population was 46,000. 54% of the population is Tibetan, which is about 44,000.[3]
The city's permanent population was 95,000 at the end of 2017. Urban population is 51,000, the rate of urbanization was 57.10 percent. The natural population growth rate was 9.57 percent. Birth rate was 15.09 percent. Population mortality rate was 5.52 percent, 0-14 year old population is 19,500, and the population of 15-64 years old is 67,200.[4]
At the end of 2019, the registered population of Hezuo City was 93,727.[3]
Natural resources
In Hezuo city, yaks and Tibetan sheep are the major animals, with total of about 300,000, about 250,000 yaks and Tibetan sheep remain at the end of year.[5] Beside two major animal, Hezuo also have a famous animal called the Juema Pig (蕨麻豬). The major trees in Hezuo are fir, spruce, pine, Huashan pine, poplar, birch, cypress, and willow. Shrubs in Hezuo city including sea buckthorn, rhododendron, cypress, plum and catalpa. Highland barley, spring wheat and rapeseed are the normal staple food people eat.
Economic
In 2020, Hezuo City expects that the city's regional GDP will reach 5.89 billion yuan, 1.8 times the level projected in the twelfth five-year plan. The added value of industrial enterprises above designated size will be 570 million yuan, an average annual growth rate of 5%.[6]
Primary industry
the city's annual primary industry industrial added value was 216.87 million yuan, of which, planting industry was 30.48 million yuan, forestry was 1.11 million yuan, animal husbandry was 184.75 million yuan, and agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry and fishery services were 520,000 yuan.[7]
Secondary industry
In 2017, all industries in Hezuo city industrial production has value of 563.84 million yuan. Industrial production of industries above designated size was 498.84 million yuan. Industrial production of industries below designated size was 65 million yuan. Export delivery value was 6.06 million yuan.[7]
Tertiary industry
At the end of 2018, it received 2.026 million tourists, with a comprehensive tourism income of 1.03 billion yuan. The city has 125 hotels and restaurants, with a total of more than 5,500 guest rooms and more than 10,000 beds.[7]
Geography and climate
With an elevation of nearly 3,000 metres (9,800 ft), Hezuo has an alpine subarctic climate (Köppen Dwc), with long, very cold, dry winters, and short, mild summers. The monthly daily mean temperature in January, the coldest month, is −9.3 °C (15.3 °F), while the same figure for July, the warmest month, is 13.3 °C (55.9 °F); the annual mean is 2.82 °C (37.1 °F). Most of the annual precipitation is delivered from May to September. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 44% in June and September to 71% in December, the city receives 2,370 hours of bright sunshine annually.
| Climate data for Hezuo (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.1 (62.8) |
18.6 (65.5) |
23.6 (74.5) |
29.2 (84.6) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.2 (81.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
28.7 (83.7) |
28.1 (82.6) |
24.6 (76.3) |
18.5 (65.3) |
15.0 (59.0) |
30.4 (86.7) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
4.4 (39.9) |
8.1 (46.6) |
12.6 (54.7) |
15.6 (60.1) |
18.3 (64.9) |
20.6 (69.1) |
20.3 (68.5) |
16.4 (61.5) |
11.5 (52.7) |
7.4 (45.3) |
3.3 (37.9) |
11.7 (53.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −9.1 (15.6) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
−0.7 (30.7) |
4.2 (39.6) |
8.1 (46.6) |
11.4 (52.5) |
13.6 (56.5) |
13.0 (55.4) |
9.3 (48.7) |
3.9 (39.0) |
−2.3 (27.9) |
−7.6 (18.3) |
3.2 (37.7) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −16.6 (2.1) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
−7.0 (19.4) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
2.0 (35.6) |
5.8 (42.4) |
8.0 (46.4) |
7.6 (45.7) |
4.7 (40.5) |
−0.9 (30.4) |
−8.5 (16.7) |
−14.9 (5.2) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −28.5 (−19.3) |
−27.1 (−16.8) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
−20.2 (−4.4) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−23.8 (−10.8) |
−27.9 (−18.2) |
−28.5 (−19.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 5.0 (0.20) |
6.8 (0.27) |
17.1 (0.67) |
33.8 (1.33) |
73.2 (2.88) |
80.4 (3.17) |
115.5 (4.55) |
95.8 (3.77) |
75.2 (2.96) |
41.6 (1.64) |
7.4 (0.29) |
1.5 (0.06) |
553.3 (21.79) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 4.4 | 5.8 | 9.8 | 10.9 | 16.7 | 18.5 | 17.4 | 17.2 | 16.3 | 12.7 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 136.9 |
| Average snowy days | 7.3 | 9.5 | 12.9 | 10.8 | 4.3 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.1 | 1.0 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 5.5 | 66.2 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 49 | 52 | 57 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 74 | 75 | 77 | 73 | 61 | 51 | 64 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 202.2 | 189.5 | 206.8 | 212.2 | 207.5 | 191.0 | 208.6 | 202.4 | 162.6 | 180.3 | 206.2 | 209.5 | 2,378.8 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 64 | 61 | 55 | 54 | 48 | 44 | 48 | 49 | 44 | 52 | 67 | 69 | 55 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[8][9][10] | |||||||||||||
Administrative divisions
Hezuo City has four subdistricts, three towns and three townships.[11]
| Name | Simplified Chinese | Hanyu Pinyin | Tibetan | Wylie | Administrative division code | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subdistricts | ||||||
| Tungchug Subdistrict (Dangzhou) |
当周街道 | Dāngzhōu Jiēdào | དུང་ཕྲུག་ཁྲོམ་གཞུང་། | dung phrug khrom gzhung | 623001001 | |
| Yagnying Subdistrict (Yihe'ang) |
伊合昂街道 | Yīhé'áng Jiēdào | གཡག་སྙིང༌ཁྲོམ་གཞུང་། | g.yag snying khrom gzhung | 623001002 | |
| Gyamkar Subdistrict (Jianmuke'er) |
坚木克尔街道 | Jiānmùkè'ěr Jiēdào | རྒྱ་མཁར་ཁྲོམ་གཞུང་། | rgyal mkhar khrom gzhung | 623001003 | |
| Toiqing Subdistrict (Tongqin) |
通钦街道 | Tōngqīn Jiēdào | ཐོད་ཆིངས་ཁྲོམ་གཞུང་། | thod chings khrom gzhung | 623001004 | |
| Towns | ||||||
| Na'og Town (Nawu, Nabug) |
那吾镇 | Nàwú Zhèn | སྣ་འོག་གྲོང་རྡལ། | sna 'og grong rdal | 623001100 | |
| Luxoi Town (Lexiu) |
勒秀镇 | Lèxiù Zhèn | ཀླུ་ཤོད་གྲོང་རྡལ། | klu shod grong rdal | 623001101 | |
| Zogemema Town (Zogamanma) |
佐盖曼玛镇 | Zuǒgàimànmǎ Zhèn | མཛོད་དགེ་སྨད་མ་གྲོང་རྡལ། | mdzod dge smad ma grong rdal | 623001102 | |
| Townships | ||||||
| Ka'gyamai Township (Kajiaman) |
卡加曼乡 | Kǎjiāmàn Xiāng | ཁ་གྱ་སྨད་ཤང་། | kha gya smad shang | 623001200 | |
| Ka'gyadoi Township (Kajiadao) |
卡加道乡 | Kǎjiādào Xiāng | ཁ་གྱ་སྟོད་ཤང་། | kha gya stod shang | 623001201 | |
| Zogetodma Township (Zuogaiduoma) |
佐盖多玛乡 | Zuǒgàiduōmǎ Xiāng | མཛོད་དགེ་སྟོད་མ་ཤང་། | mdzod dge stod ma shang | 623001202 | |
Transport
- China National Highway 213
- Gannan Xiahe Airport, 56 kilometers from Zoi was started September 2010 and completed in August 2013.
- The planned Lanzhou–Hezuo railway will terminate here
References
- "甘南州第七次全国人口普查公报" (in Chinese). Government of Gannan Prefecture. 2021-05-27.
- "甘南合作概况|合作市简介". www.114huoche8.com. Retrieved 2021-11-07.
- "甘南合作市人口_合作市人口历年数据_走势图_聚汇数据". population.gotohui.com. Retrieved 2021-11-07.
- "(甘肃省)2017年合作市国民经济和社会发展统计公报_县情资料网---有深度、有态度、接地气的县域县情站点". www.ahmhxc.com. Retrieved 2021-11-07.
- "合作市畜牧产业生产呈现新特点-甘南藏族自治州统计局". tjj.gnzrmzf.gov.cn. Retrieved 2021-11-08.
- "2020年合作市政府工作报告-合作市人民政府". www.hezuo.gov.cn. Retrieved 2021-11-08.
- "(甘肃省)2017年合作市国民经济和社会发展统计公报_县情资料网---有深度、有态度、接地气的县域县情站点". www.ahmhxc.com. Retrieved 2021-11-08.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 27 August 2023.
- 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1971-2000年). China Meteorological Administration. Archived from the original on 2013-09-21. Retrieved 2010-05-25.
- "统计用区划代码 www.stats.gov.cn" (in Chinese). XZQH. Retrieved 2012-05-26.
External links
- Official website (in Chinese)



