Hefersweiler
Hefersweiler is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Kusel district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde Lauterecken-Wolfstein.
Hefersweiler | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Hefersweiler within Kusel district 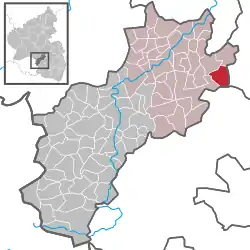 | |
 Hefersweiler  Hefersweiler | |
| Coordinates: 49°36′15″N 7°41′14″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Kusel |
| Municipal assoc. | Lauterecken-Wolfstein |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2019–24) | Bernd Degen[1] |
| Area | |
| • Total | 7.20 km2 (2.78 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 230 m (750 ft) |
| Population (2021-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 544 |
| • Density | 76/km2 (200/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| Postal codes | 67753 |
| Dialling codes | 06363 |
| Vehicle registration | KUS |
| Website | www.hefersweiler-berzweiler.de |

Geography
Location
The municipality lies on the Odenbach in the North Palatine Uplands. Both its Ortsteile lie in this river's valley at an elevation of some 225 m above sea level, Hefersweiler (main centre) up the valley on both sides of the river and Berzweiler farther down, mainly on the right bank. The Ahlbornerhof (homestead) lies across the Odenbach from Berzweiler on the left bank. The mountains either side of the valley reach more than 350 m above sea level (Reiterberg 364 m, Gründling 353 m). The municipal area measures 721 ha, of which roughly 20 ha is settled and 71 ha is wooded.[3]
Neighbouring municipalities
Hefersweiler borders in the north on the municipality of Nußbach, in the east on the municipalities of Rathskirchen and Seelen, in the south on the municipality of Niederkirchen, in the southwest on the municipality of Relsberg and in the northwest on the municipality of Reipoltskirchen.
Constituent communities
Hefersweiler's Ortsteile are Hefersweiler and Berzweiler. Also belonging to Hefersweiler is the outlying homestead of Ahlbornerhof.[4]
Municipality’s layout
The thickest part of Hefersweiler's built-up area stretches along the crossing of the road through the Odenbach valley (Talstraße) and those that branch off towards Wolfstein, Relsberg and Seelen. In the village core stands Hefersweiler's former schoolhouse. Berzweiler's built-up area stretches mainly eastwards of the road and the Odenbach, partly in the valley of a small brook flowing down from the Berzweiler Heights, and partly along a path that leads towards Rudolphskirchen. The graveyard lies between the two Ortsteile at Berzweiler's south end. Outstanding buildings on the valley road in the Ortsteil of Hefersweiler are the former schoolhouse built in 1903 and a building with particularly attractive walling around the door from 1574.[5]
History
Antiquity
From the Stone Age, the Bronze Age and the Iron Age comes no direct knowledge about any archaeological finds made within Hefersweiler's limits. Nonetheless, finds from neighbouring municipalities make it clear that the area where the municipality now lies was settled by human beings even as far back as prehistoric times. As early as 1805, Hefersweiler villagers discovered nearby, between the roads to Wolfstein and the Ausbacherhof, a Roman villa rustica. Digging then brought to light several building foundations with a hypocaust and smoke channels. The excavators also found Roman coins.[6]
Middle Ages
In 1223, Hefersweiler had its first documentary mention. Hefersweiler itself was among the earliest holdings of the Cistercian Otterberg Abbey. The two centres that today make up the municipality of Hefersweiler followed different paths of development over the course of history. Hefersweiler itself was a village under the lordship of Reipoltskirchen, and largely shared that neighbouring village's history. In the 14th century, it belonged to the Counts of Hohenfels, and in the 15th century, to the Lords of Hohenfels-Reipoltskirchen. A Huberweistum (a Weistum – cognate with English wisdom – was a legal pronouncement issued by men learned in law in the Middle Ages and early modern times; Huber refers to farmers who owned a whole Hube – roughly “oxgang” – of land) was put in writing in 1597; it was renewed in 1652 as a constituent document of the Reipoltskirchen lordship's Weistümer (the plural). For centuries, Berzweiler was made up of nothing but four estates held by Otterberg Abbey. Philipp von Bolanden, who was married to Waldgravine Beatrix, removed the village from the Monastery's ownership. Waldgravine Beatrix later married Theoderich von Heinzenberg, who in 1225 gave the village back to the Monastery. This dependent relationship remained in place until the time of the Reformation. Within municipal limits, a few border stones from the time of monasterial ownership can still be found. In 1492, the abbot of Otterberg Abbey issued a letter of entailment to the landowners in Berzweiler, according to which the estates were hereditarily transferred to them. Moreover, an extensive Weistum from mediaeval Berzweiler has survived that was first put in writing in 1469 and then renewed in 1565.[7][8]
Modern times
In the 16th century, the knight Sir Johannes, who was now and then Franz von Sickingen’s brother-in-arms, was important for the Imperial lordship's, and therefore also Hefersweiler's, history. His daughter-in-law Amalia wed, as her second husband, Count Philipp I of Leiningen-Westerburg, who introduced into all his landholds, including the lordship of Reipoltskirchen and therefore Hefersweiler too, the Reformation. In 1603, Amalia bequeathed the lordship of Reipoltskirchen to her brothers Sebastian (d. 1619) and Emich (d. 1628). In the time that followed, there were further divisions of the lordship, which often left it subject to several lords, although it remained a cohesive territorial unit. Among the lords were the Lord of Löwenhaupt, the Lord of Manderscheid-Keil, the Baron of Hillesheim (d. 1748), the Count of Ellradt (d. 1767), and lastly Caroline von Isenburg, a natural daughter of Carl Theodor, the last Elector Palatine. Berzweiler remained under Otterberg Abbey's ownership until it was dissolved in 1561. The monastery belonged to Electoral Palatinate, and thus Berzweiler, too, became an Electoral Palatinate holding. The Elector Palatine at this time was Ludwig VI, who died in 1581, and for whom Johann Casimir ruled Electoral Palatinate as administrator. Johann Casimir owned a half share in the village of Friedelhausen, but eventually acquired the other half in 1588 by trading Berzweiler to the holder of the other share, John I, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken. Even at the 1618 onset of the Thirty Years' War, there were no longer any people living at the village's estates, and long after the war, the village remained empty of people. Berzweiler belonged in a manner of speaking to Zweibrücken, but only as a pledged holding. Nevertheless, in 1694, under the terms of succession of the Palatinate-Veldenz (a cadet branch of Palatinate-Zweibrücken), it was permanently taken over by Zweibrücken. In the course of the 1778 Kübelberg Exchange, though, the village passed back to Electoral Palatinate, but was forthwith incorporated into the realm of the Lordship of Reipoltskirchen, which at that time was transferred to Countess Caroline von Isenburg. Thus did the two centres of today's municipality first find themselves together in the same lordly and administrative territory.[9]
Recent times
In 1793, French Revolutionary troops seized the Lordship of Reipoltskirchen and thereby also the neighbouring villages of Hefersweiler and Berzweiler. The inhabitants had to pay their share of contributions to them. In 1799, France dissolved the old lordships, and along with them the Lordship of Reipoltskirchen. Hefersweiler became the seat of a mairie (“mayoralty”), to which Berzweiler also belonged, within the French First Republic. This mairie in turn lay in the Canton of Wolfstein, the Arrondissement of Kaiserslautern and the Department of Mont-Tonnerre (or Donnersberg in German). After the 1814 reconquest of the German lands on the Rhine’s left bank by Prussian, Austrian and Russian troops, the region passed after a transitional period to the Kingdom of Bavaria. Hefersweiler and Berzweiler now lay within the Bavarian Rheinkreis (the Palatinate, after the Congress of Vienna had awarded it to Bavaria) in the Canton of Wolfstein and the Landkommissariat of Kusel, and Hefersweiler was still the seat of a mayoralty, only now it was called by its German word: Bürgermeisterei. In the late 1920s and early 1930s, the Nazi Party (NSDAP) was quite popular in Hefersweiler and Berzweiler. In the 1928 Reichstag elections, only 11.6% of the votes from Hefersweiler went to Adolf Hitler’s party and 21.0% from Berzweiler, but by the 1930 Reichstag elections, this had grown to 66.0% in Hefersweiler and 42.6% in Berzweiler. By the time of the 1933 Reichstag elections, after Hitler had already seized power, local support for the Nazis had swollen to 83.3% in Hefersweiler and 80.2% in Berzweiler. Hitler's success in these elections paved the way for his Enabling Act of 1933 (Ermächtigungsgesetz), thus starting the Third Reich in earnest. The municipality that exists today came into being on 7 June 1969 when the two municipalities of Hefersweiler and Berzweiler were amalgamated in the course of administrative restructuring in Rhineland-Palatinate.[10] The old mayoralty was also dissolved. Since 1972, the two villages have formed a self-administering Ortsgemeinde with two Ortsteile within the Kusel district.[11]
Population development
In both villages, the inhabitants formerly earned their livelihoods mainly at agriculture. There were, however, job opportunities in the crafts, trade and work at the quarries and collieries. As early as the late 18th century, particularly in Hefersweiler, were several Jewish families. During the 20th century, there was a fundamental shift away from farming, with ever fewer villagers working the land and ever more commuting as workers and employees to jobs in the industrial towns nearby and even farther afield. This development was enhanced by Hefersweiler's relatively favourable transport links with Kaiserslautern. The population figures reached their first peak about the turn of the 20th century, shrank in the time leading up to the Second World War and then stagnated after the war until about 1980 when there was once again a noticeable upswing. With regard to religion, the majority is Evangelical.
The following table shows population development over the centuries for Hefersweiler, with some figures broken down by religious denomination:[12]
| Year | 1802 | 1825 | 1835 | 1871 | 1905 | 1939 | 1961 |
| Total | 207 | 336 | 408 | 420 | 454 | 370 | 389 |
| Catholic | 8 | 9 | 20 | ||||
| Evangelical | 168 | 314 | 367 | ||||
| Jewish | 16 | 3 | – | ||||
| Other | – | – | 2 |
The following table shows population development over the centuries for Berzweiler, with some figures broken down by religious denomination:[13]
| Year | 1802 | 1825 | 1835 | 1871 | 1905 | 1939 | 1961 |
| Total | 53 | 69 | 107 | 136 | 137 | 127 | 133 |
| Catholic | – | 7 | |||||
| Evangelical | 53 | 125 | |||||
| Other | – | 1 |
The following table shows population development since amalgamation for the merged municipality:[14]
| Year | 1998 | 2007 |
| Total | 583 | 516 |
Municipality’s name
The bigger village's name, Hefersweiler, has the common German placename ending —weiler, which as a standalone word means “hamlet” (originally “homestead”), to which is prefixed an element that according to researchers Dolch and Greule goes back to a personal name “Hunfrid”. Thus, the name's original meaning would have been “Hunfrid’s homestead”. The name appears for the first time in a 1223 document as Hunfrideswilre. Later forms that the name took are Hunfertswilre (1377), Hunfritzwyller (1519) and Hinfurßwiller (1544). Close to the current form is the 1779 form Heffersweiler.
The smaller village, Berzweiler, is yet another of the many villages with names ending in —weiler, and in Berzweiler's case, this is prefixed with a syllable also believed to go back to a personal name, either “Berni” or “Bernhard”. Thus, the name's original meaning would have been “Berni’s homestead” or “Bernhard’s homestead”. In the 1223 document of first mention it was called Berhardesvillre. Later forms that the name took are Berssweiler (1393), Bertzweiler (1469) Berssweiler (1599) and Beersweyler (1745).
As for the Ahlenbornerhof, the ending —hof means “farm” or “estate”, and the syllables to which that is suffixed apparently refer to an old spring, for the homestead once lay near one (this would be bei einem alten Brunnen in Modern High German).[15]
Religion
Inhabitants of both constituent villages, Hefersweiler and Berzweiler, converted during the Reformation to Lutheranism under the principle of cuius regio, eius religio. Only a few Catholics and Reformed adherents settled in Hefersweiler after the Thirty Years' War. The Jewish inhabitants likely belonged to the Jewish community in Rockenhausen. To this day, most people are Evangelical. The Evangelicals belong to the Niederkirchen parish in the Protestant deaconry of Kaiserslautern, while the Catholic Christians belong to the Reipoltskirchen parish in the Catholic deaconry of Kusel.[16]
Politics
Municipal council
The council is made up of 12 council members, who were elected by majority vote at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.[17]
Mayor

Hefersweiler's mayor is Bernd Degen, and his deputies are Rainer Kattler and Christian Ehwein.[18]
Coat of arms
The municipality's arms might be described thus: Or a fess wavy issuant from which a balance and below which a lattice, all azure.
Hefersweiler itself bore no arms before the amalgamation of the two centres of Hefersweiler and Berzweiler. Thus, the current coat of arms applies to the municipality as a whole. The charge above the wavy fess is drawn from an earlier court seal. The arms have been borne since 1975 when they were approved by the now defunct Rheinhessen-Pfalz Regierungsbezirk administration in Neustadt an der Weinstraße. Before amalgamation, Berzweiler bore its own arms. They were vert a rose argent seeded and barbed Or (see illustration). It likewise was drawn from an earlier seal. These arms were never approved by any higher authority.[19]
Culture and sightseeing
Buildings
The following are listed buildings or sites in Rhineland-Palatinate’s Directory of Cultural Monuments:[20]
Hefersweiler (main centre)
- Near Talstraße 1 – warriors’ memorial 1914-1918 and 1939-1945; eagle on cube, 1931, design by Kaiserslautern State Building Office (Landbauamt), expanded after 1945
- At Talstraße 10 – doorjamb, marked 1574
- Talstraße 13 – former school; block building, schoolhouse with hipped mansard roof, house mit with hipped roof, 1902/1903, Regional Master Builder Kleinhans
- Warriors’ memorial 1914-1918, north of the village in the graveyard – stele with relief, 1931, design by Kaiserslautern State Building Office, Nessler Sculpture Workshop, Lauterecken
Berzweiler
- Bergstraße 1 – former school; two-floor plastered building, staircase with Welsche Haube, 1895
 Hefersweiler, Talstraße 13: former school
Hefersweiler, Talstraße 13: former school Hefersweiler, near Talstraße 1: warriors’ memorial 1914-1918 and 1939-1945
Hefersweiler, near Talstraße 1: warriors’ memorial 1914-1918 and 1939-1945 North of the village in the graveyard: warriors’ memorial 1914-1918
North of the village in the graveyard: warriors’ memorial 1914-1918 Berzweiler, Bergstraße 1: former school
Berzweiler, Bergstraße 1: former school
Regular events
Hefersweiler's kermis (church consecration festival) is held on the first weekend in September, while Berzweiler's is held on the last weekend in August. Since 1852, in connection with a livestock sickness that struck back then, a “Livestock Celebration Day” (Viehfeiertag) is observed each year on 2 June.[21]
Clubs
Cultural life is characterized by a great number of clubs, of which the following may be found in Hefersweiler:[22]
- Angelsportverein — angling
- Feuerwehrförderverein — fire brigade promotional association
- Gesangvereine — singing clubs (in both Hefersweiler and Berzweiler)
- Kindergartenförderverein — kindergarten promotional association
- Pfälzischer Bauern- und Winzerverein — “Palatine Farmers’ and Winegrowers’ Association”
- Schäferhundeverein — German Shepherd/Alsatian club
- SPD-Ortsverein — Social Democratic Party of Germany local chapter
- Sportverein — sport club
- Verein der Tierfreunde — “animal friends”
Hefersweiler has a football club, SV Hefersweiler 1952, whose clubhouse and playing field lie right next to the kindergarten in a central location at the village square between the two centres of Hefersweiler and Berzweiler.
Economy and infrastructure
Economic structure
While in earlier times farming was the main means whereby villagers could earn a living, today very few work the land. Other occupations in earlier times lay in forestry and mining. Within Hefersweiler's municipal limits were two collieries, the Jakobsgrube and the Heinrichsgrube, which together employed about 10 workers in the 19th century. For a time, there was also a limestone quarry. As well, the village had its customary crafts and a mill (in the forest at the municipal boundary with Niederkirchen) that had been built even before the Thirty Years' War – only to be destroyed during that war. The reconstruction planned for 1702 at first failed to win lordly approval, but eventually the project was allowed to proceed in 1714. Only after the First World War was the mill shut down. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, many Wandermusikanten – travelling musicians – also came from both the villages in the municipality. Today, Hefersweiler is mainly a residential community for many commuters.[23] Hefersweiler has a flower shop, a bakery and an inn.
Education
Beginning in the time of the Reformation, the lords generally strove to establish schools in their domains. Since the Reformation had been introduced into both Hefersweiler and Berzweiler, schoolteachers may have been teaching children even before the Thirty Years' War. In both villages, even in Hefersweiler, which belonged to the Lordship of Reipoltskirchen, schooling was organized by the Amt of Meisenheim, which belonged to the Duchy of Palatinate-Zweibrücken. Thus, appearing in the 1778 acts of the Oberamt were clues to the presence of a Lutheran schoolhouse in Hefersweiler. Noted as early as 1769 was that the municipality of Berzweiler had a kleines Schulhäuschen (a notable reference for being a double diminutive: the word kleines means “little”, and so does the ending —chen, making the translation “little little schoolhouse”). In 1777, it was further noted that the schoolchildren had to bring the school firewood along with them to school. A school's daybook has survived from Berzweiler, in which the reader can see that from the beginning of Bavarian times, a schoolteacher named Carl Dörr worked in Berzweiler, and was succeeded by his son Johann Jacob. Johann Jakob Dörr was much given to hunting and it was thus deemed fit to transfer him to Nothweiler as punishment for this unfortunate vice. Further teachers during the 19th century were Johannes Hahneberger and Johannes Klingenmayer. In 1895, the Berzweiler schoolhouse, which had been standing for a long time, was converted. Dry rot made another round of improvements necessary only five years later. During the First World War, this schoolhouse served as a prison camp, and schoolchildren had to attend classes in nearby Hefersweiler. In Hefersweiler itself, it is likely that a schoolhouse had stood as early as the late 17th century. It featured a ridge turret, hanging in which was the village bell. A new, representative schoolhouse arose in 1902. Thereafter, another schoolhouse was built in 1936 for both villages. Now housed in the old 1902 Hefersweiler schoolhouse is a bank. In 1970, the Hefersweiler-Berzweiler school was dissolved; a kindergarten can now be found there. Nowadays, primary school pupils attend school in Nußbach, while Hauptschule students go to school in Wolfstein. Gymnasien are available in Kaiserslautern and Lauterecken, while the nearest university is Kaiserslautern University of Technology (Technische Universität Kaiserslautern).[24]
Transport
Both villages lie on Landesstraße 382, which links Odenbach from the Glan valley with the city of Kaiserslautern. Branching off here are several roads, Landesstraße 384 to Wolfstein, Kreisstraße 43 to Relsberg and Kreisstraße 84 to Seelen. The nearest Autobahn interchanges, at Kaiserslautern West and Enkenbach on Autobahn A 6 (Saarbrücken–Mannheim) and near Winnweiler on Autobahn A 63, each lie some 25 km away.[25]
References
- Direktwahlen 2019, Landkreis Kusel, Landeswahlleiter Rheinland-Pfalz, accessed 2 August 2021.
- "Bevölkerungsstand 2021, Kreise, Gemeinden, Verbandsgemeinden" (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz. 2022.
- Location
- Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz – Amtliches Verzeichnis der Gemeinden und Gemeindeteile Archived 2015-11-25 at the Wayback Machine, Seite 99 (PDF)
- Municipality’s layout
- Antiquity
- Middle Ages
- Hefersweiler’s history
- Modern times
- Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis 2006, Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz Archived 2015-09-24 at the Wayback Machine, Seite 178 (PDF)
- Recent times
- Hefersweiler’s population development
- Berzweiler’s population development
- Merged municipality’s population development
- Municipality’s name
- Religion
- Kommunalwahl Rheinland-Pfalz 2009, Gemeinderat
- Hefersweiler’s executive
- Description and explanation of Hefersweiler’s arms
- Directory of Cultural Monuments in Kusel district
- Regular events
- Clubs
- Economic structure
- Education
- Transport
External links
- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)