Haloarcula
Haloarcula (common abbreviation Har.) is a genus of extreme halophilic Archaea in the class of Halobactaria.[2]
| Haloarcula | |
|---|---|
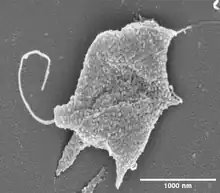 | |
| SEM image of Haloarcula quadrata. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Haloarcula |
| Species | |
| |
Cell Structure
Haloarcula species can be distinguished from other genera in the family Halobacteriaceae by the presence of specific derivatives of TGD-2 polar lipids. H. quadrata has predominantly flat, square-shaped, somewhat pleomorphic cells.[3]
Metabolism
H. quadrata was first isolated when researchers were attempting to culture Haloquadratum walsbyi, a haloarchaeon that was thought to be unculturable until 2004. Similar to other halophilic archaea, Haloarcula species grow optimally at 40–45 °C. Growth appears in sheets of up to 65 cells often in the shape of a square or triangle.
Taxonomy
The genus of Haloarcula was long grouped with other halophilic archaea such as Halobacterium until genomic analysis prompted to reorder this genus in the new family of Haloarculaceae.
Ecology
Haloarcula species are found in neutral saline environments such as salt lakes, marine salterns, and saline soils. Like other members of the family Halobacteriaceae, Haloarcula requires at least 1.5 M NaCl for growth, but grow optimally in 2.0 to 4.5 M NaCl.[4]
References
- See the NCBI webpage on Haloarcula. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
- Oren, Aharon (2014), Rosenberg, Eugene; DeLong, Edward F.; Lory, Stephen; Stackebrandt, Erko (eds.), "The Family Halobacteriaceae", The Prokaryotes: Other Major Lineages of Bacteria and The Archaea, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, pp. 41–121, Bibcode:2014prok.book...41O, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-38954-2_313, ISBN 978-3-642-38954-2, retrieved 2021-11-17
- Oren, A.; Ventosa, A.; Gutierrez, M. C.; Kamekura, M. (1999). "Haloarcula quadrata sp. nov., a square, motile archaeon isolated from a brine pool in Sinai (Egypt)". International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 49 (3): 1149–1155. doi:10.1099/00207713-49-3-1149. PMID 10425773.
- See the NCBI webpage on Haloarcula. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
Further reading
- Torreblanca M, Rodriquez-Valera F, Juez G, Ventosa A, Kamekura M, Kates M (1986). "Classification of non-alkaliphilic halobacteria based on numerical taxonomy and polar lipid composition, and description of Haloarcula gen. nov. and Haloferax gen.nov". Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 8 (1–2): 89–99. doi:10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80155-2.
- Oren A, Ventosa A (2000). "International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology Subcommittee on the taxonomy of Halobacteriaceae. Minutes of the meetings, 16 August 1999, Sydney, Australia". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50 (3): 1405–1407. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-3-1405. PMID 10843089.
- Javor B, Requadt C, Stoeckenius W (1982). "Box-shaped halophilic bacteria". J. Bacteriol. 151 (3): 1532–1542. doi:10.1128/jb.151.3.1532-1542.1982. PMC 220435. PMID 6286602.
External links
- NCBI taxonomy page for Haloarcula
- Search Tree of Life taxonomy pages for Haloarcula
- Search Species2000 page for Haloarcula
- MicrobeWiki page for Haloarcula
- LPSN page for Haloarcula
- Haloarcula at BacDive - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase