Geographical zone
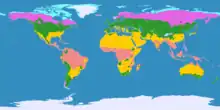
The five main latitude regions of Earth's surface comprise geographical zones,[1] divided by the major circles of latitude. The differences between them relate to climate. They are as follows:
- The North Frigid Zone, between the North Pole at 90° N and the Arctic Circle at 66°33′48.7" N, covers 4.12% of Earth's surface.
- The North Temperate Zone, between the Arctic Circle at 66°33′48.7" N and the Tropic of Cancer at 23°26'11.3" N, covers 25.99% of Earth's surface.
- The Torrid Zone, between the Tropic of Cancer at 23°26'11.3" N and the Tropic of Capricorn at 23°26'11.3" S, covers 39.78% of Earth's surface.
- The South Temperate Zone, between the Tropic of Capricorn at 23°26'11.3" S and the Antarctic Circle at 66°33'48.7" S, covers 25.99% of Earth's surface.
- The South Frigid Zone, from the Antarctic Circle at 66°33'48.7" S and the South Pole at 90° S, covers 4.12% of Earth's surface.
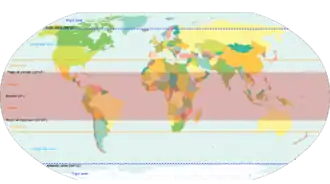
On the basis of latitudinal extent, the globe is divided into three broad heat zones.
Torrid Zone
The Torrid Zone is also known as the tropics. This zone is bounded on the north by the Tropic of Cancer and on the south by the Tropic of Capricorn; these latitudes mark the northern and southern extremes in which the Sun passes[lower-alpha 1] directly overhead. This happens once annually on these cusps, but in the tropics proper, the Sun passes overhead twice a year.
Within the northern tropics, the Sun passes overhead its first time for that year before the June solstice, at which time it does so as to the Tropic of Cancer. It passes over these latitudes in turn again, on its apparent southward journey, to and before the September equinox. After then, the center of the Sun at the high point, the zenith, of the sky (which makes for the subsolar point beneath) aligns with successive latitudes in the southern tropics. The Sun passes overhead of these then does so once per year for the Tropic of Capricorn at the December solstice, then passes back again over those latitudes to return to the equator for the March equinox.
The Torrid zone includes southern Mexico, Central America, the Caribbean, northern South America (larger parts of Brazil, the Guyanas, Caribbean South America, Andean states and the northern tip of the Southern Cone), the Sudan, the southern regions of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt, West Africa, Central Africa, East Africa, larger parts of Southern Africa (Malawi, Zambia, Zimbabwe, northern Namibia and northern Botswana), southern Middle East (southern Saudi Arabia, southern United Arab Emirates, Oman and Yemen), southern Indian subcontinent (south-central and southern India, southern Bangladesh, Sri Lanka and Maldives), Southeast Asia, northern Australia (the northern regions of the Australian states of Western Australia and Queensland, the northern regions of the Northern Territory, and the entire territory of the New Guinea island), the northern tip of Zealandia (New Caledonia), and a great part of Oceania (Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia, this later not including New Zealand).
Temperate zones
In the two temperate zones, consisting of the tepid latitudes, the Sun is never directly overhead, and the climate is mild, generally ranging from warm to cool. The four annual seasons, spring, summer, autumn, and winter, occur in these areas.
The North Temperate Zone includes North America (including northern Mexico and the northern Bahamas), Europe, North Africa (Morocco, Tunisia and the northern regions of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt), Northern Asia, East Asia, Central Asia, northern Indian subcontinent (Pakistan, northern India and northern Bangladesh) and northern Middle East (northern Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Bahrain, northern United Arab Emirates, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, the Levant (Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, Israel, Palestine), and Turkey).
The South Temperate Zone includes Southern Australia (the southern regions of the Australian states of Western Australia and Queensland, the southern regions of the Northern Territory, and the entire territories of the states of New South Wales, South Australia, Tasmania and Victoria), great part of Zealandia (New Zealand), southern South America (large part of the Southern Cone), and Southern Africa (southern Namibia, southern Botswana, great part of South Africa, the entire territories of Lesotho and Eswatini, and the southern tips of Mozambique and Madagascar).
Frigid zones
The two frigid zones, or polar regions, experience the midnight sun and the polar night for part of the year – at the edge of the zone there remains one day, the winter solstice, when the Sun is too low to rise, and one day at the summer solstice when the Sun remains above the horizon for 24 hours. In the center of the zone (the pole), the day is one year long, with six months of daylight and six months of night. The frigid zones are the coldest regions of Earth and are generally covered in ice and snow. It receives slanting rays of the Sun, as this region lies farthest from the equator. Summer in this region lasts for about 2 to 3 months, and there is almost 24-hour sunlight during summer. The sun's rays are always slanting, so provide less heat per horizontal surface area.
The North Frigid Zone includes the United States (only the state of Alaska), the northern regions of Canada (the Northwest Territories, Nunavut, and Yukon), Greenland (Denmark), Norway, Finland, Sweden, and Russia.
The South Frigid Zone includes only Antarctica.
History
The concept of a geographical zone was first hypothesized by the ancient Greek scholar Parmenides[2] and lastingly modified by Aristotle.[3] Both philosophers theorized the Earth divided into three types of climatic zones based on their distance from the equator.
Like Parmeneides, thinking that the area near the equator was too hot for habitation, Aristotle dubbed the region around the equator (from 23.5° N to 23.5° S) the "Torrid Zone." Both philosophers reasoned the region from the Arctic Circle to the pole to be permanently frozen. This region thought uninhabitable, was called the "Frigid Zone." The only area believed to be habitable was the northern "Temperate Zone" (the southern one not having been discovered), lying between the "Frigid Zones" and the "Torrid Zone". However, humans have inhabited almost all climates on Earth, including inside the Arctic Circle.
As knowledge of the Earth's geography improved, a second "Temperate Zone" was discovered south of the equator, and a second "Frigid Zone" was discovered around the Antarctic. Although Aristotle's map was oversimplified, the general idea was correct. Today, the most commonly used climate map is the Köppen climate classification, developed by Russian climatologist of German descent and amateur botanist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940), which divides the world into five major climate regions, based on average annual precipitation, average monthly precipitation, and average monthly temperature.
_no_borders.png.webp)
See also
References and footnotes
- "The Five Geographical Zones Of The World". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 2019-09-17.
- Strab. 2,2,1-2 in: A. H. Coxon and R. D. McKirahan (eds), The Fragments of Parmenides: A Critical Text With Introduction, and Translation, the Ancient Testimonia and a Commentary, 2nd edn (Phresis: Supplementary Volumes 3; Assen, Dover (NH), 2009), p. 160.
- Aristotle, Meteorology, Bekker numbers 362a33-362b29
- The "Sun passing", "reaching" or similar, implying a movement of the sun, is – in the widest context – conflating subject with object.
Astronomy, although it treats the Sun from the Earth's perspective with global, cyclical, limited northward and southern migration (in the sky, the celestial sphere), proves this is due to Earth's axial tilt, and its unlimited east-west movement is due to the Earth's orbit. If seeing and analyzing Earth and the Sun in space, Earth moves such that a geographical zone faces the Sun more or less at a certain date, or moves to align beneath the Sun, due to tilt, a particular latitude.