Exeter, California
Exeter is a city in Tulare County, California, United States. It is situated in the San Joaquin Valley near the foothills of the Sierra Nevada. The population was 10,321 at the 2020 census, down from 10,334 at the 2010 census.[5]
Exeter, California | |
|---|---|
 CA Hwy 65 through Exeter | |
| Motto: Citrus Capital of the World[1] | |
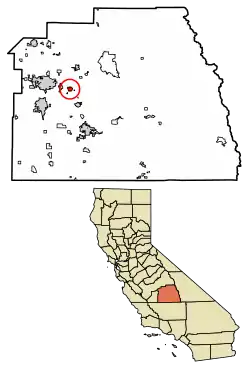 Location of Exeter in Tulare County, California. | |
 Exeter Location in California  Exeter Location in the United States | |
| Coordinates: 36°17′39″N 119°8′34″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Tulare |
| Incorporated | March 2, 1911[2] |
| Named for | Exeter |
| Government | |
| • Type | Council-Manager |
| • City council[3] | Mayor Frankie Alves Justin Mills Barbara Sally Vicki Riddle Jacob Johnson |
| • City administrator | Adam Ennis[3] |
| Area | |
| • City | 2.46 sq mi (6.37 km2) |
| • Land | 2.46 sq mi (6.37 km2) |
| • Water | 0.00 sq mi (0.00 km2) 0% |
| Elevation | 390 ft (119 m) |
| Population | |
| • City | 10,321 |
| • Estimate (2021)[5] | 10,324 |
| • Density | 4,200/sq mi (1,600/km2) |
| • Metro | 473,117 |
| Time zone | UTC-8 (Pacific) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) |
| ZIP code | 93221 |
| Area code | 559 |
| FIPS code | 06-23126 |
| GNIS feature ID | 1652707 |
| Website | www |
Exeter is located on State Highway 65, 2 miles (3.2 km) south of Highway 198 and 15 miles (24 km) east of Highway 99.
History
Before the arrival of European settlers, Yokuts settled around an area in an oak forest two miles north of Exeter. The current town site was a plain that possessed elk, antelope, frogs, and deer.[1] Rocky Hill, to the east of the city, offered shelter to native tribes when the plain flooded. Several caves on the hill contain petroglyphs, though some of the most important of these were destroyed by local vandals/looters and poorly managed and unsupervised steer.
The town site traces its roots to the construction of a railroad line through the San Joaquin Valley, by 1888 a line passed through the area. A representative of the Southern Pacific Railroad, D.W. Parkhurst, purchased the land from an early settler, John Firebaugh, and formed the town which he named after his own hometown of Exeter, England.[1]
The damming of the Kaweah valley during the 1930s provided a reliable source of water for agriculture. Cattle ranching grew at the beginning of the 20th century, led by the Gill Cattle Company, which opened in the late 1800s and was once the largest such business in the United States.[1] The town incorporated in 1911. In October, 1929, Exeter was the site of a large Anti-Filipino race riot. A mob stormed a Filipino work camp, bludgeoning 50 Filipino laborers and burning their camp to the ground. This race-riot sparked a wave of Anti-Filipino hatred.[7]
Professional artists depicting the history of the area have painted huge murals on exterior walls throughout the downtown area. There are currently 31 murals in this outdoor art gallery.[8]
Geography
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 2.5 square miles (6.5 km2), all of it land.
Climate
| Exeter, California | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demographics
| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1920 | 1,852 | — | |
| 1930 | 2,685 | 45.0% | |
| 1940 | 3,883 | 44.6% | |
| 1950 | 4,078 | 5.0% | |
| 1960 | 4,264 | 4.6% | |
| 1970 | 4,475 | 4.9% | |
| 1980 | 5,606 | 25.3% | |
| 1990 | 7,276 | 29.8% | |
| 2000 | 9,168 | 26.0% | |
| 2010 | 10,334 | 12.7% | |
| 2020 | 10,321 | −0.1% | |
| 2021 (est.) | 10,324 | [5] | 0.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[9] | |||
2020
The 2020 United States Census reported that Exeter had a population of 10,321.
2010
At the 2010 census Exeter had a population of 10,334. The population density was 4,195.6 inhabitants per square mile (1,619.9/km2). The racial makeup of Exeter was 7,150 (69.2%) White, 67 (0.6%) African American, 171 (1.7%) Native American, 138 (1.3%) Asian, 8 (0.1%) Pacific Islander, 2,416 (23.4%) from other races, and 384 (3.7%) from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 4,703 persons (45.5%).[10]
The census reported that 10,261 people (99.3% of the population) lived in households, 57 (0.6%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 16 (0.2%) were institutionalized.
There were 3,378 households, 1,552 (45.9%) had children under the age of 18 living in them, 1,801 (53.3%) were opposite-sex married couples living together, 575 (17.0%) had a female householder with no husband present, 227 (6.7%) had a male householder with no wife present. There were 233 (6.9%) unmarried opposite-sex partnerships, and 12 (0.4%) same-sex married couples or partnerships. 652 households (19.3%) were one person and 313 (9.3%) had someone living alone who was 65 or older. The average household size was 3.04. There were 2,603 families (77.1% of households); the average family size was 3.45.
The age distribution was 3,285 people (31.8%) under the age of 18, 1,020 people (9.9%) aged 18 to 24, 2,586 people (25.0%) aged 25 to 44, 2,255 people (21.8%) aged 45 to 64, and 1,188 people (11.5%) who were 65 or older. The median age was 31.2 years. For every 100 females, there were 94.5 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 90.4 males.
There were 3,600 housing units at an average density of 1,461.6 per square mile, of the occupied units 2,036 (60.3%) were owner-occupied and 1,342 (39.7%) were rented. The homeowner vacancy rate was 3.4%; the rental vacancy rate was 6.3%. 6,111 people (59.1% of the population) lived in owner-occupied housing units and 4,150 people (40.2%) lived in rental housing units.
2000
At the 2000 census there were 9,168 people in 3,001 households, including 2,325 families, in the city. The population density was 4,110.9 inhabitants per square mile (1,587.2/km2). There were 3,168 housing units at an average density of 1,420.5 per square mile (548.5/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 69.73% White, 0.69% African American, 1.47% Native American, 1.30% Asian, 0.04% Pacific Islander, 23.20% from other races, and 3.57% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 38.25%.[11]
Of the 3,001 households 45.1% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 55.6% were married couples living together, 15.6% had a female householder with no husband present, and 22.5% were non-families. 18.8% of households were one person and 9.9% were one person aged 65 or older. The average household size was 3.02 and the average family size was 3.43.
The age distribution was 33.7% under the age of 18, 10.1% from 18 to 24, 26.8% from 25 to 44, 18.2% from 45 to 64, and 11.1% 65 or older. The median age was 30 years. For every 100 females, there were 92.9 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 89.9 males.
The median income for a household in the city was $33,738, and the median family income was $37,033. Males had a median income of $32,308 versus $27,371 for females. The per capita income for the city was $13,795. About 14.2% of families and 19.4% of the population were below the poverty line, including 24.8% of those under age 18 and 12.0% of those age 65 or over.
Economy
Major employers in Exeter include Waterman Industries, Svenhard's Swedish Bakery and Peninsula Packaging.[12]
Government
Local government
The current mayor is Frankie Alves.[3]
State and federal
In the California State Legislature, Exeter is in the 12th Senate District, represented by Republican Shannon Grove, and in the 32nd Assembly District, represented by Republican Vince Fong.[13]
In the United States House of Representatives, Exeter is in California's 21st congressional district, represented by Democrat Jim Costa.[14]
Education
The public school system in Exeter consists of: Exeter Union High School (9-12), the Wilson Middle School (6-8), Rocky Hill Elementary (K-5), Lincoln Elementary (K-5) and Kaweah High School (a continuation high school). The 1999-2000 enrollment was: grades K-8, 1,936 and grades 9-12, 1101 students.
Notable people
- Joseph James DeAngelo, convicted as the Golden State Killer and the Visalia Ransacker in 2020, was a police officer in Exeter from 1973 to 1976, same time as when the Ransacker crimes occurred in neighbouring Visalia.[15]
- Jim Qualls, former Major League Baseball outfielder for the Chicago Cubs
- Ron Robinson, former Major League Baseball pitcher for the Cincinnati Reds and the Milwaukee Brewers
- Brad Mills, former player and coach of Major League Baseball
- Jeriome Robertson, former baseball pitcher with Houston Astros and Cleveland Indians, grew up and died in Exeter.[16][17]
- Satoshi Hirayama, former baseball star for Hiroshima Toyo Carp, born and raised in Exeter.[18]
- Kenny Guinn, former governor of Nevada
- Robert List, former governor of Nevada
Gallery
 The Exeter Historical Museum is housed in the old Mt. Whitney Power Company Substation, formerly the headquarters of the Exeter Police Department.
The Exeter Historical Museum is housed in the old Mt. Whitney Power Company Substation, formerly the headquarters of the Exeter Police Department. Downtown Exeter boasts its own outdoor art gallery featuring 31 murals depicting local history, folklore, and culture[8]
Downtown Exeter boasts its own outdoor art gallery featuring 31 murals depicting local history, folklore, and culture[8] The Exeter Public Library building, a Carnegie library, is on the National Register of Historic Places; it now serves as a community center.
The Exeter Public Library building, a Carnegie library, is on the National Register of Historic Places; it now serves as a community center. City Hall and Fire Department
City Hall and Fire Department
References
- , City of Exeter, Accessed August 6, 2009.
- "California Cities by Incorporation Date". California Association of Local Agency Formation Commissions. Archived from the original (Word) on November 3, 2014. Retrieved August 25, 2014.
- "Exeter City Council". City of Exeter. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved July 1, 2020.
- "U.S Census Bureau QuickFacts: Exeter city, California". census.gov. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- "2020 Population and Housing State Data". United States Census Bureau. August 12, 2021. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- "Racial Hatred Once Flared on Central Coast". The Weekend Pinnacle Online. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved June 6, 2010.
- "Mural Guide" (PDF). Exeter Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved March 26, 2017.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "2010 Census Interactive Population Search: CA - Exeter city". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on July 15, 2014. Retrieved July 12, 2014.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- Tulare Valley Economic Development Corporation Major Employers
- "Statewide Database - Map Viewer - California Districts". UC Regents. Retrieved April 20, 2023.
- "California's 21st Congressional District - Representatives & District Map". Civic Impulse, LLC. Retrieved May 9, 2023.
- The New York Times, April 25, 2018
- "Robertson killed in auto accident". milb.com. June 1, 2010. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- Camarena, Andrea (June 2, 2010). "Exeter pitcher dies in motorcycle accident". thesungazette.com. Retrieved July 18, 2020.
- K, Fitts, Robert (2005). Remembering Japanese Baseball. SIU Press. ISBN 978-0-8093-8973-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
