Etrasimod
Etrasimod, sold under the brand name Velsipity, is a medication that is used for the treatment of ulcerative colitis (UC).[1] It is a selective sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor modulator that modifies the activity of the immune system.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
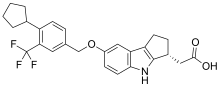 Skeletal formula of etrasimod | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Velsipity |
| Other names | APD334, APD-334 |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| Drug class | Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor modulator |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 97.9% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP2C8, 2C9, 3A4) |
| Elimination half-life | 30 hours |
| Excretion | Feces (82%), kidneys (5%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C26H26F3NO3 |
| Molar mass | 457.493 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Etrasimod was discovered by Arena Pharmaceuticals, with subsequent development by Pfizer.[2]
Medical uses
Etrasimod is used for the treatment of moderate to severe ulcerative colitis.[1]
Mechanism of action
It works by causing T cells to become trapped in the lymph nodes, preventing them from entering the bloodstream, from where they would travel to other tissues in the body and mediate inflammation.[3][4][5][6][7][8]
Society and culture
Legal status
Velsipity was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in October 2023.[1][9][10]
Names
Etrasimod is the international nonproprietary name.[11]
References
- Pfizer (12 October 2023). "Velsipity (etrasimod) tablets, for oral use" (PDF). U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Retrieved 18 October 2023.
- Bayer M (2 May 2023). "Pfizer tosses newly acquired meds out of the Arena". Fierce Biotech. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- Atreya R, Neurath MF (April 2023). "The sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonist etrasimod in ulcerative colitis". Lancet. 401 (10383): 1132–1133. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00228-3. PMID 36871570.
- Sandborn WJ, Vermeire S, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Dubinsky MC, Panes J, Yarur A, et al. (April 2023). "Etrasimod as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis (ELEVATE): two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 studies". Lancet. 401 (10383): 1159–1171. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00061-2. PMID 36871574.
- Dal Buono A, Gabbiadini R, Alfarone L, Solitano V, Repici A, Vetrano S, et al. (July 2022). "Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Modulation in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Keeping Lymphocytes Out of the Intestine". Biomedicines. 10 (7). doi:10.3390/biomedicines10071735. PMC 9313037. PMID 35885040.
- Argollo M, Furfaro F, Gilardi D, Roda G, Allocca M, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. (April 2020). "Modulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate in ulcerative colitis". Expert Opin Biol Ther. 20 (4): 413–420. doi:10.1080/14712598.2020.1732919. PMID 32093531.
- Al-Shamma H, Lehmann-Bruinsma K, Carroll C, Solomon M, Komori HK, Peyrin-Biroulet L, et al. (June 2019). "The Selective Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptor Modulator Etrasimod Regulates Lymphocyte Trafficking and Alleviates Experimental Colitis". J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 369 (3): 311–317. doi:10.1124/jpet.118.254268. PMID 30872391.
- Peyrin-Biroulet L, Christopher R, Behan D, Lassen C (May 2017). "Modulation of sphingosine-1-phosphate in inflammatory bowel disease". Autoimmun Rev. 16 (5): 495–503. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2017.03.007. PMID 28279838.
- Brooks M (13 October 2023). "FDA Approves New Drug for Ulcerative Colitis". Medscape. Retrieved 13 October 2023.
- https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/appletter/2023/216956Orig1s000ltr.pdf
- World Health Organization (2017). "International nonproprietary names for pharmaceutical substances (INN): recommended INN: list 78". WHO Drug Information. 31 (3). hdl:10665/330961.