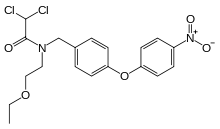
Etofamide
Etofamide (INN, also known as eticlordifene) is an antiprotozoal drug used in the treatment of amoebiasis.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.522 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H20Cl2N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 427.28 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Its effect against Giardia lamblia has been described as modest.[1]
References
- Cedillo-Rivera R, Muñoz O (September 1992). "In-vitro susceptibility of Giardia lamblia to albendazole, mebendazole and other chemotherapeutic agents". Journal of Medical Microbiology. 37 (3): 221–4. doi:10.1099/00222615-37-3-221. PMID 1518040.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.