Etamiphylline
Etamiphylline or etamiphyllin (INN)[1] is a xanthine intended for use as an anti-asthma agent. It has shown poor to absent effects in human clinical trials.[2][3]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
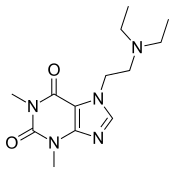
7-[2-(Diethylamino)ethyl]-1,3-dimethyl-3,7-dihydro-1H-purine-2,6-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.678 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H21N5O2 | |
| Molar mass | 279.33814 |
| Pharmacology | |
| R03DA06 (WHO) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- "International Non-Proprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Preparations. Recommended International Non-Proprietary Names (Rec. I.N.N.): List 3" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 467. Retrieved 29 December 2016.
- Vazquez, C; Labayru, T; Rodriguez-Soriano, J (1984). "Poor bronchodilator effect of oral etamiphylline in asthmatic children". Lancet. 1 (8382): 914. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91380-1. PMID 6143224.
- Addis, GJ (1984). "Absence of bronchodilatory effect from etamiphylline". Lancet. 1 (8385): 1083. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91497-1. PMID 6144017.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.