Estuaries of Texas
The U.S. state of Texas has a series of estuaries along its coast on the Gulf of Mexico, most of them bounded by the Texas barrier islands. Estuaries are coastal bodies of water in which freshwater from rivers mixes with saltwater from the sea. Twenty-one drainage basins terminate along the Texas coastline, forming a chain of seven major and five minor estuaries: listed from southwest to northeast, these are the Rio Grande Estuary, Laguna Madre, the Nueces Estuary (Corpus Christi Bay), the Mission–Aransas Estuary (Aransas Bay), the Guadalupe Estuary (San Antonio Bay), the Colorado–Lavaca Estuary (Matagorda Bay), East Matagorda Bay, the San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary, the Brazos River Estuary, Christmas Bay, the Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary (Galveston Bay), and the Sabine–Neches Estuary (Sabine Lake).[1] Each estuary is named for its one or two chief contributing rivers, excepting Laguna Madre, East Matagorda Bay, and Christmas Bay, which have no major river sources. The estuaries are also sometimes referred to by the names of their respective primary or central water bodies, though each also includes smaller secondary bays, inlets, or other marginal water bodies.[2]
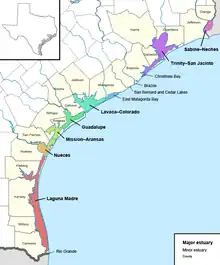
These water bodies include some of the largest and most ecologically productive coastal estuaries in the United States and contribute significantly to the ecological and economic resources of Texas. They are included in a number of national protected areas such as National Wildlife Refuges, a National Seashore, and a National Estuarine Research Reserve, as well as various state parks and other regional protected areas. The two most economically important (the Nueces and Trinity–San Jacinto Estuaries) have been designated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency as estuaries of national significance under the National Estuary Program. The Gulf Intracoastal Waterway runs through each of the major estuaries, linking Texas ports with others along the Gulf Coast of the United States.
Overview
Twenty-one drainage basins terminate along the Gulf Coast of Texas, and the freshwater from these rivers and the adjacent coastal watersheds mixes with saltwater from the Gulf to form a series of estuaries. The seven major estuaries are all separated from the Gulf of Mexico by the Texas barrier islands and various peninsulas on the mainland, making them into sheltered bays,[1] whereas several of the minor estuaries have no barrier islands or embayments but are riverine estuaries that empty directly into the Gulf.[3] The Texas coastline has changed significantly over the past million years as a result of sea level fluctuations, caused mainly by the passing of glacial periods. The current chain of barrier islands and peninsulas formed between 8,000 and 5,000 years ago as the Gulf of Mexico stabilized around its current level after the end of the Last Glacial Period, shaping the estuary systems along the present coast.[4] The Texas estuaries support productive and biodiverse aquatic and coastal ecosystems, and they contribute significant economic value to the state, both by directly supporting industries such as fishing and tourism, and by providing services such as runoff filtration and shoreline stabilization.[1]
Laguna Madre Estuary

The Laguna Madre Estuary is located along the southern coast of Texas in Nueces, Kenedy, Kleberg, Willacy, and Cameron Counties, extending almost to the border with Mexico.[5] It is a long, shallow lagoon with no major river sources, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Padre Island and Brazos Island and connecting with it through the Port Mansfield Channel and Brazos-Santiago Pass. Laguna Madre is the second largest of the Texas estuaries, approximately 130 miles (210 km) long and 4 to 6 miles (6 to 10 km) wide, with a surface area of 280,910 acres (113,680 ha) including Laguna Madre and its westward extensions in Baffin Bay and South Bay. The lagoon is split by a 20-mile (32 km) stretch of sand flats named the Saltillo Flats, which divide it into "upper" (northern) and "lower" (southern) sections. The natural portions have an average depth of around 4.5 feet (1.4 m), though deeper shipping channels have been dredged through. Its low rate of freshwater recharge and high evaporation rate make it hypersaline.[6]
The shores of the lagoon are sparsely populated, with the small towns of Port Isabel and Port Mansfield on the mainland side and South Padre Island on the barrier island as the only significant settlements; all three are located on the Lower Laguna Madre. Tourism and commercial fishing (especially for penaeid shrimp) are major industries in the region,[7] and much of the mainland shore is part of King Ranch. The lagoon's rich ecosystem is maintained by a number of protected areas, including the Laguna Atascosa National Wildlife Refuge and Padre Island National Seashore.[8][9]
Nueces Estuary

The Nueces Estuary is located on the Texas Coastal Bend in San Patricio and Nueces Counties, adjoining the city of Corpus Christi. It is fed by the Nueces River and Oso Creek and separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Mustang Island.[10] The Nueces Estuary is the sixth largest of the Texas estuaries, with a surface area of 106,990 acres (43,300 ha) including Corpus Christi Bay and its western and southern extensions in Nueces Bay and Oso Bay.[11] The natural portions have a depth of up to 13 feet (4 m).[12]: III–1 Smaller settlements around the bay include Portland, Ingleside, and Ingleside on the Bay, all located on the north shore.[13][14]
Corpus Christi Bay is a deep-water natural harbor, and the shipping industry in the Port of Corpus Christi has been a major driver of human development in the region.[10] Other significant industries include petroleum and natural gas extraction, tourism, commercial fishing, and military facilities such as Naval Air Station Corpus Christi.[15] The United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the Nueces Estuary system as an estuary of national significance under the National Estuary Program.[16]
Mission–Aransas Estuary

The Mission–Aransas Estuary is located on the Texas Coastal Bend in Aransas, Refugio, and San Patricio Counties. It is fed by the Mission and Aransas Rivers, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by San José Island and connecting with it through Aransas Pass and Cedar Bayou. The Mission–Aransas Estuary is the fifth largest of the Texas estuaries, with a surface area of 111,780 acres (45,240 ha) including Aransas Bay and its extensions in Redfish Bay to the southwest, Copano Bay to the northwest, and Saint Charles Bay to the north. The natural portions have an average depth of around 5.5 feet (1.7 m).[17]
The shores of the estuary are sparsely populated, with the small towns of Aransas Pass, Port Aransas, Rockport, and Fulton as the only significant settlements. Historically Aransas Bay was a center for the meat packing industry, but today the region's economy centers around commercial fishing and tourism.[18] The Mission–Aransas Estuary is the site of the Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's only National Estuarine Research Reserve in Texas. It serves as a wintering ground for the endangered whooping crane.[19]
Guadalupe Estuary

The Guadalupe Estuary is located near the middle of the Texas coast in Calhoun, Aransas, and Refugio Counties. It is fed by the Guadalupe River, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Matagorda Island and connecting with it through Cedar Bayou.[20] The Guadalupe Estuary is the fourth largest of the Texas estuaries, with a surface area of 143,000 acres (58,000 ha) including San Antonio Bay and its extensions to the southwest and northeast in Mesquite Bay and Espiritu Santo Bay. The natural portions have an average depth of around 2.5 feet (0.8 m).[21]: 6
The estuary is remote and difficult for shipping to access, and its shores are almost uninhabited, with the small towns of Seadrift and Austwell as the only significant settlements. The leading industries in the region are oyster farming, fish processing and the chemical industry.[22] The southwestern shore and much of Matagorda Island are protected within the Aransas National Wildlife Refuge.[23]
Colorado–Lavaca Estuary

The Colorado–Lavaca Estuary is located on the upper-mid Texas coast in Matagorda, Jackson, Victoria, and Calhoun Counties. It is fed by the Colorado, Lavaca, and Tres Palacios Rivers, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by the Matagorda Peninsula and connecting with it through Matagorda Ship Channel and Pass Cavallo. The Colorado–Lavaca Estuary is the third largest of the Texas estuaries, with a surface area of 244,490 acres (98,940 ha) including Matagorda Bay and its extensions in Lavaca Bay and several smaller bays.[24] The natural portions have depths ranging from 6 to 13 feet (2 to 4 m).[25]: III–1
The shores of the estuary are sparsely populated, with the small towns of Port Lavaca, Palacios, Port O'Connor, and Point Comfort as the only significant settlements.[26] Matagorda Bay is a major center for the commercial fishing and fish processing industries, with the Port of Port Lavaca driving much of the regional economy; tourism and manufacturing are also significant contributors.[27] The bay was the site of La Salle's failed French colony, and the shipwreck of one of his ships, La Belle, was discovered and excavated in the 1990s and 2000s.[28]
Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary

The Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary is located on the northeastern Texas coast in Chambers, Harris, Galveston, and Brazoria Counties, adjoining the city of Houston. It is formed by the confluence of the Trinity and San Jacinto Rivers, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Galveston Island and Bolivar Peninsula and connecting with it through Rollover Pass, Bolivar Roads, and San Luis Pass. The Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary is the largest of the Texas estuaries, with a surface area of 345,280 acres (139,730 ha) including Galveston Bay and its extensions in East Bay to the east, Trinity Bay to the northeast, West Bay to the southwest, and several smaller bays and inlets.[29] The natural portions of the estuary have mean low-water depths ranging from 6 to 10 feet (2 to 3 m).[30]: III–1
The Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary is almost surrounded by the Greater Houston urban area, and its shores are relatively urbanized and industrialized, especially to the west.[30]: III–12 Other significant settlements on the shores include Baytown, Texas City, and Galveston.[31][32][33] The estuary is a major shipping center, the heart of the Houston Ship Channel, and the Port of Houston, Port of Texas City, and Port of Galveston drive much economic activity on the waterways.[34] Petrochemical industries are concentrated along the western shore, and the estuary also supports Texas's largest commercial fishery.[30]: III–12, 15 The United States Environmental Protection Agency has designated the Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary system as an estuary of national significance under the National Estuary Program.[35] Portions of the northeastern shore are protected within the Anahuac National Wildlife Refuge.[36] The museum ship USS Texas is moored in the mouth of the San Jacinto River at the northwest end of the estuary, next to the San Jacinto Monument.[37]
Sabine–Neches Estuary

The Sabine–Neches Estuary is located on the Louisiana border at the corner of Southeast Texas in Jefferson and Orange Counties, adjoining the city of Port Arthur. It is an almost totally enclosed lake, formed by the confluence of the Neches and Sabine Rivers and connecting to the Gulf of Mexico through Sabine Pass. The Sabine–Neches Estuary is the smallest of the seven major estuaries, with a surface area of 45,320 acres (18,340 ha) including Sabine Lake and a number of adjoining bayous, and its small size and high rate of freshwater inflow make it the least saline of the seven.[38] The natural portions of the estuary have a mean low-water depth of at most around 10 feet (3 m).[39]: III–1
The channelization of the Sabine–Neches Estuary has made it an important industrial waterway, the heart of the Sabine–Neches Waterway. The three ports it links to the Gulf of Mexico (Port Arthur, Beaumont, and Orange) form a major nexus for the shipping and petrochemical industries, the so-called Golden Triangle of Texas.[40] The largest industries around the estuary are petroleum and natural gas extraction, petrochemical processing, shipping, and shipbuilding. Agriculture also forms a significant component of the regional economy, principally rice and soybean cultivation, livestock ranching, and commercial fishing (mainly for shellfish).[39]: III–20
Minor estuaries
Texas has five minor estuaries interspersed among its seven major estuary systems. These are smaller, less complicated estuaries with less significance to the state's hydrology, ecology, and economy. Several of these are simply the lower tidal reaches of particular rivers, without barrier islands or embayments to separate them from the Gulf of Mexico.[3]
Rio Grande Estuary
The Rio Grande Estuary is located on the Texas–Mexico border in Cameron County, south of Laguna Madre at the southern extremity of the Texas coast. It is a riverine estuary system consisting only of the lower reaches of the Rio Grande, with no associated bay.[41]
East Matagorda Bay Estuary
East Matagorda Bay is a minor estuary located on the upper-mid Texas coast in Matagorda County immediately northeast of the Colorado–Lavaca Estuary (Matagorda Bay). It has no significant river sources and is separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Matagorda Peninsula, only intermittently connecting with it through Brown Cedar Cut. The estuary has a surface area of 37,810 acres (15,300 ha), and its natural portions have an average depth of around 3.4 feet (1.0 m)[42]
San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary
The San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary is one of three minor estuaries located on the upper-mid Texas coast in Brazoria County between Matagorda Bay and Galveston Bay. It includes Cedar Lakes, Cowtrap Lake, and the lower reaches of the San Bernard River, covering a surface area of 3,760 acres (1,520 ha) with an average depth of 2.1 feet (0.6 m).[43]
Brazos River Estuary
The Brazos River Estuary is the second of three minor estuaries located on the upper-mid Texas coast in Brazoria County between Matagorda Bay and Galveston Bay. It is a riverine estuary system consisting only of the lower reaches of the Brazos River, with no associated bay.[44]
Christmas Bay Estuary
Christmas Bay is a minor estuary located on the upper-mid Texas coast in Brazoria County immediately southwest of the Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary (Galveston Bay). It is fed by Bastrop Bayou, separated from the Gulf of Mexico by Follet's Island and connecting with it through San Luis Pass and Cold Pass. Its minor extensions are Bastrop Bay to the north and Drum Bay to the southwest.[45] The estuary has a surface area of 4,173 acres (1,689 ha). Much of its shoreline is protected within the Brazoria National Wildlife Refuge.[46]
References
- "Bays & Estuaries". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Major Estuaries of Texas". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Minor Estuaries of Texas". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Weddle, Robert S. "Gulf of Mexico". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 24, 2020.
- Leatherwood, Art. "Laguna Madre". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Laguna Madre". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Garza, Alicia A. "Port Isabel, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Laguna Atascosa National Wildlife Refuge Map". United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Padre Island National Seashore Map". United States National Park Service. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Leatherwood, Art. "Corpus Christi Bay". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Nueces Estuary (Corpus Christi Bay)". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Nueces and Mission–Aransas Estuaries: A Study of the Influence of Freshwater Inflows" (PDF). Texas Water Development Board. Texas Department of Water Resources. January 1981. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Guthrie, Keith. "Portland, Texas (San Patricio County)". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Guthrie, Keith. "Ingleside, Texas (San Patricio County)". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Long, Christopher. "Corpus Christi, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Coastal Bend Bays & Estuaries Program". Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Mission–Aransas Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Long, Christopher. "Aransas County". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Mission-Aransas National Estuarine Research Reserve". National Estuarine Research Reserves. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Guadalupe Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Guadalupe Estuary: An Analysis of Bay Segment Boundaries, Physical Characteristics, and Nutrient Processes" (PDF). Texas Water Development Board. Texas Department of Water Resources. March 1981. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Rubert, Rebecca. "Seadrift, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Leatherwood, Art. "San Antonio Bay". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Colorado–Lavaca Estuary (Matagorda Bay)". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Lavaca–Tres Palacios Estuary: A Study of the Influence of Freshwater Inflows" (PDF). Texas Water Development Board. Texas Department of Water Resources. June 1980. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Leatherwood, Art. "Matagorda Bay". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Maywald, Lonnie Ficklen. "Port Lavaca, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "La Belle: The Ship That Changed History". Bullock Texas State History Museum. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary (Galveston Bay)". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Trinity–San Jacinto Estuary: A Study of the Influence of Freshwater Inflows" (PDF). Texas Water Development Board. Texas Department of Water Resources. March 1981. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Young, Buck A. "Baytown, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Benham, Priscilla Myers. "Texas City, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- McComb, David G. "Galveston, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Sibley, Marilyn M. "Houston Ship Channel". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Galveston Bay Estuary Program". Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Anahuac National Wildlife Refuge Map". United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Battleship Texas State Historic Site". Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Sabine-Neches Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved February 11, 2020.
- "Sabine–Neches Estuary: A Study of the Influence of Freshwater Inflows" (PDF). Texas Water Development Board. Texas Department of Water Resources. July 1981. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- Isaac, Paul E. "Beaumont, Texas". Handbook of Texas Online. Texas State Historical Association. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Rio Grande Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "East Matagorda Bay". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "San Bernard River and Cedar Lakes Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Brazos River Estuary". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Christmas Bay". Texas Water Development Board. Retrieved March 11, 2020.
- "Texas GEMS — Christmas Bay Coastal Preserve". Texas Parks and Wildlife Department. Retrieved April 2, 2020.