Crossognathiformes
Crossognathiformes is an extinct order of ray-finned fish that lived from the Late Jurassic to the Eocene. Its phylogenetic placement is disputed; some authors have recovered it as part of the teleost stem group,[1] while others place it in a basal position within crown group Teleostei.[2]
| Crossognathiformes Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Rhacolepis fossil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Infraclass: | Teleostei |
| Order: | †Crossognathiformes Taverne, 1989 |
| Subgroups | |
|
See text | |
Classification
Order Crossognathiformes Taverne, 1989[1][3]
- Bavarichthys Arratia & Tischlinger, 2010[4]
- Kradimus Veysey et al., 2020[5]
- Family Varasichthyidae Arratia, 1981
- Bobbichthys Arratia, 1986
- Domeykos Arratia & Schultze, 1985
- Luisichthys White, 1942
- Protoclupea Arratia et al., 1975
- Varasichthys Arratia, 1981
- Family Chongichthyidae Arratia, 1982
- Chongichthys Arratia, 1982
- Suborder Crossognathoidei Taverne, 1989
- Family Crossognathidae Woodward, 1901 [Apsopelicidae Romer, 1966; Syllaemidae Cragin, 1901; Pelecorapidae Cragin, 1901]
- Apsopelix Cope, 1871 [Helmintholepis Cockerell, 1919; Leptichthys Stewart, 1899; Palaeoclupea Dante, 1942; Pelecorapis Cope, 1874; Syllaemus Cope, 1875]
- Crossognathus Pictet, 1858
- Family Crossognathidae Woodward, 1901 [Apsopelicidae Romer, 1966; Syllaemidae Cragin, 1901; Pelecorapidae Cragin, 1901]
- Suborder Pachyrhizodontoidei Forey, 1977
- Family Notelopidae Forey, 1977
- Notelops Woodward, 1901
- Family Pachyrhizodontidae Cope, 1872 [Greenwoodellidae Taverne, 1973; Thrissopatrinae Boulenger, 1904b]
- Apricenapiscis Taverne, 2013
- Aquilopiscis Cumbaa & Murray, 2008
- Cavinichthys Taverne & Capasso, 2019
- Elopopsis Heckel, 1856
- Goulmimichthys Cavin, 1995
- Greenwoodella Taverne & Ross, 1973
- Hemielopopsis Bassani, 1879
- Lebrunichthys Taverne & Capasso, 2020
- Michin Alvarado-Ortega et al., 2008
- Motlayoichthys Arratia et al., 2018
- Nardopiscis Taverne, 2008
- Pachyrhizodus Dixon, 1850 [Acrodontosaurus Mason, 1869; Eurychir Jordan, 1924; Oricardinus Cope, 1872; Thrissopater Günther, 1872 sensu Forey, 1977]
- Phacolepis Agassiz, 1841 [Rhacolepis Agassiz, 1841 non Frenguelli, 1942]
- Platinx Agassiz, 1835
- Polcynichthys London & Shimada, 2020[6]
- Rhacolepis Agassiz, 1843
- Stanhopeichthys Taverne & Capasso, 2020
- Tingitanichthys Taverne, 1996
- Family Notelopidae Forey, 1977
Timeline of genera
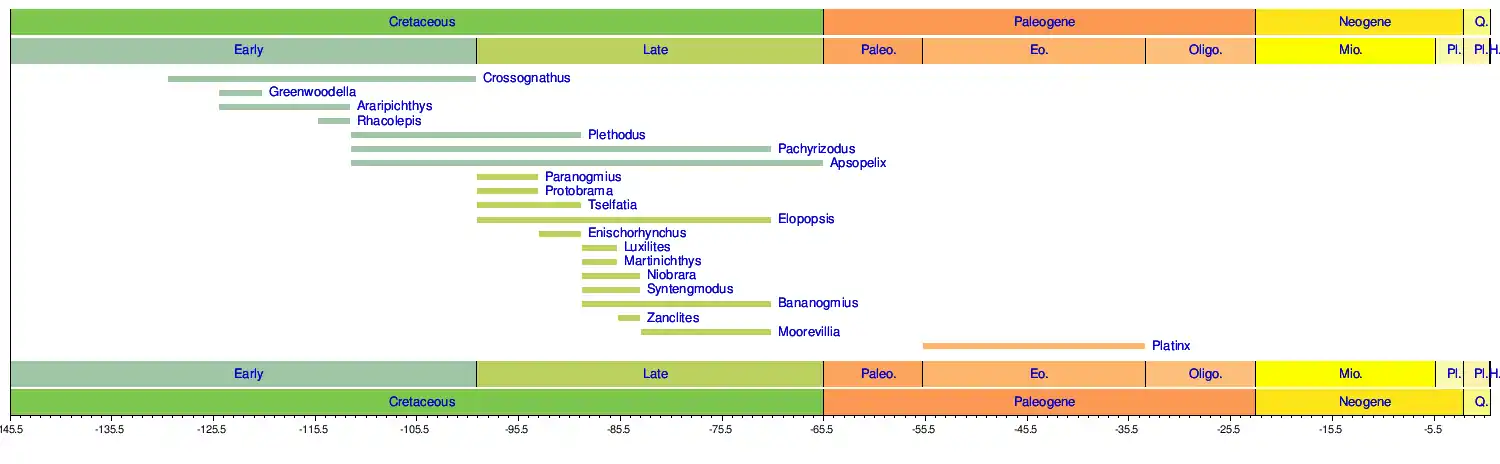
Bibliography
- Sepkoski, Jack (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology. 363: 1–560. Archived from the original on July 23, 2011. Retrieved 2011-05-17.
References
- Nelson, J. S.; Grande, T. C.; Wilson, M. V. H. (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781118342336.
- Sferco, E.; López-Arbarello, A.; Báez, A. M. (2015). "Phylogenetic relationships of †Luisiella feruglioi (Bordas) and the recognition of a new clade of freshwater teleosts from the Jurassic of Gondwana". BMC Evolutionary Biology. 15 (1): 268. doi:10.1186/s12862-015-0551-6. PMC 4668602. PMID 26630925.
- van der Laan, R. (2016). "Family-group names of fossil fishes".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Arratia, G.; Tischlinger, H. (2010). "The first record of Late Jurassic crossognathiform fishes from Europe and their phylogenetic importance for teleostean phylogeny". Fossil Record. 13 (2): 317–341. doi:10.1002/mmng.201000005.
- Veysey, A. J.; Brito, P. M.; Martill, D. M. (2020). "A new crossognathiform fish (Actinopterygii, Teleostei) from the Upper Cretaceous (Turonian) of southern Morocco with hypertrophied fins". Cretaceous Research. 114: 104207. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2019.104207. S2CID 202200253.
- London, M. G.; Shimada, K. (2020). "A new pachyrhizodontid fish (Actinopterygii: Teleostei) from the Tarrant Formation (Cenomanian) of the Upper Cretaceous Eagle Ford Group in Texas, USA". Cretaceous Research. 113: 104490. doi:10.1016/j.cretres.2020.104490. S2CID 219066064.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.






