Curonian colonisation
Curonian colonisation refers to the colonisation efforts of the Duchy of Courland and Semigallia (today part of Latvia). Small, but wealthy, the Duchy took a modest part in the European colonization settlement attempts of West Africa and the Caribbean.
History
Like Brandenburg, which had far larger German colonising power before the formation of the German Empire, Courland had a European crusading past. The colonies were established under Jakob, Duke of Courland and Semigallia, and were one of the two Latvian colonies. Second colony was Gambia River in Africa. During his reign (1642–1682), the Duchy established trading relations with all of the major European powers.
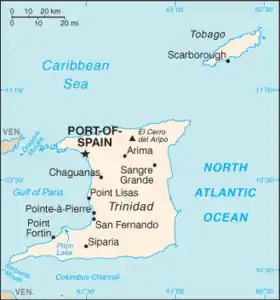
Jakob established one of the largest merchant fleets in Europe, with its main harbours in Windau (today Ventspils), and Libau (today Liepāja). His fleet made voyages to the West Indies as early as 1637 when the settlers established the first colony on Tobago. The first colony was a failure, but it was refounded in 1639.
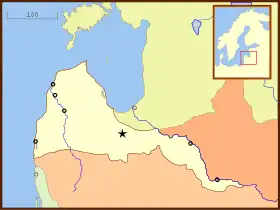
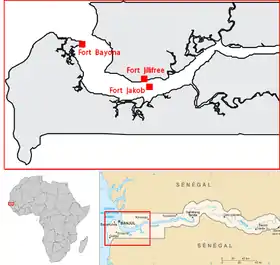
In 1651, the Courland and Semigallia gained a colony in Africa on St. Andrew's Island in the Gambia River and went on to build Fort Jakob on the island. The Duchy also gained control of additional land, which happened to include St. Mary Island (modern-day Banjul) and Fort Jillifree. The Courland and Semigallia's colonies exported sugar, tobacco, coffee, cotton, ginger, indigo, rum, cocoa, tortoise shells, as well as tropical birds and their much sought after feathers. In the end, the Duchy would manage to retain control of these lands for less than a decade and the colonies were formally ceded to England in 1664.
The colonies were lost when the Courland and Semigallia's neighbours took advantage of its weakened defences during the Northern Wars, when Jakob was held captive by the Swedish Army from 1658 to 1660. After the end of the war, the island of Tobago was returned to Courland. However, the Duchy ended up abandoning the island in 1666. In 1668, a Courish ship attempted to reoccupy Fort Jacob but was driven off by the Dutch garrison stationed on the island. The Courland Monument near Great Courland Bay commemorates the Duchy's settlements.
Former colonies
- St. Andrews Island or Courlander Gambia was also the later British Fort James. (1651–1660, 1660–1661)
- New Courland, on Tobago (1637, 1642, 1654–1659, 1680–1690)
