Cluj-Napoca metropolitan area
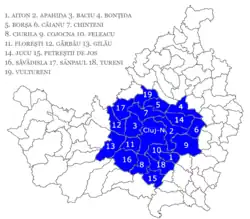
The Cluj metropolitan area is a metropolitan area in Cluj County, which includes Cluj-Napoca and 19 communes nearby: Aiton, Apahida, Baciu, Bonțida, Borșa, Căianu, Chinteni, Ciurila, Cojocna, Feleacu, Florești, Gilău, Gârbau, Jucu, Petreștii de Jos, Săvădisla, Sânpaul, Tureni, Vultureni.
Cluj Metropolitan Area | |
|---|---|
Metropolitan area | |
 | |
| Coordinates: 46°46′N 23°35′E | |
| Country | |
| County | Cluj County |
| Central Municipality | Cluj-Napoca |
| Other localities | Aiton, Apahida, Baciu, Bonțida, Borșa, Căianu, Chinteni, Ciurila, Cojocna, Feleacu, Florești, Gârbău, Gilău, Jucu, Săvădisla, Sânpaul, Tureni, Vultureni |
| Functional | 2008 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,603 km2 (619 sq mi) |
| Population (2021 census)[1] | |
| • Total | 425,130 |
| • Density | 266/km2 (690/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal Code | 40wxyz1 |
| Area code | +40 x642 |
| Website | http://www.adizmc.ro |
| 1w, x, y, and z are digits that indicate the street, part of the street, or even the building of the address 2x is a digit indicating the operator: 2 for the former national operator, Romtelecom, and 3 for the other ground telephone networks | |
The total area of the metropolitan area is 1,603 square kilometres (619 sq mi), which comprises 24% of the territory of Cluj County. According to the 2021 census, the population of the 20 administrative units totals 425,130 people, of whom 286,598 live in Cluj-Napoca.[1]
Population
| Population census | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | 2011 | 2021 |
| Pop. | 418,153 | 425,130 |
| ±% | — | +1.7% |
| Source: [1][2] | ||
According to the 2011 census, this is the population of each of the administrative units that comprise the Cluj Metropolitan Area:[3]
| Administrative unit | Inhabitants | Romanians | Hungarians | Roma |
| Cluj-Napoca | 324576 | 249002 | 49425 | 824 |
| Florești | 22813 | 17578 | 3258 | 730 |
| Apahida | 10685 | 9493 | 408 | 75 |
| Baciu | 10317 | 6580 | 3095 | 325 |
| Gilău | 8300 | 7141 | 706 | 109 |
| Bonțida | 4856 | 3613 | 765 | 297 |
| Săvădisla | 4392 | 1975 | 2264 | 60 |
| Jucu | 4270 | 3608 | 501 | 21 |
| Cojocna | 4194 | 2826 | 689 | 387 |
| Feleacu | 3923 | 2932 | 891 | 4 |
| Chinteni | 3065 | 2370 | 539 | 10 |
| Gârbău | 2440 | 1248 | 1075 | 49 |
| Sânpaul | 2382 | 1972 | 22 | 261 |
| Căianu | 2355 | 1431 | 852 | - |
| Tureni | 2278 | 1633 | 562 | 5 |
| Borșa | 1600 | 1431 | 107 | 18 |
| Ciurila | 1594 | 1500 | 18 | * |
| Vultureni | 1516 | 1273 | 165 | 36 |
| Petreștii de Jos | 1512 | 1446 | 3 | 4 |
| Aiton | 1085 | 918 | 118 | - |
| Total | 418153 | 319970 | 65463 | 3215 |
History
The Cluj Metropolitan Area was legally established in the fall of 2008 as an inter-community development association,[4] having as founders the municipality of Cluj-Napoca, the Cluj County Council and 17 communes in the vicinity of Cluj. In 2009, the commune of Sânpaul joined the metropolitan area, and in 2016, the commune of Săvădisla joined in.
Objectives
The objectives pursued by the Cluj Metropolitan Area Intercommunity Development Association are:[4]
- Enhancing knowledge-based economic competitiveness;
- The development and upgrading of transport infrastructure;
- To protect and improve the quality of the environment;
- Human resources development, employment growth and the fight against social exclusion;
- The development of the rural economy and the increase of productivity in the agricultural sector;
- Balanced participation to the socio-economic development process for all the administrative units of the Cluj Metropolitan Area.
Projects
The Cluj Metropolitan Area, as a leader or partner, has carried out or runs a number of projects with European Union funding or from EEA and Norwegian Grants. They include:
- “European Digital Citizens” (Eudigit)
- URBforDAN. Management and Use of Urban Foreres as Natural Heritage in Danube Cities
- The Lab Cluj. Metropolitan Laboratory for Social Innovation
- Pata 2. Replicable integrated interventions for inclusive housing and combating marginalisation in Cluj Metropolitan Area
- Cluj Future of Work, „Informal Work” Work Package[5]
References
- "Population at 2021 Census" (in Romanian). INSSE. 31 May 2023.
- "Population at 20 October 2011" (in Romanian). INSSE. 5 July 2013.
- "Recensământul Populației și Locuințelor, 2011. Rezultate definitive, Tabelul 10. Populația stabilă după limba maternă – județe, municipii, orașe, comune". Archived from the original on 2013-09-29. Retrieved 2020-05-19.
- "Despre noi". Zona Metropolitană Cluj. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "Participatory budgeting in the vulnerable community at Pata Rât". Urban Innovation Unit. Archived from the original on 2021-01-25. Retrieved 2020-05-21.