Chlorophacinone
Chlorophacinone is an anticoagulant used as a rodenticide.[1] It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002) and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
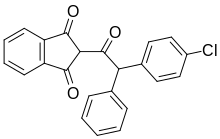
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[(4-Chlorophenyl)phenylacetyl]-1H-indene-1,3(2H)-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.020.912 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H15ClO3 | |
| Molar mass | 374.82 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
See also
References
- "Rodenticides: Topic Fact Sheet". National Pesticide Information Center.
- "40 C.F.R.: Appendix A to Part 355—The List of Extremely Hazardous Substances and Their Threshold Planning Quantities" (PDF) (July 1, 2008 ed.). Government Printing Office. Retrieved October 29, 2011.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.