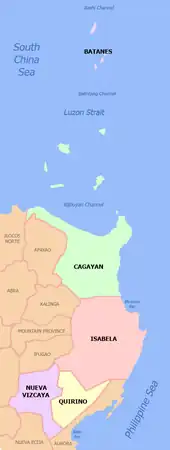
Cabarroguis
Cabarroguis, officially the Municipality of Cabarroguis (Ilocano: Ili ti Cabarroguis; Tagalog: Bayan ng Cabarroguis), is a 3rd class municipality and capital of the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,533 people.[4]
Cabarroguis | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Cabarroguis | |
 Cabarroguis Town Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
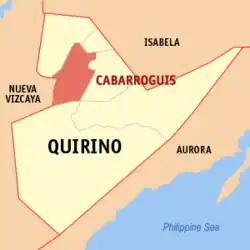 Map of Quirino with Cabarroguis highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap | |
.svg.png.webp) Cabarroguis Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 16°30′37″N 121°31′20″E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Cagayan Valley |
| Province | Quirino |
| District | Lone district |
| Founded | June 21, 1969 |
| Named for | Leon Cabarroguis |
| Barangays | 17 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Avelino N. Agustin, Jr. |
| • Vice Mayor | Francisco M. Dulnuan, Jr. |
| • Representative | Junie E. Cua |
| • Municipal Council | Members |
| • Electorate | 20,999 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 260.20 km2 (100.46 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 112 m (367 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 534 m (1,752 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 95 m (312 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[4] | |
| • Total | 33,533 |
| • Density | 130/km2 (330/sq mi) |
| • Households | 7,966 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 3rd municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 9.32 |
| • Revenue | ₱ 176 million (2020) |
| • Assets | ₱ 346.3 million (2020) |
| • Expenditure | ₱ 144.6 million (2020) |
| • Liabilities | ₱ 83.88 million (2020) |
| Service provider | |
| • Electricity | Quirino Electric Cooperative (QUIRELCO) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 3400 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)78 |
| Native languages | Ilocano Bugkalot Tagalog |
| Website | www |
History
Prior to the advent of settlement, Cabarroguis was a vast forested area and formed parts of the municipalities of Saguday, Diffun and Aglipay. It was originally occupied by the Aetas who were later displaced by the Ilongot tribe because the Aetas were known to be of nomadic character. Many years later, permanent settlements were made by different civilized ethnic groups like Ilocanos, Tagalog and others in search of good fortune in this virgin land. As the population and settlement increased, regular barrios were created. These were the barrios of Zamora, Banuar, Burgos, Del Pilar, Dibibi, Eden, Villamor and five more sitios of Villapeña, Villarose, Tucod, Calaocan and Dingasan at the municipality of Aglipay: barrios of San Marcos, Gundaway and portion of Mangandingay at the municipality of Diffun and the other part of Mangandingay at the municipality of Saguday. The above stated barrios of different municipalities became the territorial jurisdiction of Cabarroguis by virtue of Republic Act No. 5554 enacted by the Philippine Congress authored by then Senator Leonardo Perez on June 21, 1969. The newly created municipality of Cabarroguis was named in honor of the late Congressman of Nueva Vizcaya, Leon Cabarroguis.
Cabarroguis operated as a regular municipality after the 1971 local polls wherein Anastacio dela Pena become the first Local Chief Executive. Barangay Mangandingay also became the temporary seat of the municipal government, Years later, when Diomedes Dumayas was appointed as the town's executive, the seat of the Local Government officially transferred to Barangay Zamora where a 12 hectares lot was donated.
Cityhood
In the 19th Congress of the Philippines, house bills were filed by various representatives which seeks Cabarroguis including other capital towns of provinces with no current component cities, independent component cities or highly urbanized cities to automatically convert into cities.[6][7][8]
Geography
Cabarroguis is located in the northwestern part of the province of Quirino. It is bounded on the north, northwest and northeast by the municipalities of Diffun and Saguday respectively, on the east and southeast by the municipality of Aglipay, on the south by the municipalities of Maddela and Nagtipunan, and on the west by the province of Nueva Vizcaya. It is 380 kilometres (240 mi) from Manila.
The municipal area of Cabarroguis covers 26,902 hectares approximately. The area is further distributed into the seventeen (17) barangays comprising the municipality including barangay Didipio which remains to be in the municipality and the province of Nueva Vizcaya and Quirino.
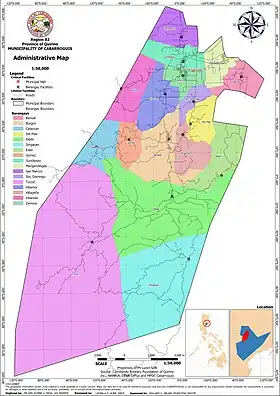
Barangays
Cabarroguis is politically subdivided into 17 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks and some have sitios.
| Barangay | Land Area (has.) |
|---|---|
| Urban: | |
| Gundaway | 629.6612 |
| Zamora | 427.1250 |
| Mangandingay | 500.7266 |
| San Marcos | 667.7311 |
| Sub-total: | 2,255.2439 |
| Rural: | |
| Villarose | 843.1654 |
| Banuar | 546.6502 |
| Villamor | 865.3353 |
| Del Pilar | 550.1530 |
| Villapeña | 642.1622 |
| Burgos | 1,288.4090 |
| Eden | 1,001.8760 |
| Gomez | 491.8008 |
| Dingasan | 3,108.0650 |
| Calaocan | 677.9979 |
| Dibibi | 3,491.2367 |
| Sto. Domingo | 299.6062 |
| Tucod (including Didipio) | 10,869.8230 |
| Sub-total: | 24,646.7561 |
| Total: | 26,902 |
Climate
| Climate data for Cabarroguis, Quirino | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 25 (77) |
26 (79) |
28 (82) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
27 (81) |
25 (77) |
29 (84) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 19 (66) |
20 (68) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 119 (4.7) |
83 (3.3) |
54 (2.1) |
37 (1.5) |
133 (5.2) |
132 (5.2) |
161 (6.3) |
163 (6.4) |
153 (6.0) |
142 (5.6) |
160 (6.3) |
224 (8.8) |
1,561 (61.4) |
| Average rainy days | 18.4 | 13.6 | 11.6 | 9.4 | 19.3 | 21.9 | 23.9 | 23.4 | 21.1 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 21.4 | 218.4 |
| Source: Meteoblue[9] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[10][11][12][13] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Initially, year 1970 recorded a population of 7,835 person followed by census year 1975 which registered a total population of 12,226 that manifested a growth rate of 9.29%. Another increase of population was observed during census year 1980 which recorded 17,450 displaying a growth rate of 2.2% and for census year 1995, it manifested a 22,812 person displaying a growth rate of 2.25%. Base year of 2000 recorded a total population of 25,832 which manifested a growth rate of 2.25%. As of census year 2007, the population increased to 28,024 which manifested a growth rate of 1.21%.
Economy
Income class
Cabarroguis is a third-Class municipality with an agricultural base economy where majority of the population derived their income from agricultural related industries and businesses. The municipality is 99% dependent on the Internal Revenue Allotment (IRA) now National Tax Allocation (NTA). For the year 2022, the Local Income is Four Million Five Hundred Ninety-One Three Hundred forty-seven and 92/100 (4,591,347.92) and the total external income is Two Hundred Ten Million Five Hundred Eighty-seven Fifty-three thousand (210,587,053.00)
Government
Local government
Cabarroguis, belonging to the lone congressional district of the province of Quirino, is governed by a mayor designated as its local chief executive and by a municipal council as its legislative body in accordance with the Local Government Code. The mayor, vice mayor, and the councilors are elected directly by the people through an election which is being held every three years.
Elected officials
| Position | Name |
|---|---|
| Congressman | Dakila Carlo E. Cua |
| Municipal Mayor | Avelino N. Agustin Jr. |
| Vice-Mayor | Francisco M. Dulnuan, Jr. |
| Councilors | Jann Graceal Bert N. Binlayan |
| Danuel S. Galgaleng | |
| Virgilio A. Lopez | |
| Marciano G. Immapa | |
| Tirso V. Abuan | |
| Zernan B. Cariño | |
| Florencio L. Valdez Jr. | |
| Leilani R. Vinluan | |
| David G. Bangsoyao | |
| Reynaldo S. Marzo | |
| Jannette R. Orpia | |
Education
The Schools Division of Quirino governs the town's public education system.[22] The division office is a field office of the DepEd in Cagayan Valley region.[23] The office governs the public and private elementary and public and private high schools throughout the municipality.
References
- Municipality of Cabarroguis | (DILG)
- "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- "Cabarroguis, Quirino".
- Census of Population (2020). "Region II (Cagayan Valley)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 15, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- Yap, Eric (June 30, 2022). "AN ACT AUTOMATICALLY CONVERTING THE CAPITAL TOWN OF PROVINCES WITH NO COMPONENT CITIES, INDEPENDENT COMPONENT CITIES OR HIGHLY URBANIZED CITIES WITHIN ITS TERRITORIAL JURISDICTION, INTO A COMPONENT CITY" (PDF). House of Representatives of the Philippines. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- Palma, Wilter (August 9, 2022). "AN ACT AUTOMATICALLY CONVERTING THE CAPITAL TOWN OF PROVINCES WITH NO COMPONENT CITIES, INDEPENDENT COMPONENT CITIES, OR HIGHLY URBANIZED CITIES WITHIN ITS TERRITORIAL JURISDICTION, INTO A COMPONENT CITY" (PDF). House of Representatives of the Philippines. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- Daza, Paul (August 11, 2022). "AN ACT CONVERING INTO COMPONENT CITIES THE CAPITAL TOWNS OF PROVINCES WITHOUT A CITY, AMENDING FOR THE PURPOSE SECTION 450 OF REPUBLIC ACT NO. 7610, AS AMENDED BY REPUBLIC ACT NO. 9009, OTHERWISE KNOWN AS THE LOCAL GOVERNMENT CODE OF 1991, AND FOR OTHER PURPOSES" (PDF). House of Representatives of the Philippines. Retrieved April 1, 2023.
- "Cabarroguis: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved July 4, 2021.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region II (Cagayan Valley)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region II (Cagayan Valley)" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region II (Cagayan Valley)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- "Province of Quirino". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
- "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. November 29, 2005.
- "2003 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. March 23, 2009.
- "City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates; 2006 and 2009" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. August 3, 2012.
- "2012 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. May 31, 2016.
- "Municipal and City Level Small Area Poverty Estimates; 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. July 10, 2019.
- "PSA Releases the 2018 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. December 15, 2021. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- "2019 National and Local Elections" (PDF). Commission on Elections. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 6, 2020. Retrieved March 10, 2022.
- "THE SCHOOLS DIVISION OF QUIRINO". deped quirino | SDO Quirino Website. Retrieved March 13, 2022.
- "DEPED REGIONAL OFFICE NO. 02". DepED RO2 | The official website of DepED Regional Office No. 02.