Butaclamol
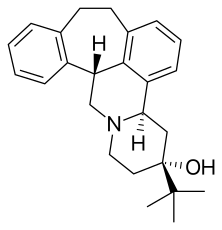
Butaclamol (AY-23,028) is a type of antipsychotic which was never marketed.[1] Sold as the hydrochloride salt for use in research, the compound acts as a dopamine receptor antagonist.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H31NO |
| Molar mass | 361.529 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Chemistry
pKa = 7.15 (uncorrected for ionic strength)[3]
References
- Buckingham J (1985). Dictionary of organic compounds - Google Books. ISBN 978-0-412-54090-5.
- Hall DA, Strange PG (June 1997). "Evidence that antipsychotic drugs are inverse agonists at D2 dopamine receptors". British Journal of Pharmacology. 121 (4): 731–6. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0701196. PMC 1564749. PMID 9208141.
- Chrzanowski FA, McGrogan BA, Maryanoff BE (March 1985). "The pKa of butaclamol and the mode of butaclamol binding to central dopamine receptors". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (3): 399–400. doi:10.1021/jm00381a022. PMID 2579238.
| σ1 |
|
|---|---|
| σ2 |
|
| Unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |
| Classes | |
|---|---|
| Antidepressants (Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)) |
|
| Antihistamines |
|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Anticonvulsants | |
| Anticholinergics | |
| Others |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.