Black-tailed trogon
The black-tailed trogon (Trogon melanurus) is a species of bird in the family Trogonidae, the quetzals and trogons. It is found Panama and northern South America.[2]
| Black-tailed trogon | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Trogoniformes |
| Family: | Trogonidae |
| Genus: | Trogon |
| Species: | T. melanurus |
| Binomial name | |
| Trogon melanurus Swainson, 1838 | |
 | |
Taxonomy and systematics
The black-tailed trogon has three subspecies according to the International Ornithological Committee (IOC): the nominate T. m. melanurus, T. m. macroura, and T. m. eumorphus. The Clements taxonomy adds a fourth subspecies, T. m. occidentalis. What is now the Ecuadorian trogon (T. mesurus) was until the early 2000s considered another subspecies. A subspecies of slaty-tailed trogon (T. massena australis) is sometimes treated as a subspecies of black-tailed trogon, and T. m. macroura has been suggested as a separate species.[2][3][4][5]
.jpg.webp)

Description
The black-tailed trogon is 28 to 30 cm (11 to 12 in) long and weighs 52 to 122 g (1.8 to 4.3 oz). The male of the nominate subspecies has a yellow bill and a blackish face and throat with an orange-red ring around the eye. The crown, nape, upperparts, and breast are green. A white band separates the breast from the red belly and vent. The upperside of the tail is deep blue and the underside is slaty gray. The folded wing has fine vermiculation that looks gray at a distance. The female's maxilla is slaty. She is gray where the male is green, and the gray of the breast extends further into the upper belly. Instead of the orange-red ring around the eye there are white arcs before and after it. The male T. m. macroura's wing has coarser vermiculation than the nominate and the upper tail is more turquoise. Its wings and tail are longer. The male T. m. eumorphus is similar to the nominate, but its wings are darker, the tail bluer, and the white breast band narrower. T. m. occidentalis is indistinguishable from eumorphus.[5]
Distribution and habitat
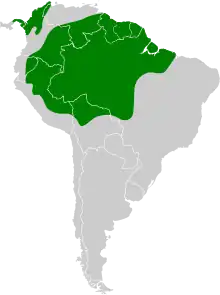
The range of T. m. macroura is separate from that of the other subspecies. It is found in Panama east of the Canal Zone through northern Colombia into extreme northwestern Venezuela. The nominate T. m. melanurus is found from eastern Colombia through southern Venezuela and the Guianas and south in northeastern Brazil as far as Maranhão state. T. m. eumorphus is found south of melanurus, from southern Colombia through eastern Ecuador and Peru into northern Bolivia and east into Amazonian Brazil. When treated separately, T. m. occidentalis is found in the São Paulo region of southeastern Brazil, but that area does not appear on the range maps of black-tailed trogon.[2][5][3][6]
The black-tailed trogon inhabits various landscapes in different parts of its large range. In Panama it occurs in the interior and edges of humid lowland and foothill forests, both primary and secondary. In Venezuela and French Guiana it inhabits rainforest. In Amazonia it is found in several forest types including transitional and swamp forest, gallery forest, and terra firme and várzea forests. In Colombia west of the Andes it ranges as high as 2,200 m (7,200 ft) but is mostly much lower; east of the Andes it reaches only 500 m (1,600 ft). In Venezuela north of the Orinoco River it is found only below 100 m (330 ft) but ranges up to 1,000 m (3,300 ft) south of the river.[5]
Behavior
Movement
The black-tailed trogon is resident throughout most of its range, but in Bolivia it is known to move seasonally between dry forest and lowland rainforest.[5]
Feeding
The black-tailed trogon's diet includes a wide variety of insects, and also fruits and occasionally small amphibians and reptiles. It sometimes joins mixed-species foraging flocks in the canopy but also forages lower down.[5]
Breeding
The black-tailed trogon's breeding season varies widely across its large range, from March in Panama to September and October in Peru. It nests in cavities in arboreal termitaria and possibly in decayed trees, though the latter is not well documented. The clutch size is two or three eggs.[5]
Vocalization
The black-tailed trogon's song is "'kwo-kwo-kwo...' in [a] series of up to 46 notes". It also gives "a bubbly purring trill".[5]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the black-tailed trogon as being of Least Concern. It has a very large range, and though its population has not been quantified it is believed to be stable.[1] It is generally common throughout its range.[5]
References
- BirdLife International (2016). "Black-tailed Trogon Trogon melanurus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
- Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (July 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.2)". Retrieved July 14, 2021.
- Clements, J. F., T. S. Schulenberg, M. J. Iliff, S. M. Billerman, T. A. Fredericks, J. A. Gerbracht, D. Lepage, B. L. Sullivan, and C. L. Wood. 2021. The eBird/Clements checklist of Birds of the World: v2021. Downloaded from https://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/ Retrieved August 25, 2021
- Remsen, J. V., Jr., J. I. Areta, E. Bonaccorso, S. Claramunt, A. Jaramillo, D. F. Lane, J. F. Pacheco, M. B. Robbins, F. G. Stiles, and K. J. Zimmer. Version 24 August 2021. A classification of the bird species of South America. American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm retrieved August 24, 2021
- Collar, N. and G. M. Kirwan (2020). Black-tailed Trogon (Trogon melanurus), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (J. del Hoyo, A. Elliott, J. Sargatal, D. A. Christie, and E. de Juana, Editors). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.blttro1.01 retrieved October 26, 2021
- "Species Map: Black-tailed Trogon". Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved October 26, 2021.
