Battle of Dry Wood Creek
The Battle of Dry Wood Creek, also known as the Battle of the Mules, was fought on September 2, 1861, in Vernon County, Missouri, during the American Civil War. After his victory at the Battle of Wilson's Creek on August 10, Sterling Price and the Missouri State Guard moved further north into Missouri. A force of Union troops under James H. Lane moved from Fort Scott, Kansas to attempt an interception of Price's army, and set an ambush along Dry Wood Creek. Price's Missouri State Guard troops outnumbered Lane's Kansas troops, and after a two hour skirmish forced Lane to retreat to Fort Scott. In their retreat, Lane's troops abandoned their supplies and mules to the Missourians. Price followed up his victory by continuing his northward march, culminating in another victory at the siege of Lexington, September 13 to 20, before returning south shortly afterwards.
| Battle of Dry Wood Creek | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War | |||||||
 Battle of Dry Wood Creek (Missouri) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Units involved | |||||||
| Missouri State Guard | Lane's Kansas Brigade | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 6,000 or 10,000 | 600 or 1,200 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
25 total * 2 killed * 23 wounded |
11 total * 5 killed * 6 wounded | ||||||
Background
After the outbreak of the American Civil War in April 1861, Missouri was considered to be a border state, as slavery was legal within the state, but it did not vote to secede. Governor of Missouri Claiborne F. Jackson supported the Confederate States of America, and began to use militia to support the Confederate cause in Missouri by marching towards the arsenal in St. Louis. Brigadier General Nathaniel Lyon, commander of the Union forces in St. Louis, acted quickly and forced Jackson's militia to surrender in the Camp Jackson affair. After the debacle at Camp Jackson, Jackson formed a new organization named the Missouri State Guard and appointed Sterling Price to command it. Lyon moved to confront Price's new force, defeating it at the Battle of Boonville. Price and the Missouri State Guard retreated to the vicinity of Springfield in southwestern Missouri, where it was joined by a Confederate States Army force commanded by Brigadier General Benjamin McCulloch. On August 10, Lyon decided to attack the combined forces of Price and McCulloch while they were encamped along Wilsons Creek, despite being outnumbered by the Confederates and Missourians by a factor of over two-to-one. In the ensuing Battle of Wilson's Creek, the Union forces were defeated and Lyon was killed.[1]
After Wilson's Creek, the Union army retreated to Rolla, Missouri. McCulloch and his forces withdrew to Arkansas, and Price's Missouri State Guard occupied Springfield.[2] John C. Fremont arrived to take control of Union forces in the state, and James H. Lane took command of several Kansas regiments stationed at Fort Scott. Meanwhile, Price began to advance north with a force estimated to number at either 6,000[3] or 10,000 men.[4] In response to Price's incursion, Fremont declared Missouri to be subject to martial law.[5]
Battle
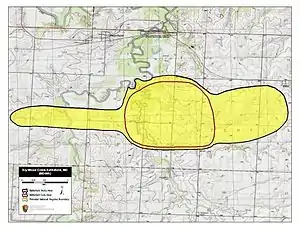
Lane sent his forces, estimated to number either 600[3] or 1,200 men, out to intercept Price's army, and set an ambush along Dry Wood Creek in Vernon County, Missouri on September 2.[6] The area around Dry Wood Creek was wooded, giving Lane the element of surprise. The leading portions of the Missouri State Guard fell into Lane's trap. Price then brought up more troops, and the Missourians' numerical advantage was a deciding factor in the engagement. Lane's skirmishers were driven back from an advanced position, and the main Union force used the covers of the woods to hold off Price for about two hours. However, Price's men eventually overwhelmed the Kansans, and Lane's troops retreated to Fort Scott. During the retreat, Lane's men abandoned their supplies and mules to the Missouri State Guard. Price stated that an important factor in the victory was the fighting experience the Missouri State Guard had gained at Wilson's Creek.[7] The capture of the mules led the battle to be sometimes known as the "Battle of the Mules".[3] The victory at Dry Wood Creek had allowed Price to be able to continue his northward expedition.[8] and his army then headed to Johnson County, Missouri.[9]
In a report filed after the battle, Lane stated that his forces lost five men killed and six wounded.[10] In his post-action report, Price estimated his loss to be two men killed and twenty-three wounded, although he noted that most of the wounds were not serious.[11]
Aftermath and legacy
After reaching Johnson County, Price continued to Lexington, Missouri, where a Union garrison was defending the town. Price's men surrounded the garrison, initiating the siege of Lexington. The Missouri State Guard subdued the Union garrison, at one point using hemp bales as cover while attacking uphill. After forcing the Union garrison to surrender, the Missouri State Guard remained in the Lexington area for two weeks before Price ordered the unit to return south.[12]
Today, the site of the battle is commemorated with a series of markers near Deerfield, Missouri. A museum in nearby Nevada, Missouri provides coverage of both the Battle of Dry Wood Creek and the American Civil War in Missouri as a whole.[13]
Notes
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 19–23.
- Monaghan 1984, p. 182.
- "Dry Wood Creek (Big Dry Wood Creek, Battle of the Mules)". ehistory.osu. Ohio State University. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- Monaghan 1984, p. 184.
- Monaghan 1984, pp. 182–185.
- Gerteis 2012, p. 99.
- Gerteis 2012, pp. 99–100.
- Castel 1993, p. 50.
- Gerteis 2012, p. 100.
- Lane, James H. "Action at Dry Wood Creek". ehistory.osu.edu. Ohio State University. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- "The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies: Series 1, Volume 53". babel.hathitrust.org. United States War Department. pp. 435–436. Retrieved 16 March 2020.
- Monaghan 1984, pp. 185–194.
- Weeks 2009, p. 42.
References
- Castel, Albert (1993). General Sterling Price and the Civil War in the West. Baton Rouge, Louisiana: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 0-8071-1854-0.
- Gerteis, Louis S. (2012). The Civil War in Missouri. Columbia, Missouri: University of Missouri Press. ISBN 978-0-8262-1972-5.
- Kennedy, Frances H., ed. (1998). The Civil War Battlefield Guide (2nd ed.). Boston & New York: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-74012-5.
- Monaghan, Jay (1984). Civil War on the Western Border, 1854–1865. Lincoln, Nebraska: University of Nebraska Press. ISBN 978-0-8032-8126-4.
- Weeks, Michael (2009). The Complete Civil War Road Trip Guide. Woodstock, Vermont: The Countryman Press. ISBN 978-0-88150-860-4.