Arago (Martian crater)
Arago is an impact crater in the Arabia quadrangle on Mars at 10.22 N and 29.93° E. It is 152 km (94 mi) in diameter and is in the northernmost part of Terra Sabaea. Its name was approved in 1973 and refers to the French astronomer François Arago.[1]
 Viking Orbiter 1 image | |
| Planet | Mars |
|---|---|
| Region | Arabia quadrangle |
| Coordinates | 10.22°N 29.93°E |
| Quadrangle | Arabia |
| Diameter | 152 km (94 mi) |
| Eponym | François Arago |
Arago is highly eroded and subdued and is thus ancient. Arago is believed to have once held a giant lake that drained into the 4,500 km-long (2,800 mi) Naktong-Scamander-Mamers lake-chain system.[2] Naktong Vallis is to the south of Arago and Scamander Vallis is to the north. Water flowed from the south to the north and pooled in Arago and also in the larger Tikhonravov crater to the northeast of Arago.
Henry crater is to the west of Arago, and Barth is to the southwest.
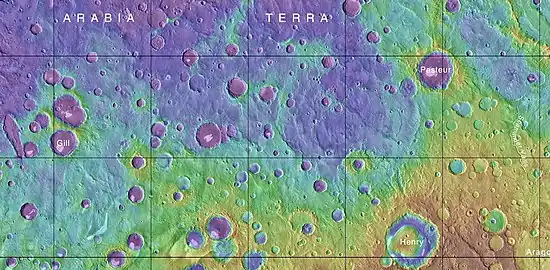
MOLA map, showing Arago crater and other nearby craters. Colors indicate elevations, Arago is mapped on the lower right end.
Map of Arabia quadrangle with major craters. Arago is between Henry and Tikhonravev but the name is not shown
References
- "Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature | Arago". US Geological Survey. International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 20 August 2017.
- Fassett, C. and J. Head III. 2008. "Valley network-fed, open-basin lakes on Mars: Distribution and implications for Noachian surface and subsurface hydrology". Icarus: 198. 39-56.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.