AIR synthetase (FGAM cyclase)
Phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine cyclo-ligase (AIR synthetase) is the fifth enzyme (EC 6.3.3.1) in the de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides. It catalyzes the reaction to form 5-aminoimidazole ribotide (AIR) from formylglycinamidine-ribonucleotide FGAM. This reaction closes the ring and produces a 5-membered imidazole ring of the purine nucleus (AIR):
| Phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine cyclo-ligase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 6.3.3.1 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9023-53-4 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
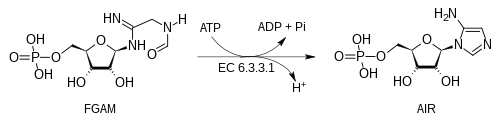
AIR synthetase catalyzes the transfer of the oxygen of the formyl group to phosphate. It is a sequential mechanism in which ATP binds first to the enzyme and ADP is released last. This enzyme hydrolyzes ATP to activate the oxygen of the amide in order to carry out a nucleophilic attack by nitrogen. In humans and many other animals, this enzyme is contained within the trifunctional purine biosynthetic protein adenosine-3 polypeptide.
Nomenclature
The systematic name of this enzyme class is 2-(formamido)-N1-(5-phosphoribosyl)acetamidine cyclo-ligase (ADP-forming). Other names in common use include:
- AIR synthetase,
- 5'-aminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase,
- 2-(formamido)-1-N-(5-phosphoribosyl)acetamidine cyclo-ligase (ADP-forming),
- phosphoribosylaminoimidazole synthetase, and
- phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine cyclo-ligase.
Purine Synthesis
Purines are one of the two types of nitrogenous heterocyclic bases, which are one of the three components of the nucleotides that make up nucleic acids. Synthesis can be de novo or salvage — AIR synthetase is a component of the de novo pathway. The first committed step of the de novo pathway begins with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) and the end product is inosine monophosphate (IMP). IMP is eventually converted to either AMP or GMP purines. The purine ring structure is composed by the attachment of 1 or 2 atoms at a time to the ribose sugar. The de novo pathway tends to be conserved across most organisms.
Cowpea AIR synthetase
AIR synthetase is found in both mitochondria and plastids; the mitochondrial form has 5 more amino acids than the plastid form.[1] The enzyme is encoded by a single gene in cowpeas despite the fact that it exists in different forms in plastids and mitochondria. This suggests that the different versions may be derived from a single transcript. One study proposes that there is tight transcriptional control of pur5, the gene encoding AIR synthetase.[2]
References
- Goggin DE, Lipscombe R, Fedorova E, Millar AH, Mann A, Atkins CA, Smith PM (March 2003). "Dual Intracellular Localization and Targeting of Aminoimidazole Ribonucleotide Synthetase in Cowpea". Plant Physiol. 131 (3): 1033–41. doi:10.1104/pp.102.015081. PMC 166869. PMID 12644656.
- Smith PM, Mann AJ, Goggin DE, Atkins CA (April 1998). "AIR synthetase in cowpea nodules: a single gene product targeted to two organelles?". Plant Mol. Biol. 36 (6): 811–20. doi:10.1023/A:1005969830314. PMID 9520274.
Further reading
- Levenberg B, Buchanan JM (1957). "Biosynthesis of the purines. XII. Structure, enzymatic synthesis, and metabolism of 5-amino-imidazole ribotide". J. Biol. Chem. 224 (2): 1005–18. PMID 13405929.
- Levenberg B, Buchanan JM (1957). "Biosynthesis of the purines. XIII. Structure, enzymatic synthesis, and metabolism of (alpha-N-formyl)-glycinamidine ribotide". J. Biol. Chem. 224 (2): 1019–27. PMID 13405930.
- Li C, Kappock TJ, Stubbe J, Weaver TM, Ealick SE (1999). "X-ray crystal structure of aminoimidazole ribonucleotide synthetase (PurM), from the Escherichia coli purine biosynthetic pathway at 2.5 A resolution". Structure. 7 (9): 1155–66. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(99)80182-8. PMID 10508786.
External links
- AIR+synthetase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)