5-MeO-NMT
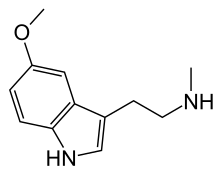
5-MeO-NMT (5-methoxy-N-methyltryptamine) is an organic chemical compound, being the 5-methoxy analog of N-methyltryptamine (NMT). It was first isolated from Phalaris arundinacea (reed canary grass).[1] It has also been synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and reported in his book TiHKAL.[2] Like other members of the N-methyltryptamine family of compounds, 5-MeO-NMT is believed to produce few or no psychedelic effects, although very little data exists about its pharmacological properties or toxicity.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(5-Methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-N-methylethan-1-amine | |
| Other names
5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H16N2O | |
| Molar mass | 204.273 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Legal Status
In the U.S. this substance is a schedule 1 isomer of Bufotenin.
References
- Wilkinson, S. (1958). "428. 5-Methoxy-N-methyltryptamine: a new indole alkaloid from Phalaris arundinacea L.". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2079. doi:10.1039/jr9580002079.
- 5-MeO-NMT Entry in TIHKAL
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.