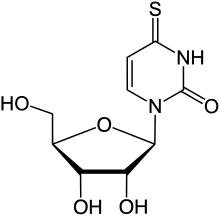
4-Thiouridine
4-Thiouridine is an atypical nucleotide formed with the 4-thiouracil base found in transfer RNA (tRNA).[1] Its biosynthesis has been determined.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-4-sulfanylidene-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.034.291 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Thiouridine |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H12N2O5S | |
| Molar mass | 260.26 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Alberts, Bruce (18 November 2014). Molecular biology of the cell (Sixth ed.). New York, NY. p. 337. ISBN 978-0-8153-4432-2. OCLC 887605755.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - Park, Chung-Min; Weerasinghe, Laksiri; Day, Jacob J.; Fukuto, Jon M.; Xian, Ming (2015). "Persulfides: Current knowledge and challenges in chemistry and chemical biology". Molecular BioSystems. 11 (7): 1775–1785. doi:10.1039/c5mb00216h. PMC 4470748. PMID 25969163.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.