4-Thiouracil
4-Thiouracil is a heterocyclic organic compound having a pyrimidine skeleton. It is a derivative of the nucleobase uracil with a sulfur instead of oxygen in position 4. It is found naturally in the 4-thiouridine nucleotide.
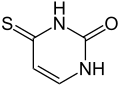 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-Sulfanylidene-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.155.914 |
| MeSH | Thiouracil |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4N2OS | |
| Molar mass | 128.15 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 295 °C (563 °F; 568 K) (decomp.)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 | |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Sigma-Aldrich Co., 4-Thiouracil. Retrieved on 19 March 2019.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.