X
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 9 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time.
This article has been viewed 26,598 times.
Learn more...
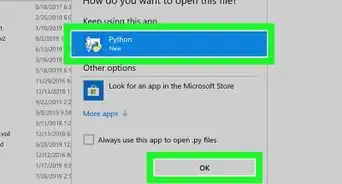
Python is a high-level programming language. The language utilizes a straightforward syntax which can make it easy for new users to get started.
Steps
Part 1
Part 1 of 4:
Installing Dependencies
-
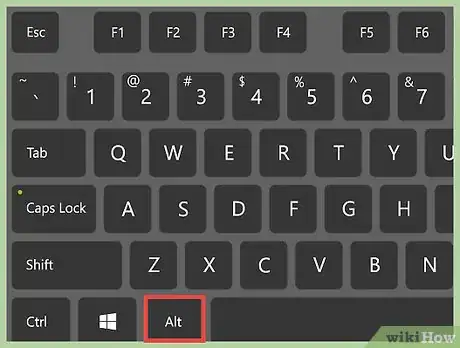
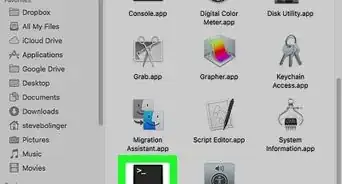
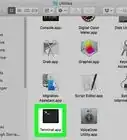
1Open the Terminal. On Linux, you can press the Alt button to open a search bar. Type "terminal" and click on Terminal.
-
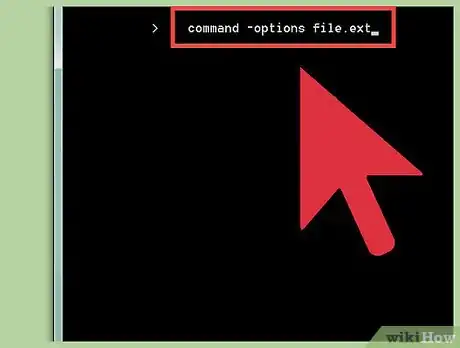
2Know the commands. Terminal commands are shown in this document as:
command -options filename.ext-
sudo apt-get install build-essential
- The "sudo" command gives permission to the terminal to modify your computer. This is necessary to install any program. You will be required to enter your password.
- The "apt-get install" command tells the computer to install the package "build-essential" which is required to install Python.
sudo apt-get install libreadline-gplv2-dev libncursesw5-dev libssl-dev libsqlite3-dev tk-dev libgdbm-dev libc6-dev libbz2-dev
- These are programs that Python uses to run correctly. They are also known as “dependencies”.
Advertisement
Part 2
Part 2 of 4:
Downloading and Installing Python
-
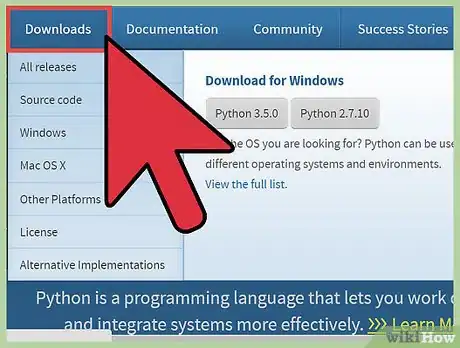
1Download the latest version of Python from the Internet. Use the following command:
cd ~/Downloads/- The "cd" command changes to the correct working directory so the computer can find and put programs in the right place.
wget http://python.org/ftp/python/2.7.5/Python-2.7.5.tgz
-
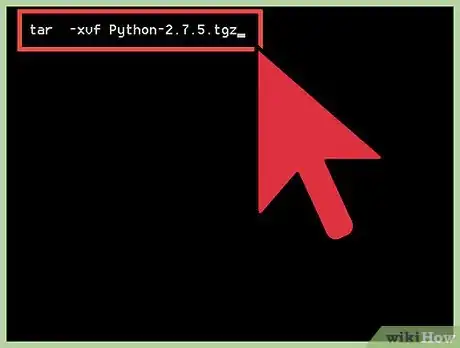
2Decompress the Python file using the following command:
tar -xvf Python-2.7.5.tgz
cd Python-2.7.5- Once again, we need to change the working directory. This time, we change to the newly created Python directory.
-
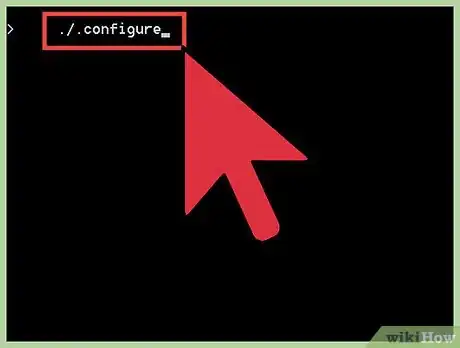
3Use the ./configure command checks your computer to ensure you have all the necessary components to install Python. It will alert you of any critical errors.
./configure
-
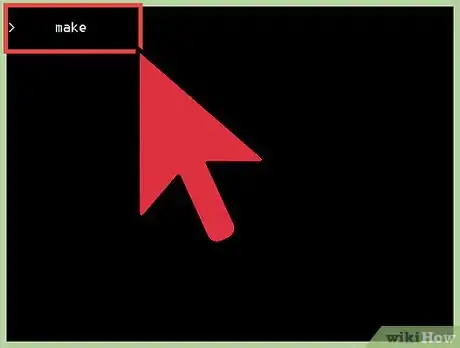
4Use the make command. It compiles the source code and creates the executables.
make
-
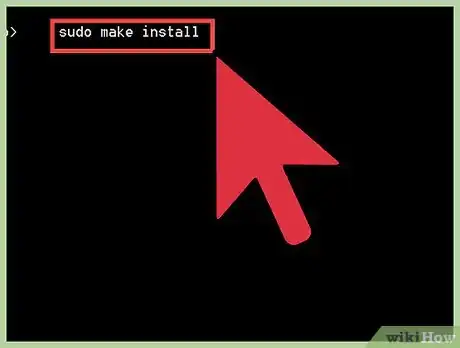
5Move the applications and libraries. With the following command, all of the applications and libraries associated with Python are moved into the correct places on your computer.
sudo make install
Advertisement
Part 3
Part 3 of 4:
Writing the Script
-
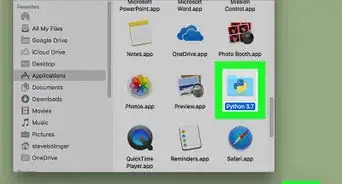
1Open a text editor.
- Any text editor that can save files with a ".py" extension will do. Ubuntu 12.04 or greater is packaged with the Gedit editor.
-
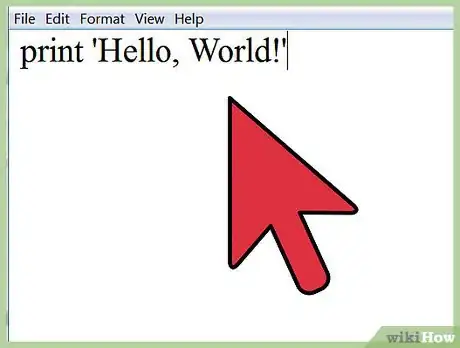
2Type
print 'Hello, World!'
- In Python, whatever is enclosed in quotes after the word print will be printed out to the screen.
-
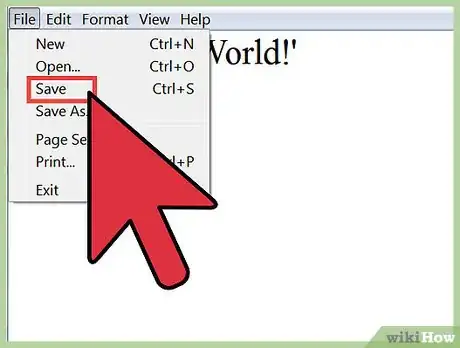
3Save the file as "hello_world.py.
- Be careful that the file is not saved as "hello_world.py.txt".
Advertisement
Part 4
Part 4 of 4:
Running the Script =
-
1Open the Terminal again.
-
2Navigate to the directory where "hello_world.py" is located.
- Remember to use the "cd" command to change directories.
- If you need a list of all subdirectories at your current location, use the "ls" command. "ls" stands for "list subdirectories".
-
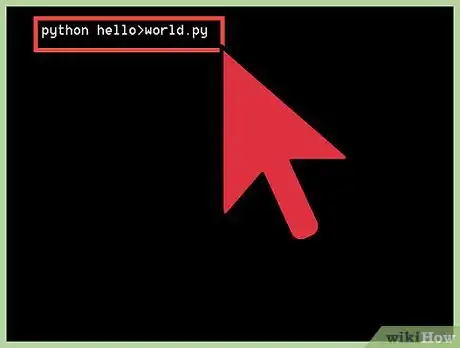
3Run the script:
python hello_world.py
Advertisement
Community Q&A
-
QuestionHow can I learn how to use Python as an absolute beginner?
 Simeon WatsonCommunity AnswerUse internet guides or books to teach yourself. This will follow a regular path from newbie to experienced. Usually the path is: print() variables input numbers lists strings. And more.
Simeon WatsonCommunity AnswerUse internet guides or books to teach yourself. This will follow a regular path from newbie to experienced. Usually the path is: print() variables input numbers lists strings. And more. -
QuestionI am not familiar with lists and tuples. How do i go about it?
 Simeon WatsonCommunity AnswerStart with an online tutorial. If you don't have time for that: here is an explanation: Lists are created this way: listname = []. That creates an empty list. If you want a list containing 1, 8, "hi" and 3.14, you write: listname = [1, 8, "hi", 3.14]. The contents of a list can be canged by the following commands: listname.append(whatever_to_add_to_the_end_of_the_list) listname.remove(watever_to_remove_the_first_occurence_of). Tuples are created this way: tuplename = (). That creates an empty tuple. If you want a tuple containing 1, 8, "hi" and 3.14 you write tuplename = (1, 8, "hi", 3.14). A tuple can not be changed after creation.
Simeon WatsonCommunity AnswerStart with an online tutorial. If you don't have time for that: here is an explanation: Lists are created this way: listname = []. That creates an empty list. If you want a list containing 1, 8, "hi" and 3.14, you write: listname = [1, 8, "hi", 3.14]. The contents of a list can be canged by the following commands: listname.append(whatever_to_add_to_the_end_of_the_list) listname.remove(watever_to_remove_the_first_occurence_of). Tuples are created this way: tuplename = (). That creates an empty tuple. If you want a tuple containing 1, 8, "hi" and 3.14 you write tuplename = (1, 8, "hi", 3.14). A tuple can not be changed after creation.
Advertisement
Things You'll Need
- Ubuntu 12.04 or greater
- Your account password
About This Article
Advertisement