< Messier Index
| Messier 100 | |
|---|---|
 Credit: w:ESO w:VLT view revealing complex spiral arm structure | |
| Observation data (w:J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | w:Coma Berenices[1] |
| Right ascension | 12h 22m 54.9s[2] |
| Declination | +15° 49′ 21″[2] |
| Redshift | 1571 ± 1 km/s[2] |
| Distance | 52.5 Mly[3] |
| Type | SAB(s)bc[2] |
| Apparent dimensions (V) | 7′.4 × 6′.3[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 10.1[2] |
| Other designations | |
| NGC 4321 | |
Messier 100 (also known as NGC 4321) is a w:spiral galaxy about 52.5 million w:light-years away in the w:constellation w:Coma Berenices. It was discovered by w:Pierre Méchain in w:1781. It is one of the brightest galaxies in the w:Virgo cluster. Five w:supernovae have been identified in M100: w:SN 1901B, w:SN 1914A, w:SN 1959E, w:SN 1979C and w:SN 2006X. M100 also has a w:satellite galaxy named w:NGC 4323.
Other images

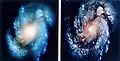 Before and after HST repair mission. Credit: NASA
Before and after HST repair mission. Credit: NASA SN 2006X in Messier 100. Credit: w:ESO
SN 2006X in Messier 100. Credit: w:ESO
External links
References
- ↑ R. W. Sinnott, editor (1988). The Complete New General Catalogue and Index Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters by J. L. E. Dreyer. Sky Publishing Corporation and Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-933-34651-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 4321. http://nedwww.ipac.caltech.edu/. Retrieved 2006-08-31.
- ↑ "Pattern Speeds BIMA-SONG Galaxies with Molecule-Dominated ISMs Using the Tremaine-Weinberg Method". (Ferrarese et al. 1996). http://arxiv.org/abs/astro-ph/0406426. Retrieved 2006-08-31.
| |||||
This article is issued from Wikibooks. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.