Introduction — Issues in Providing Care — Primary Assessment & Basic Life Support — Secondary Assessment — Circulatory Emergencies
Respiratory Emergencies — Soft Tissue Injuries — Bone & Joint Injuries — Environmental Illness & Injury
Medical Conditions & Poisoning — Advanced Topics — Appendices — Meta content
Introduction
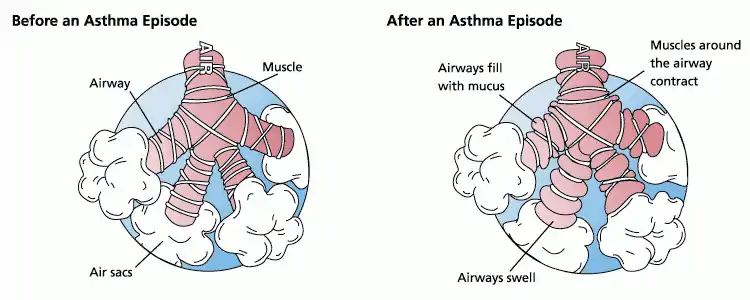
Asthma is a medical condition which causes swelling of the airway, constricting airflow.
Hyperventilation is simply breathing at an inappropriately high rate.
Recognition
Asthma is characterized by difficulty breathing, wheezing, increased secretions in the airway, and a history of asthma. Hyperventilation can be recognized by fast breathing which is inappropriate for the circumstances, a feeling of not being able to catch one's breath, and lightheadedness.
Treatment
For Asthma

- If the victim has a fast-acting inhaler for asthma attacks, encourage them to use it. You may assist with finding the inhaler.
- Have the victim match your breathing patterns - calm the victim while slowing their breathing rate
- Assist the casualty to sit in a position which relieves pressure on the chest. The tripod position is ideal - sitting up, leaning slightly forward, supporting their weight with their arms either on their knees or on a table or the like in front of them.
- Call EMS if the victim's condition does not improve or if the victim's level of consciousness is lowered
For Hyperventilation The aim is to calm the casualty down, to reduce their rate of breathing, and if possible to increase the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air they breathe, perhaps by getting them to breathe into a paper bag.