This wikibook aims to be a high quality calculus textbook through which users can master the discipline. Standard topics such as limits, differentiation and integration are covered, as well as several others. Please contribute wherever you feel the need. You can simply help by rating individual sections of the book that you feel were inappropriately rated!
Precalculus
Limits
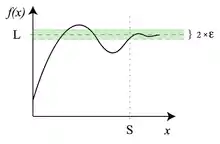
2.5 Formal Definition of the Limit
2.6 Proofs of Some Basic Limit Rules
Differentiation
Basics of Differentiation
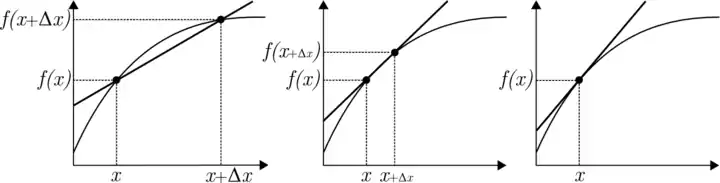
3.2 Product and Quotient Rules
3.3 Derivatives of Trigonometric Functions
3.5 Higher Order Derivatives: an introduction to second order derivatives
3.7 Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithm Functions
Applications of Derivatives
3.11 Extrema and Points of Inflection
Integration

Basics of Integration
4.2 Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
Integration Techniques
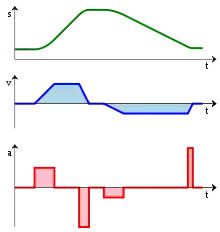
- an acceleration function a(t);
- the integral of the acceleration is the velocity function v(t);
- and the integral of the velocity is the distance function s(t).
4.6 Derivative Rules and the Substitution Rule
4.8 Trigonometric Substitutions
4.10 Rational Functions by Partial Fraction Decomposition
4.11 Tangent Half Angle Substitution
Applications of Integration
4.18 Volume of Solids of Revolution
Parametric and Polar Equations
Parametric Equations
5.1 Introduction to Parametric Equations
5.2 Differentiation and Parametric Equations
5.3 Integration and Parametric Equations
Polar Equations
5.5 Introduction to Polar Equations
5.6 Differentiation and Polar Equations
Sequences and Series
Sequences
Series
6.5 Limit Test for Convergence
6.6 Comparison Test for Convergence
6.7 Integral Test for Convergence
Series and calculus
Exercises
Multivariable and Differential Calculus
Introduction to Multivariable Calculus
7.2 Curves and Surfaces in Space
7.4 Introduction to Multivariable Calculus
Differentiation
7.8 Directional Derivatives and the Gradient Vector
Integration
7.9 Riemann Sums and Iterated Integrals
7.12 Derivatives of Multivariate Functions
7.13 The Chain Rule and Clairaut's Theorem
7.14 Inverse Function Theorem, Implicit Function Theorem
7.16 Vector Calculus Identities
7.17 Inverting Vector Calculus Operators
7.18 Points, Paths, Surfaces, and Volumes
7.19 Helmholtz Decomposition Theorem
7.20 Discrete Analog to Vector Calculus
Differential Equations
8.1 Ordinary Differential Equations
Extensions
Advanced Integration Techniques
Further Analysis
9.2 Systems of Ordinary Differential Equations
Formal Theory of Calculus
References
- Lester R. Ford, Sr. & Jr. (1963) Calculus, McGraw-Hill via HathiTrust
- w:Mellen W. Haskell (1895) On the introduction of the notion of hyperbolic functions Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 1(6):155–9.