Vietnamese (Tiếng Việt) is one of the most spoken languages in the world, with around 90 million native speakers. It is the official language in Vietnam and also widely spoken in places where the Vietnamese have immigrated such as the United States, France, Australia and Canada. It is also the native language of the Gin or Jing ethnic group from some islands off the coast of Guangxi province in southern China, who are ethnically and culturally Vietnamese but citizens of China.
Vietnamese is part of the Mon-Khmer language family, which includes the Khmer language spoken in neighbouring Cambodia, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible.
Vietnamese grammar is very simple: nouns and adjectives don't have genders, and verbs aren't conjugated. Vietnamese is a tonal language; the meaning of a word depends on how high or low your voice is. Vietnamese is not related to Chinese, though it contains many loan words from Chinese due to centuries of Chinese rule in Vietnam, and even used Chinese-based characters as its writing system, called "chữ Nôm", until Vietnam was colonised by the French. As a result of the French colonisation, modern Vietnamese also contains numerous loan words from French.
In modern times, Vietnamese is generally written in the Latin alphabet, with chữ Nôm mostly having fallen out of use, except for certain ceremonial and religious purposes, and among the small ethnic Vietnamese community of China.
Vietnamese is traditionally divided into three different regional dialect groups: North, Central and South. The Northern dialect, as spoken in Hanoi, is the prestige dialect that is used in news broadcasts, and all Vietnamese pop singers are expected to sing in the Northern dialect regardless of what dialect they speak. That said, if you are based in Vietnam's main economic centre in the South (around Ho Chi Minh City), the Southern dialect is what you will hear in everyday life. The Southern dialect also tends to be more prevalent in overseas Vietnamese communities, due to the Southern origin of most of the refugees who fled in the aftermath of the Vietnam War.
Pronunciation guide
Vietnamese spelling is more or less phonetic, and generally similar to Portuguese (which it is based on). Once you figure out how to pronounce each letter and tone, you have a pretty good idea of how to pronounce Vietnamese, which has very few exceptions compared to English.
Unless otherwise indicated, pronunciation throughout this phrasebook is for Southern (Saigon) Vietnamese, which is quite different from Northern (Hanoi), North Central (Vinh) or Central (Hue) Vietnamese.
Vowels
Vowels in the middle of triphthongs are often silent in the South, but pronounced in the North.
- a
- like 'a' in "laugh": ba (means "three"); in the South may be pronounced like 'a' in "apple" in some words.
- ă
- like 'a' in "basket": chăn (means "blanket").
- â
- like 'o' in "person": sân (means "yard" in front of back of a house).
- e
- like 'e' in "wed": tre (means "bamboo").
- ê
- like 'ay' in "say": cà phê (means "coffee").
- i
- like 'ee' in "see" or "deed": thi (means "test/exam"), same pronunciation as "y". In the South like 'u' in "hurl" when followed by 'nh'.
- o
- like 'o' in "dog": lý do (means "reason").
- ô
- like the first component of the diphthong 'ow' in "low" or 'o' in "go": á-lô ("Hello" on the phone).
- ơ
- like â, except longer, or 'ir' in "bird": bơ (means "avocado" or "butter").
- u
- like 'oo' in "hoop": thu (means "autumn/fall").
- ư
- like 'oo' in "book", with a hint of the 'i' in "lick", or like saying "you" without moving your lips, keeping your mouth wide open, like 'i' in "Halifax": thư (means "mail" or "letter").
- y
- like 'ee' in "see". Same pronunciation as "i".
Consonants
- b
- like 'b' in "bed". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- c
- like 'c' in "scale" (unaspirated), same pronunciation as "k".
- d
- in the South (Ho Chi Minh City), like 'y' in "yes"; in the North (Hanoi), like 'z' in "zip". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- đ
- like 'd' in "dog". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- g
- before "i", "e" or "ê", like 'z' in "zip" in the North, or like 'y' in "yes" in the South. Like 'g' in "go" otherwise.
- h
- like 'h' in "help", silent in the South if before a 'u'.
- k
- like 'k' in "ski" (unaspirated), same pronunciation as "c" Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- l
- like 'l' in "love". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- m
- like 'm' in "mother".
- n
- like 'n' in "nice", in the South like 'ng' in "sing when at the end of a syllable.
- p
- like 'p' in "pig". Used mostly at the end of a syllable.
- r
- in the South (Ho Chi Minh City), like 'r' in "red" or 's' in "pleasure"; in the North (Hanoi), like 'z' in "zip". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- s
- in the South like 'sh' in "shoot" but softer, in the North like 's' in "see". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- t
- like 't' in stop (unaspirated), in the South like 'c' in "scale" when at the end of a syllable.
- v
- in the North, like 'v' in "victory"; in the South, like 'y' in "yes". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- x
- like 's' in "see". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- y
- like 'y' in "yes".
- ch
- at the beginning of a syllable, similar to 'ch' in "touch", aspirated in the North but unaspirated in the South; at the end, like 'ck' in "sick" (but it is never enunciated).
- gh
- like 'g' in "go". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- kh
- like 'ch' in Scottish "loch", identical to the "ach-Laut" sound in German. Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- ng, ngh
- like 'ng' in "sing-along": Nga.
- nh
- similar to 'ny' in canyon, basically the same as Portuguese nh, Spanish ñ or French/Italian gn.
- ph
- like 'ph' in "phone".
- th
- like 't' in "time" (aspirated). Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- tr
- similar to 'ch' in "touch". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
Other combinations
- gi
- in the North, like 'z' in "zip"; in the South, like 'y' in "yes". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- qu
- like 'qu' in "quest", in the South, like 'w' in "win". Used only at the beginning of a syllable.
- uy
- like 'wi' in "win", except faster.
Tones
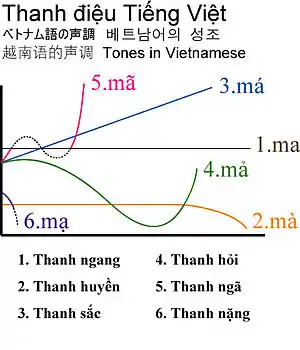
In Vietnamese, syllables can have six different tones, with five of them indicated by tone marks applied to the syllable's main vowel. Tone marks can be combined with the other diacritics.
- a
- flat
- à
- low
- á
- high rising; example: đấy, like saying "day?"
- ả
- falling, then rising
- ã
- creaky
- ạ
- a low "a'ah"
Grammar
One important difference between Vietnamese and Western languages is that Vietnamese has no polite equivalent of the second-person pronoun, "you." Only very close acquaintances and friends use the second-person pronoun "Mày" (pronounced "mhay" with a heavy A and accentuated Y), as it is considered very impolite between strangers. It is roughly equivalent to the pronoun "Omae" in Japanese. Consider it the extreme version of misusing "Toi" in place of "Vous" in French, except there is no equivalent of "Vous" in Vietnamese. Like with many other Asian cultures, it is more socially acceptable to be aware of your formal/informal relationship to another person, and imply it through the word you use to address them.
Strange as it might sound, conversational Vietnamese takes place almost entirely in the second and third persons. For example, instead of saying "I think you are very beautiful" to a girl you like, you might say, "This older male thinks you (the younger female) very beautiful" or abridge it to "You (the younger female) are very beautiful." There is always an overt implication in how you address someone according to their age and sex.
To Western ears, talking in the third person sounds stilted and pretentious, but to Vietnamese ears, it is the social norm. Vietnamese has a word for "I", tôi, but Vietnamese would use it only in abstract or formal situations (such as public speaking, addressing a television camera, or writing in a book.) Only foreigners use tôi in conversation, which sounds stilted to Vietnamese, but they understand why it is done and come to expect it.
In conversational Vietnamese, the proper way to refer to yourself and others depends on a hierarchy of age and sex. Many of the terms have a literal meaning of family relationships, though they are used for all people on all occasions. Options include:
- Bạn (friend, pronounced "bhang" with a heavy A. Easily confused with the word "table" to hilarious effect.)
- Con (child, pronounced "kon", and – parents will be amused – also means animal, for example "Con chim" literally means "(that) animal (which is a) bird".)
- Em (literally, younger person, generally reserved for a younger sister, younger female relative, or a female acquaintance whom you consider equal to or younger than you – refers to anyone younger than you but older than a child. It is the usual way to address your wife, girlfriend, or female lover, regardless of your own age or sex, with implications of endearment beyond daily usage of the word. Can be considered the equivalent of "my dear".)
- Anh (older brother – man older than you by up to 10-20 years depending on how close they are. Or refers to a man of the same age as you, but whom you hold in high regard even if you are slightly older. It is also the usual way to address a husband, boyfriend, or male lover, regardless of your own age or sex, with implications of endearment beyond daily usage.)
- Chị (older sister – woman older than you by up to 10-20 years depending on how close they are, with the implication that you feel the age between you and her does not matter. Generally only used for females slightly older than you.)
- Chú (literally, "Mister" with implications toward "uncle". Also used to address your father's younger brother – man older than you and who you feel deserves the distinction beyond "Anh".)
- Cô (literally, "Miss" or "Young Mrs." – woman older than you by 10+ years, or your female teacher prior to college. Implies that you feel she is a generation older than you, but you still think she is too young to be called "Madam" or "Mrs.")
- Bác (unisex term, used for both Sir and Madam, – refers to a mature person, generally 40 to 60 years old. Polite in that it implies you do not think the person is a senior or elderly yet.)
- Ông (literally, "old gentleman", grandfather – refers specifically to a senior man, 50-60+ years old depending on how close you are.)
- Bà (literally, "Madam" or "elderly lady", grandmother – refers specifically to a senior woman, 50-60+ years old depending on how close you are.)
Choose one from the list to represent yourself, and one to represent the person you are talking to, depending on sex and relative age. For example, to get the attention of a waiter or waitress in a restaurant, say em/anh/chị ơi (ơi being the ubiquitous Vietnamese term for "hey"). If you listen closely, when people address you or talk about you in Vietnamese, they will be using these terms. They will be very impressed if you can master this! Nonetheless, even between native Vietnamese speakers, it can get awkward when you try to figure out how to address someone who appears to be the same sex and, as far as you can tell, about the same age as you. Once you figure out their age and sex, they may have you use one of the above terms, or simply be amiable and ask you to call them "Ban", or "friend".
In formal situations, Vietnamese people generally refer to each other by a title and their second given name. Surnames are generally not used to address people in Vietnam. For instance, Hồ Chí Minh has the surname Hồ, but would ordinarily be address as Bác Minh in Vietnamese.
For simplicity, however, many phrases below are translated without the relevant terms for you and/or your listener: For example, "How are you" is literally translated as "Healthy or not?" It is generally impolite to speak to a person without directly addressing them unless they're a subordinate, but Vietnamese usually don't take offense when foreigners omit this. Wherever you see tôi below, you can substitute one of the words above according to the circumstance.
Phrase list
The following are very commonly-used phrases. They are listed in a general order of importance:
Basics
|
Common signs
|
- Hello. (informal)
- Chào. (jow)
- Hello. (formal)
- Xin chào. (seen jow)
- Hello. (on the phone)
- A-lô. (AH-loh)
- How are you? (Are you healthy?)
- Khỏe không? (kweah kohng?)
- Fine, thank you. (I am healthy, thank you.)
- Tôi khoẻ, cảm ơn. (thoy kweah, gam uhhn)
- What is your name? (formal, to a man (forties or older, depending on the sensitivity of the person you address))
- Ông tên là gì? (ohng theyn la yi)
- What is your name? (formal, to a woman (forties or older, depending on the sensitivity of the person you address))
- Bà tên là gì? (ba theyn la yi)
- What is your name? (informal, to a male who is not quite middle-aged AND/OR is not significantly older than you)
- Anh tên là gì? (ayng theyn la yi) Anh is an umbrella term for any older male figure. Its literal meaning is "older brother".
- What is your name? (informal and also flattering, to a female who is not quite middle-aged AND not significantly older than you)
- Cô tên là gì? (goh theyn la yi) There is a distinction between this and the last phrase, because in Vietnamese culture, one generally assumes that a woman, regardless of whether she looks middle-aged or not, is either not yet married, or does not yet have children, or is younger than she looks. Using "Cô" instead of "Bà" implies that you are giving her the benefit of your lack of knowledge about her. Thus, if she feels the need, she will (as a result of your flattery and politeness) correct you to use the mature "Bà" or the gender-disregarding term for an adult who is anywhere in their late thirties to fifties, "Bac" which is equivalent to "Sir" or "Madam". Some men and women prefer to be addressed as the polite and age-ambiguous "Bac" indefinitely, until they feel it is appropriate to be addressed in more mature terms.
- My name is ______ .
- Tôi tên là ______ . (Thoye theyn la _____ .)
- Please.
- Làm ơn. (lam uhhn)
- Thank you.
- Cảm ơn. (gam uhhn)
- You're welcome.
- Không sao đâu. (kohng sao doh)
- Yes.
- Vâng (affirmative). (vuhng); Dạ (affirmative, respectful) (ya'a) ; Đúng (correct) (duhn)
- No.
- Không. (kohng)
- I'm sorry.
- Xin lỗi. (seen loh'EE)
- Goodbye
- Chào. (jow), Tạm biệt
- I can't speak Vietnamese [well].
- Tôi không biết nói tiếng Việt [giỏi lắm]. (thoy kohng bee-IT noh-Y thee-IHNG vee'it [yi-oh-i lahm])
- Do you speak English?
- Biết nói tiếng Anh không? (bee-IT noh-Y thee-IHNG ayng kohng)
- Is there someone here who speaks English?
- Có ai ở đây biết nói tiếng Anh không? (GAW ai dey bee-IT noh-Y thee-IHNG ayng kohng)
- Help!
- Cứu (tôi) với! (gih-OO (thoy) vuh-y!)
- Look out!
- Cẩn thận! (guhn tuh'n!)
- I don't understand.
- Tôi không hiểu. (thoy kohng hee-oh)
- Where is the toilet?
- Nhà vệ sinh ở đâu? (...)
- Be back soon
- Tôi sẽ quay lại sớm (...)
Problems
- Leave me alone.
- Đừng làm phiền tôi. (DUHung LAHm fien Thoy) (beware that "Thoi" with a fat and long sounding "T" translates to "enough!" in standard Vietnamese)
- Don't touch me!
- Đừng chạm vào tôi! (...)
- I'll call the police.
- Tôi sẽ gọi cảnh sát./Tôi sẽ gọi công an. (Thoy seEh GAWoy Kanh Sat/ Thoy seEH GAWoy Kong aanh)
- Police!
- Công an!/Cảnh sát! (Kong aanh!/Kanh Sat)
- Stop! Thief!
- Ngừng lại! Ăn trộm! (GNoong LAai! Anh Chom!)
- I need your help.
- Tôi cần (second person pronoun) giúp. (Thoy Khan yip )
- It's an emergency.
- Việc này khẩn cấp. (VAHech nuhay Khan gup)
- I'm lost.
- Tôi bị lạc. (Thoi bee lack)
- I lost my bag.
- Tôi bị mất cái túi. (Thoi bee mUHtt kai Thuii)
- I lost my wallet.
- Tôi bị mất cái ví. (Thoi bee mUHtt kai veee)
- I'm sick.
- Tôi bị bệnh. (Thoi bee binh)
- I've been injured.
- Tôi bị thương. (Thoi bee Tahuung)
- I need a doctor.
- Tôi cần một bác sĩ. (Thoi Khan moat back see)
- Can I use your phone?
- Tôi dùng điện thoại của (second person pronoun) được không? (Thoi young dean tahoaI KOOa DUHuc KHAong)
Numbers
(Phonetic approximations are in italics, and English words that sound very similar are in quotes.) When giving your age, it is common to say just the digits, e.g., "three-one" instead of "thirty-one".
- 0
- không (kumm, kowm, humm, or howm depending on the speaker and adjacent words)
- 1
- một (mo'oht, though most of the time comes out "moke" with a very slight swallowing of the final "k" sound)
- 2
- hai ("high")
- 3
- ba (bah)
- 4
- bốn ("bone")
- 5
- năm ("nahm")
- 6
- sáu (sao)
- 7
- bảy (bai-ee, almost like "buy" in English)
- 8
- tám (tahm)
- 9
- chín ("chean")
- 10
- mười (meui)
- 11
- mười một (muh-uh-ee mo'oht)
- 12
- mười hai (muh-uh-ee hai)
- 13
- mười ba (muh-uh-ee bah)
- 14
- mười bốn (muh-uh-ee bohn?)
- 15
- mười lăm (muh-uh-ee lahm)
- 16
- mười sáu (muh-uh-ee sao?)
- 17
- mười bảy (muh-uh-ee buh-ee)
- 18
- mười tám (muh-uh-ee thahm?)
- 19
- mười chín (muh-uh-ee jeen?)
- 20
- hai mươi (hai muh-uh-ee)
- 21
- hai mươi mốt (hai muh-uh-ee moht?)
- 22
- hai mươi hai (hai muh-uh-ee hai)
- 23
- hai mươi ba (hai muh-uh-ee bah)
- 30
- ba mươi (bah muh-uh-ee)
- 40
- bốn mươi (bohn? muh-uh-ee)
- 50
- năm mươi (nahm muh-uh-ee)
- 60
- sáu mươi (sao? muh-uh-ee)
- 70
- bảy mươi (buh-ee muh-uh-ee)
- 80
- tám mươi (thahm? muh-uh-ee)
- 90
- chín mươi (jeen? muh-uh-ee)
- 100
- một trăm (moht cham or often just "cham")
- 200
- hai trăm (hai cham)
- 300
- ba trăm (bah cham)
- 1000
- một ngàn/nghìn (mo'oht ngang/ngeen...)
- 2000
- hai ngàn/nghìn (hai ngang/ngeen...)
- 1,000,000
- một triệu (mo'oht chee'ou)
- 1,000,000,000
- một tỷ (mo'oht thee'ee?)
- 1,000,000,000,000
- một ngàn/nghìn tỷ
- number _____ (train, bus, etc.)
- số _____ ("so?")
- half
- nửa (neu-uh?)
- less
- ít hơn (eet huhhhn)
- more
- hơn (huhhhn), thêm (tehm)
Time
- now
- bây giờ (bee yuh...) (northern dialect example: 'buy zaa')
- later
- lát nữa (laht? neu'uh?)
- before
- trước (jyeuck?) (northern dialect example: 'Tchuck')
- morning
- sáng (sahng?)
- afternoon
- chiều (jee-oh) (northern dialect example: hard 'ch', like TR down tone)
- evening, night
- tối (thoh-ee), đêm (dehm)
Clock time
- one o'clock AM
- một giờ sáng (moht. yuh sahng?)
- two o'clock AM
- hai giờ sáng (hai yuh sahng?)
- noon
- trưa (jyeu-uh)
- one o'clock PM
- một giờ chiều (moht. yuh jee-oh)
- two o'clock PM
- hai giờ chiều (hai yuh jee-oh)
- midnight
- nửa đêm (neu-uh dehm)
Duration
- _____ minute(s)
- phút (foodt) _____
- _____ hour(s)
- tiếng (thee-uhng?) _____
- _____ day(s)
- ngày (ngai) _____
- _____ week(s)
- tuần (thoo-uhn) _____
- _____ month(s)
- tháng (tahng?) _____
- _____ year(s)
- năm (nahm) _____
Days
- today
- hôm nay (home nye)
- yesterday
- hôm qua (hohm gwah)
- tomorrow
- mai (my)
- this week
- tuần này (thoo-uhn nai)
- last week
- tuần qua (thoo-uhn gwah)
- next week
- tuần sau (thoo-uhn sao)
The days of the week are simply numbered, with the exception of Sunday:
- Sunday
- chủ nhật (joo nyuht.)
- Monday
- thứ hai (teu? hai)
- Tuesday
- thứ ba (teu? ba)
- Wednesday
- thứ tư (teu? theu)
- Thursday
- thứ năm (teu? nahm!)
- Friday
- thứ sáu (teu? sao?!)
- Saturday
- thứ bảy (teu? buh-ee?)
Months
Vietnamese does not have special names for each month. Instead, the months are simply numbered. Take the word tháng and add the month's number (see #Numbers above). For example:
- March
- tháng 3 / tháng ba (tahng? ba)
Writing time and date
- Friday, December 17, 2004
- Thứ sáu, ngày 17 tháng 12 năm 2004
- 12/17/2004
- 17/12/2004
- 2:36 AM
- Hai giờ 36 sáng
- 2:36 PM
- Hai giờ 36 chiều
- Two in the morning
- Hai giờ sáng
- Two in the afternoon
- Hai giờ chiều
- Ten in the evening
- Mười giờ đêm
- Half past two
- Hai giờ rưỡi
- Noon
- Trưa; 12 giờ trưa
- Evening
- Nửa đêm; 12 giờ đêm
Colors
When describing the color of an object etc., use the word below. When referring to the color itself, use màu or mầu followed by the word below.
- black
- đen (Dan)
- white
- trắng (chahng?!)
- gray
- xám (sahm?)
- red
- đỏ (daw... aw?)
- blue
- xanh nước (sahyng neu-uhk?)
- yellow
- vàng (vahng...)
- green
- xanh (lá cây) (sahyng lah? kay)
- orange
- cam (kahm)
- purple
- tím (just as it is written, tim but long 'i' )
- brown
- nâu (know)
Transportation
Bus and train
- How much is a ticket to _____?
- Một vé đến _____ là bao nhiêu? (mo'oht veah? dehn? _____ lah... bao nyee-oh)
- One ticket to _____, please.
- Xin cho tôi một vé đến _____. (seen jyaw thoh-ee mo'oht veah? dehn? _____)
- Where does this train/bus go?
- Tàu/xe này đi đâu? (thoe.../seah nay...! dee doh)
- Where is the train/bus to _____?
- Tàu/xe đi đến _____ ở đâu? (thoe.../seah dee dehn _____ uh...uh? doh)
- Does this train/bus stop in _____?
- Tàu/xe này có dừng tại _____ không? (thoe.../seah nay...! goh? zeung... thah'ee _____ kohng)
- When does the train/bus for _____ leave?
- Tàu/xe đi _____ chạy lúc nào? (thoe.../seah dee _____ jyah'ee loohk? nahh-oh...)
- When will this train/bus arrive in _____?
- Khi nào tàu/xe này sẽ đến _____? (kee nahh-oh thoe.../seah nay...! seah'uh? dehn? _____)
Directions
- How do I get to _____ ?
- Làm cách nào để tôi đến _____ ? (...)
- ...the train station?
- ...nhà ga? (...)
- ...the bus station?
- ...trạm xe buýt? (...)
- ...the airport?
- ...sân bay? (son bye...)
- ...downtown?
- ...thành phố? (...)
- Đường xuống phố như thế nào? (...)
- ...the youth hostel?
- ...nhà trọ cho khách du lịch? (...)
- ...the _____ hotel?
- ...khách sạn _____? (...)
- ...the American/Canadian/Australian/British consulate?
- ...tòa lãnh sự Mỹ/Canada/Úc/Anh? (...)
- Where are there a lot of...
- Nơi nào có nhiều... (...)
- ...hotels?
- ...khách sạn? (...)
- ...restaurants?
- ...nhà hàng? (...)
- ...bars?
- ...quán rượu? (...)
- ...sites to see?
- ...thắng cảnh? (...)
- Can you show me on the map?
- Chỉ trên bản đồ cho tôi được không? (...)
- street
- đường (...)
- Turn left.
- Rẽ trái. (...)
- Turn right.
- Rẽ phải. (...)
- left
- trái (...)
- right
- phải (...)
- straight ahead
- đi thẳng (...)
- towards the _____
- tiến đến _____ (...)
- past the _____
- đi qua _____ (...)
- before the _____
- trước _____ (...)
- Watch for the _____.
- Coi chừng _____. (...)
- intersection
- ngã ba/tư/năm/sáu/bảy (3/4/5/6/7-way intersection) (...)
- north
- bắc (...)
- south
- nam (...)
- east
- đông (...)
- west
- tây (...)
- uphill
- lên dốc (...)
- downhill
- xuống dốc (...)
Taxi
- Taxi!
- Taxi! (tha? see)
- Take me to _____, please.
- Vui lòng đưa tôi đến_____,. (...)
- How much does it cost to get to _____?
- Đến _____ giá bao nhiêu? (...)
- Take me there, please.
- Vui lòng đưa tôi đến đó. (...)
Lodging
- Do you have any rooms available?
- Bạn còn phòng không? (...)
- How much is a room for one person/two people?
- Giá phòng cho một/hai người là bao nhiêu? (...)
- Does the room come with...
- Trong phòng có ... không? (...)
- ...bedsheets?
- ...ga trải gường? (...)
- ...a bathroom?
- ...phòng vệ sinh? (...); ...phòng cầu tiêu (...)
- ...a telephone?
- ...điện thoại? (dee-ehn twhy)
- ...a TV?
- ...TV? (thee vee)
- May I see the room first?
- Tôi xem phòng trước có được không? (...)
- Do you have anything quieter?
- Có phòng nào yên tĩnh hơn không? (...)
- ...bigger?
- ...lớn hơn không? (...)
- ...cleaner?
- ...sạch hơn không? (...)
- ...cheaper?
- ...rẻ hơn không? (...)
- OK, I'll take it.
- OK, tôi sẽ lấy phòng này. (...)
- I will stay for _____ night(s).
- Tôi sẽ ở đây _____ đêm. (...)
- Can you suggest another hotel?
- Có thể giới thiệu cho tôi một khách sạn khác được không? (...)
- Do you have a safe?
- Có két an toàn không? (...)
- ...lockers?
- ... tủ đồ? (...)
- Is breakfast/supper included?
- Có kèm theo bữa sáng/tối không? (...)
- What time is breakfast/supper?
- Ăn sáng/tối lúc mấy giờ? (...)
- Please clean my room.
- Làm ơn dọn phòng giúp tôi. (...)
- Can you wake me at _____?
- Xin đánh thức tôi dậy lúc _____? (...)
- I want to check out.
- Tôi muốn check out. (...)
Money
- Do you accept American/Australian/Canadian dollars?
- Có chấp nhận đô la Mỹ/Úc/Canada không? (...)
- Do you accept British pounds?
- Có chấp nhận bảng Anh không? (...)
- Do you accept credit cards?
- Có chấp nhận thẻ tín dụng không? (...)
- Can you change money for me?
- Bạn đổi tiền cho tôi được không? (...)
- Where can I get money changed?
- Tôi có thể đi đổi tiền ở đâu? (...)
- Can you change a traveler's check for me?
- Có thể đổi séc du lịch cho tôi được không? (...)
- Where can I get a traveler's check changed?
- Tôi có thể đổi séc du lịch ở đâu? (...)
- What is the exchange rate?
- Tỷ giá là bao nhiêu? (...)
- Where is an automatic teller machine (ATM)?
- Máy rút tiền (ATM) ở đâu? (...)
Eating
- A table for one person/two people, please.
- Cho tôi một bàn cho một/hai người. (...)
- Can I look at the menu, please?
- Làm ơn cho tôi xem menu? (...)
- Can I look in the kitchen?
- Cho tôi xem nhà bếp được không? (...)
- Is there a house specialty?
- Quán ăn này có món đặc sản nào không? (...)
- Is there a local specialty?
- Ở vùng này có món đặc sản nào không? (...)
- I'm a vegetarian.
- Tôi là người ăn chay. (...)
- I don't eat pork.
- Tôi không ăn thịt lợn. (...)
- I don't eat beef.
- Tôi không ăn thịt bò. (...)
- I eat only kosher food.
- (...)
- Can you make it "lite", please? (less oil/butter/lard)
- Vui lòng làm nó ít béo được không? (ít dầu/bơ/mỡ heo...)
- fixed-price meal
- fixed-price meal (...)
- à la carte
- gọi theo món (...)
- breakfast
- bữa sáng (boo... ee? sahng?)
- lunch
- bữa trưa (boo... ee? cheu-uh)
- tea (meal)
- trà (...)
- supper
- bữa tối (boo... ee? chee-oh...)
- I want _____.
- Xin _____. ("seen")
- I want a dish containing _____.
- Cho tôi một đĩa có _____. (...)
- chicken
- (thịt) gà (teet. gah...)
- beef
- (thịt) bò (teet. baw...)
- fish
- cá (gah?)
- ham
- jambon (zhahm bohng)
- sausage
- xúc xích (sook? sick?)
- cheese
- phô mai (...)
- eggs
- trứng (cheung?)
- salad
- sa lát (...)
- (fresh) vegetables
- rau (tươi) (rao theu-uh-ee)
- (fresh) fruit
- trái cây (tươi) (chai? gai)
- bread
- bánh mì (ba'in me...)
- toast
- bánh mì nướng (bain mee... neu-uhng?)
- noodles
- mì (me...)
- rice (cooked; as a dish)
- cơm (guhm)
- rice (uncooked)
- gạo ("gah-ow.")
- beans (like mung beans)
- đậu (duh-oh.)
- beans (like coffee beans)
- hột (hoht.)
- May I have a glass of _____?
- Cho tôi một ly _____? (...)
- May I have a cup of _____?
- Cho tôi một cốc _____? (...)
- May I have a bottle of _____?
- Cho tôi một chai _____? (...)
- coffee
- cà phê (ga... fey)
- tea (drink)
- nước trà (neu-uk? chah...)
- _____ juice
- nước ép _____ (...)
- bubbly water
- nước ngọt (neu-uk? ngawt.)
- water
- nước (neu-uk?)
- beer
- rượu (rih-oh.), bia (pronounce "beer" with a British accent)
- red/white wine
- rượu đỏ/trắng (rih-oh. daw... aw? / chahng?!)
- May I have some _____?
- Có thể cho tôi _____? (...)
- salt
- muối (moo-ee?)
- black pepper
- hạt tiêu (haht. thee-oh)
- fish sauce
- nước mắm
- soy sauce
- xì dầu (in the north) / nước tương (in the south)
- butter
- bơ (buh)
- Excuse me, waiter? (getting attention of server)
- Phục vụ! Làm ơn... (...)
- I'm finished.
- Xong rồi. (sah-ohng roh-ee...)
- It was delicious.
- Nó rất ngon. (...)
- Please clear the plates.
- Xin hãy dọn đĩa đi. (...)
- The check, please.
- Thanh toán tiền giúp tôi. (...)
Bars
- Do you serve alcohol?
- Có rượu ở đây không? (...)
- Is there table service?
- (...)
- A beer/two beers, please.
- Cho tôi một/hai cốc bia. (...)
- A glass of red/white wine, please.
- Cho tôi một ly rượu đỏ/trắng. (...)
- A pint, please.
- (...)
- A bottle, please.
- Cho tôi một chai. (...)
- _____ (hard liquor) and _____ (mixer), please.
- (...)
- whiskey
- uytky (...)
- vodka
- (...)
- rum
- (...)
- water
- nước (neu-uhck?)
- soda pop
- nước ngọt (neu-uhck? ngawt.)
- club soda
- (...)
- tonic water
- (...)
- orange juice
- nước cam (neu-uhck? gam)
- Coke (soda)
- Côca-Côla (koh-kah? koh-la)
- Do you have any bar snacks?
- (...)
- One more, please.
- Cho tôi một ly/chai nữa. (...)
- Another round, please.
- (...)
- When is closing time?
- Bao giờ đóng cửa? (Bow yuh... downg? geu-uh?)
Shopping
- Do you have this in my size?
- (...)
- How much (money) is this?
- Bao nhiêu (tiền)? (bahw nyee-oh thee-uhn...)
- That's too expensive.
- Đắt quá. (daht?! kwahh?)
- Would you take _____?
- Bạn lấy _____ được không? (ley? _____ deu'uhk kohng)
- expensive
- đắt (daht?!)
- cheap
- rẻ (reah...uh?)
- I can't afford it.
- Tôi không có đủ tiền mua. (thoh-ee kohng kaw? doo...oo? thee-uhn... moo-uh)
- I don't want it.
- Tôi không muốn. (thoh-ee kohng moo-uhn?)
- You're cheating me.
- Mày ăn gian tôi. (my ang yang Thoy)
- I'm not interested.
- Tôi không thích lắm. (...)
- OK, I'll take it.
- OK, tôi sẽ lấy nó. (...)
- Can I have a bag?
- Bạn có túi không? (...)
- Do you ship (overseas)?
- Có thể gởi đồ (ngoài nước) không? (...)
- I need...
- Tôi cần... (thoh-ee cuhn...)
- ...toothpaste.
- ...kem đánh răng. (keahm dayng? rahng)
- ...a toothbrush.
- ...bàn chải đánh răng. (bahn... chah-ee? dayng? rahng)
- ...tampons.
- băng vệ sinh
- ...soap.
- ...xà bông. (sah... bohng)
- ...shampoo.
- ...dầu gội. (...)
- ...pain reliever. (e.g., aspirin or ibuprofen)
- ...thuốc giảm đau. (too-uhc? yah...ahm? dahw!)
- ...cold medicine.
- ...thuốc cảm. (...)
- ...stomach medicine.
- ...thuốc đau bụng. (...)
- ...a razor.
- ...dao cạo râu. (yahw kah'oh ruh-oo)
- ...an umbrella.
- ...dù/ô. (...)
- ...sunblock lotion.
- ...kem chống nắng. (...)
- ...a postcard.
- ...bưu thiếp. (...)
- ...postage stamps.
- ...tem. (tham)
- ...batteries.
- ...pin. (bean)
- ...writing paper.
- ...giấy. (yay?!)
- ...a pen.
- ...bút mực. (boot?!)
- ...a pencil.
- ...bút chì. (boot?! chee...)
- ...English-language books.
- ...sách Anh ngữ. (...)
- ...English-language magazines.
- ...tạp chí Anh ngữ. (thuh'p chee? ayng-eu'eu?)
- ...an English-language newspaper.
- ...báo Anh ngữ. (bahw? ayng-eu'eu?)
- ...an English-English dictionary.
- ...từ điển Anh-Anh. (theu... dee-n? ayng-ayng)
Driving
- I want to rent a car.
- Tôi muốn thuê xe. (...)
- Can I get insurance?
- Có bảo hiểm cho tôi không? (koh? bah...oo hee...m? chaw thoh-ee khohng)
- stop (on a street sign)
- dừng (...)
- one way
- một chiều (...)
- yield
- yield (...)
- no parking
- không đỗ xe (...)
- speed limit
- tốc độ cho phép (...)
- gas (petrol) station
- cây xăng (keh-ee sahng!)
- petrol
- xăng (sahng!)
- diesel
- ("...")
Authority
- I haven't done anything wrong.
- Tôi chưa làm gì sai. (thoh-ee cheu-uh lam zee sai?)
- It was a misunderstanding.
- Chỉ là hiểu lầm thôi. (chee...ee? lah... hee...oh? luhm... toh-ee)
- Where are you taking me?
- Bạn đang dẫn tôi đi đâu? (bahn dahng yuh'n? thoh-ee dee duhw)
- I am an American/Australian/British/Canadian citizen.
- Tôi là công dân Mỹ/Australia/Anh/Canada. (toh-ee lah... kohng yuhn mee'ee? / australia / ayng / kah-nah-dah)
- I want to talk to the (American/Australian/British/Canadian) (embassy/consulate).
- Tôi cần phải nói chuyện với (đại sứ quán/lãnh sự) (Mỹ/Australia/Anh/Canada). (thoh-ee kuhn... fah...ee? naw-ee? cheu-ee'n vuh-ee? (dah'i seu? kwahn?/lay'ng? seu'eu) (mee'ee?/australia/ayng/kah-nah-dah)
- I want to talk to a lawyer.
- Tôi muốn nói chuyện với luật sư. (...)
- Can I just pay a fine now?
- Tôi chỉ trả tiền phạt thôi được không? (...)
Learning more
- Vietnamese textbook at Wikibooks
- Learn Vietnamese Your Way Learn Vietnamese fast from English
- Vietnamese Online Web Application with 40 Interactive Free Lessons