Zazacatla
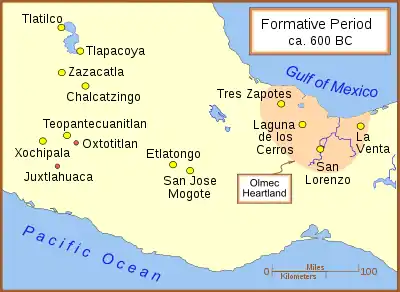
Zazacatla is a pre-Columbian archaeological site of Mesoamerica's central Mexican plateau region, in Xochitepec, dating to the mid-Formative period of Mesoamerican chronology. The site was first excavated in 2006 underneath a modern commercial and housing development site, some 13 km (8.1 mi) south of Cuernavaca, capital of the Mexican state of Morelos, and 40 km (25 mi) south of Mexico City. Initial investigations by archaeologists from Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) reported finding evidence of Olmec cultural influences at the site, the first such known for the western Morelos region.[1]
Site description
A fraction of Zazacatla's ceremonial center has been investigated, amounting to some 9,000 m2 (approx. 2.2 acres) of excavations.[2] The total area of the site is estimated to occupy some 2.5 km2, or slightly less than one square mile.[3]
Zazacatla's occupation is dated to between 800 and 500 BCE, making it roughly contemporary with the Olmec center of La Venta, 400 km (250 mi) to the east. Several sculptures of what appear to be Olmec-style "priests" have been uncovered. These sculptures, as well as Olmec-style architecture, have led to speculation on the role that Olmec culture played in Zazacatla.
Archaeologist Giselle Canto told Associated Press that the inhabitants adopted Olmec styles when they changed from a simpler egalitarian society to a more complex hierarchical one:
When their society became stratified, the new rulers needed emblems ... to justify their rule over people who used to be their equals.[4]
In January 2007 the governor of Morelos, Marco Adame Castillo, announced an offer for the state to underwrite the preservation of the site and to incorporate it into the tourism and cultural heritage plans for Morelos. He foreshadowed that a tourism project would be initiated at the site's location once the archaeological investigations had further developed.[5]
Notes
- Lovgren (2007), p.2.
- Confirma hallazgo arqueológico influencia olmeca en Zazacatla, 2007
- Lovgren (2007), p.2; Stevenson (2007).
- Quoted by Stevenson (2007).
- García (2007).
References
- "Confirma hallazgo arqueológico influencia olmeca en Zazacatla". El Sol de México (in Spanish). Organizacíon Editorial Mexicana. 2007-02-01. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
- García, Miguel Ángel (2007-01-26). "Posible, nuevo plan arqueológico en Xochitepec". La Jornada Morelos (in Spanish). Editora de Medios de Morelos. Retrieved 2007-02-09.
- Lovgren, Stefan (2007-01-26). "Ancient City Found in Mexico; Shows Olmec Influence". National Geographic News. National Geographic Society. Retrieved 2007-02-08.
- Pérez de Lara, Jorge (2007). "Olmec Discovery at Zazacatla". Mesoweb Reports and News. Mesoweb. Retrieved 2007-02-19.
- Stevenson, Mark (2007-01-25). "Olmec-influenced city found in Mexico". NBC News. Retrieved 2008-09-22. Also available as Gale General OneFile document number A158381284.
- Canto Aguilar, Giselle; Castro Mendoza; Víctor Mauricio (2007). "Los señores de Zazacatla, Morelos". Arqueología Mexicana. XIV (85): 16–19.
External links
- Olmec-Style Effigies from Zazacatla, photographs by Jorge Pérez de Lara, reproduced at Mesoweb
- Photo of the Olmec-style sculptures—note the downturned mouths.