YecM bacterial protein domain
In molecular biology, YecM refers to a protein domain found in Escherichia coli. It is a conserved, hypothetical protein with sequence homologues found exclusively in bacteria. Several bacterial YecM proteins in this particular family are of unknown function.
| YecM | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 structural genyyecn yecmyeyepomics, protein ec4020 | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | YecM | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF06185 | ||||||||
| Pfam clan | CL0104 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR010393 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1k4n / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Function
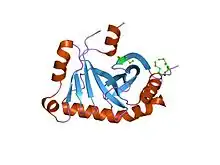
The precise function of the YecM domain remains to be elucidated. However, YecM structural homologues reveal that all the proteins bind a divalent metal cation. This comparison suggests that YecM may be a metal-binding protein and therefore may function as an enzyme.[1]
Structure
The protein domain, YecM, is a monomer. The eight, mostly antiparallel beta-strands form around C-terminal alpha-helix. There are four alpha helices in total.[1]
References
- Ling SH, Decker CJ, Walsh MA, She M, Parker R, Song H (2008). "Crystal structure of human Edc3 and its functional implications". Mol Cell Biol. 28 (19): 5965–76. doi:10.1128/MCB.00761-08. PMC 2547010. PMID 18678652.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.