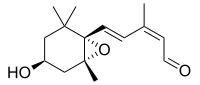
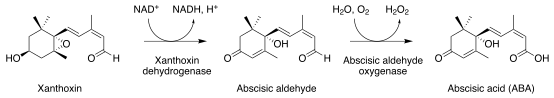
Xanthoxin
Xanthoxin is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the plant hormone abscisic acid.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2Z,4E)-5-[(1S,4S,6R)-4-Hydroxy-2,2,6-trimethyl-7-oxabicyclo[4.1.0]heptan-1-yl]-3-methylpenta-2,4-dienal | |
| Other names
Xanthoxal | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.547 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H22O3 | |
| Molar mass | 250.338 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.15 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 371.1 °C (700.0 °F; 644.2 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Seo, M; Koshiba, T (2002). "Complex regulation of ABA biosynthesis in plants". Trends in Plant Science. 7 (1): 41–8. doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(01)02187-2. PMID 11804826.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.