ipconfig
ipconfig (standing for "Internet Protocol configuration") is a console application program of some computer operating systems that displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings.[1]
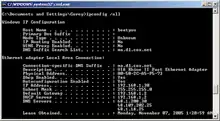 Screenshot of ipconfig /all output in Windows XP | |
| Developer(s) | Microsoft, ReactOS Contributors, Apple Inc. |
|---|---|
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Windows, ReactOS, macOS |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | Command |
| License | Windows: Proprietary commercial software ReactOS: GPLv2 |
Implementations
The command is available in Microsoft Windows, ReactOS, and in Apple macOS. The ReactOS version was developed by Ged Murphy and is licensed under the GPL.[2]
Microsoft Windows, ReactOS
The ipconfig command supports the command-line switch /all. This results in more detailed information than ipconfig alone.
An important additional feature of ipconfig is to force refreshing of the DHCP IP address of the host computer to request a different IP address. This is done using two commands in sequence. First, ipconfig /release is executed to force the client to immediately give up its lease by sending the server a DHCP release notification which updates the server's status information and marks the old client's IP address as "available". Then, the command ipconfig /renew is executed to request a new IP address.[3][4] Where a computer is connected to a cable or DSL modem, it may have to be plugged directly into the modem network port to bypass the router, before using ipconfig /release and turning off the power for a period of time, to ensure that the old IP address is taken by another computer.[5]
The /flushdns parameter can be used to clear the Domain Name System (DNS) cache to ensure future requests use fresh DNS information by forcing hostnames to be resolved again from scratch.[6]
Apple macOS
ipconfig in Mac OS X serves as a wrapper to the IPConfiguration agent, and can be used to control the Bootstrap Protocol and DHCP client from the command-line interface.[7] For example, you can release and renew an IP address if it happened to be assigned incorrectly by the DHCP server during the automated assignment process.[8] Like most Unix-based operating systems, Mac OS X also uses ifconfig for more direct control over network interfaces, such as configuring static IP addresses. The Ifconfig command in Linux has been replaced by the IP command
References
- "ipconfig". Microsoft Docs. 16 October 2017. Retrieved 25 August 2020.
- "Reactos/Ipconfig.c at master · reactos/Reactos". GitHub.
- Release and Renew Your IP Address
- Windows – Displaying, Releasing and Renewing a DHCP Lease
- whatsmyipaddress: How to change your IP address
- Windows 8.1 PCs Connect to the Network but not the Internet
- OS X developer manual
- "Ipconfig – network administration via the command line". IONOS Digitalguide. Retrieved 2022-08-23.
Further reading
- Frisch, Æleen (2001). Windows 2000 Commands Pocket Reference. O'Reilly. ISBN 978-0-596-00148-3.
- Stanek, William R. (2008). Windows Command-Line Administrator's Pocket Consultant, 2nd Edition. Microsoft Press. ISBN 978-0735622623.
- Barrett, Daniel J. (2012). Macintosh Terminal Pocket Guide: Take Command of Your Mac. O'Reilly. ISBN 978-1449328986.