Western Hockey League (1952–1974)
The Western Hockey League (WHL) was a minor professional ice hockey league based in Western Canada that operated from 1952 to 1974. The league was managed for most of its history by Al Leader, and had roots in the Pacific Coast Hockey League and the Western Canada Senior Hockey League. The championship trophy of the WHL was the Lester Patrick Cup.
| Sport | Ice hockey |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1952 |
| Founder | Al Leader |
| Ceased | 1974 |
| Countries | |
| Last champion(s) | Phoenix Roadrunners |
| Most titles | Vancouver Canucks (4) |
History
The league was founded in 1948 as the Pacific Coast Hockey League (PCHL). In 1951, it absorbed three teams from the Western Canada Senior Hockey League. In 1952, it adopted the WHL name.[1] In the late 1950s, Ron Butlin and Arthur Ryan Smith hosted a hot stove league on radio broadcasts of the league.[2]
The Western Hockey League was managed for most of its history by Al Leader.
During the 1960s, the WHL moved into a number of large west coast markets including Los Angeles and San Francisco. There was speculation that the WHL could grow into a major league capable of rivalling even the long-entrenched National Hockey League (NHL).[3]
In the 1965–66 and 1967–68 seasons, the WHL played an interlocking schedule with the American Hockey League. Fears that the WHL (or a WHL/AHL merger) could become a rival major league was among the factors that finally convinced the NHL to expand for the 1967–68 season.[4]
Several factors led to the WHL's decision to cease operations after the 1973–74 season. The Vancouver Canucks, who had earlier applied for the 1967 NHL expansion, were finally accepted into the league as an expansion team for the 1970–71 season. The NHL and World Hockey Association had moved into many of its traditional markets, and the talent pool had become strained by the fast growth in the number of professional teams. When the NHL announced in June 1974 that the owners of both the Denver Spurs and Seattle Totems had been granted "conditional" NHL franchises (neither of which came to fruition), the WHL announced the same day that it was folding. A few of its surviving teams were absorbed into the Central Hockey League (CHL). The Phoenix Roadrunners franchise jumped to the WHA for the 1974–75 season, while the Spurs jumped from the CHL to the WHA for the 1975–76 season (but folded mid-season).
The championship trophy of the WHL was the Lester Patrick Cup, which is currently on display at the Hockey Hall of Fame.
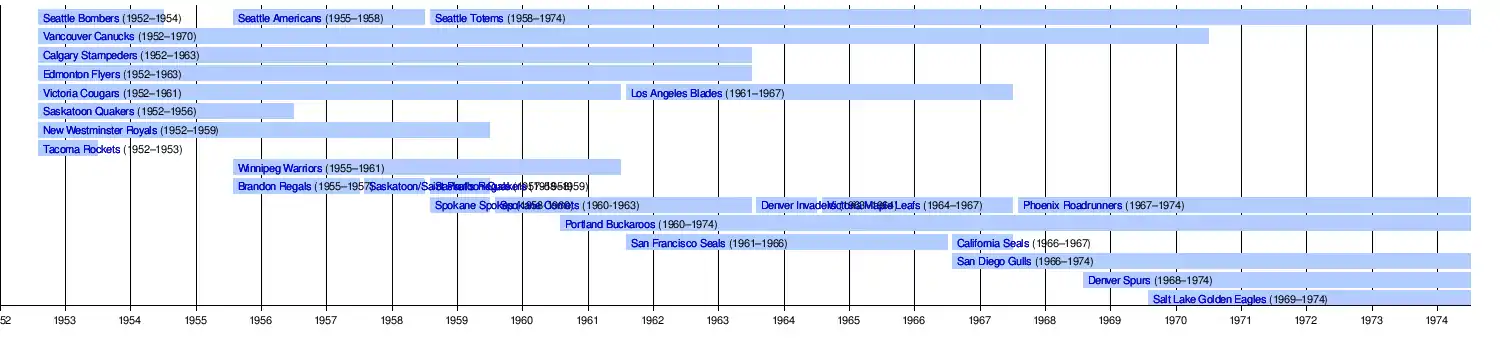
Teams
- Brandon Regals (1955–1957)
- Calgary Stampeders (1952–1963)
- California Seals (1966–1967)
- Denver Invaders (1963–1964)
- Denver Spurs (1968–1974)
- Edmonton Flyers (1952–1963)
- Los Angeles Blades (1961–1967)
- New Westminster Royals (1952–1959)
- Phoenix Roadrunners (1967–1974)
- Portland Buckaroos (1960–1974)
- Salt Lake Golden Eagles (1969–1974)
- San Diego Gulls (1966–1974)
- San Francisco Seals (1961–1966)
- Saskatoon Quakers (1952–1959)
- Seattle Americans (1955–1958)
- Seattle Bombers (1952–1954)
- Seattle Totems (1958–1975)
- Spokane Comets (1959–1963)
- Spokane Spokes (1958-1959)
- Tacoma Rockets (1952–1953)
- Vancouver Canucks (1952–1970)
- Victoria Cougars (1952–1961)
- Victoria Maple Leafs (1964–1967)
- Winnipeg Warriors (1955–1961)
Timeline
List of champions
| Season | Winner | Runner-up |
|---|---|---|
| 1952–53 | Edmonton Flyers | Saskatoon Quakers |
| 1953–54 | Calgary Stampeders | Edmonton Flyers |
| 1954–55 | Edmonton Flyers | Calgary Stampeders |
| 1955–56 | Winnipeg Warriors | Vancouver Canucks |
| 1956–57 | Brandon Regals | New Westminster Royals |
| 1957–58 | Vancouver Canucks | Calgary Stampeders |
| 1958–59 | Seattle Totems | Calgary Stampeders |
| 1959–60 | Vancouver Canucks | Victoria Cougars |
| 1960–61 | Portland Buckaroos | Seattle Totems |
| 1961–62 | Edmonton Flyers | Spokane Comets |
| 1962–63 | San Francisco Seals | Seattle Totems |
| 1963–64 | San Francisco Seals | Los Angeles Blades |
| 1964–65 | Portland Buckaroos | Victoria Maple Leafs |
| 1965–66 | Victoria Maple Leafs | Portland Buckaroos |
| 1966–67 | Seattle Totems | Vancouver Canucks |
| 1967–68 | Seattle Totems | Portland Buckaroos |
| 1968–69 | Vancouver Canucks | Portland Buckaroos |
| 1969–70 | Vancouver Canucks | Portland Buckaroos |
| 1970–71 | Portland Buckaroos | Phoenix Roadrunners |
| 1971–72 | Denver Spurs | Portland Buckaroos |
| 1972–73 | Phoenix Roadrunners | Salt Lake Golden Eagles |
| 1973–74 | Phoenix Roadrunners | Portland Buckaroos |
Championships by team
| Team | Championships | Runner-up |
|---|---|---|
| Vancouver Canucks | 4 | 2 |
| Seattle Totems | 3 | 2 |
| Portland Buckaroos | 3 | 6 |
| Edmonton Flyers | 3 | 1 |
| Phoenix Roadrunners | 2 | 1 |
| San Francisco Seals | 2 | 0 |
| Brandon Regals | 1 | 0 |
| Calgary Stampeders | 1 | 3 |
| Denver Spurs | 1 | 0 |
| Victoria Maple Leafs | 1 | 1 |
| Winnipeg Warriors | 1 | 0 |
| Saskatoon Quakers | 0 | 1 |
| New Westminster Royals | 0 | 1 |
| Victoria Cougars | 0 | 1 |
| Spokane Comets | 0 | 1 |
| Los Angeles Blades | 0 | 1 |
| Salt Lake Golden Eagles | 0 | 1 |
References
- Stott, Jon C. (2008). Ice Warriors: The Pacific Coast/Western Hockey League 1948–1974. Surrey, British Columbia: Heritage House Publishing. p. 45. ISBN 978-1-894974-54-7.
- Slade, Daryl (2014-06-26). "Calgary sporting pioneer dies in B.C. at age 89". Calgary Herald. Retrieved June 26, 2020.
- Los Angeles Times, 27 March 1959, p.C1: Official Says Hockey Would Go Big Here
- David Cruise; Alison Griffiths (1991). Net Worth: Exploding the Myths of Pro Hockey. Stoddart Publishing.