Wading River, New York
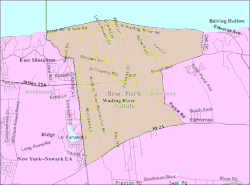
Wading River is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, New York, United States, on the North Shore of Long Island. As of the 2010 census, the CDP population was 7,719.[2] It is adjacent to Shoreham and shares a school district.
Wading River, New York | |
|---|---|
 The c.1820 Tuthill-Lapham House | |
 | |
 Wading River  Wading River  Wading River | |
| Coordinates: 40°57′9″N 72°49′48″W | |
| Country | United States |
| State | New York |
| County | Suffolk |
| Town | Brookhaven and Riverhead |
| Area | |
| • Total | 12.52 sq mi (32.41 km2) |
| • Land | 9.78 sq mi (25.33 km2) |
| • Water | 2.73 sq mi (7.08 km2) |
| Elevation | 92 ft (28 m) |
| Population (2020) | |
| • Total | 7,731 |
| • Density | 790.41/sq mi (305.19/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP code | 11792 |
| Area code(s) | 631, 934 |
| FIPS code | 36-77772 |
| GNIS feature ID | 0968624 |
| Website | www.brookhavenny.gov |
Most of Wading River lies within the Town of Riverhead, but a small portion is in the Town of Brookhaven. The name of the hamlet comes from the original Algonquian name for the area, Pauquaconsuk, meaning "the place where we wade for thick, round-shelled clams". It was also previously known as “Lonsefekwa”. "Wading in the River" or Wading River was adopted by the first English colonists.
History
1671
The earliest English records show a settlement known as Wading River was founded by eight colonial families. "The spot for the village was chosen with care. There was a stream adequate for water power and abounding in seafood...good water for drinking...soil rich enough to grow essential crops, woodland for fuel, building material and food, topography to offer protection from the elements, meadowland for its grass."[3]
Until 1947
Between 1895 and 1938, the Port Jefferson Branch of the Long Island Rail Road extended to Wading River. It was once planned to continue eastward to rejoin the Main Line at Riverhead or Calverton. From 1905 to 1928, Wading River was also the site of an LIRR demonstration farm. Another was east of Medford Station on the Main Line. The Wading River station closed in 1938. During World War II the Benson House was used by the FBI as the site of a secret counterintelligence operation to feed the Nazis deceptive information.
The hamlet of Wading River had a year-round population of less than 500. But during the summer months, hundreds of visitors filled the town to use Wildwood State Park, the cottages on the cliffs and dunes and, of course, the beaches.
It was in Wading River that Walter Lippmann wrote his books Public Opinion and The Phantom Public in the summers of 1921 and 1923 respectively [4]
1947
This year was a landmark year of change for the sleepy little hamlet; noteworthy accomplishments include:
- Returning service men from World War II began building homes in Wading River
- The formation of Wading River's own volunteer fire department, Wading River Fire Department
- The military installation known as Camp Upton was converted for use as Brookhaven National Laboratory
- The Wading River Historical Society was formed.[5]
Geography
Wading River is located at 40°57′9″N 72°49′48″W (40.952599, -72.829907).[6]
According to the United States Census Bureau, the CDP has a total area of 9.8 square miles (25.5 km2), of which 0.04 square miles (0.1 km2), or 0.40%, is water.[2]
Demographics of the CDP
As of the census[8] of 2000, there were 6,668 people, 2,370 households, and 1,813 families residing in the CDP. The population density was 680.5 inhabitants per square mile (262.7/km2). There were 2,713 housing units at an average density of 276.9 per square mile (106.9/km2). The racial makeup of the CDP was 95.10% White, 1.96% African American, 0.04% Native American, 0.97% Asian, 0.13% Pacific Islander, 0.81% from other races, and 0.97% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.69% of the population.
There were 2,370 households, out of which 35.6% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 68.7% were married couples living together, 5.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 23.5% were non-families. 18.7% of all households were made up of individuals, and 7.6% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.75 and the average family size was 3.16.
In the CDP, the population was spread out, with 27.0% under the age of 18, 5.5% from 18 to 24, 30.7% from 25 to 44, 26.5% from 45 to 64, and 10.3% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females, there were 100.1 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 97.1 males.
The median income for a household in the CDP was $63,938, and the median income for a family was $73,059. Males had a median income of $58,214 versus $34,594 for females. The per capita income for the CDP was $26,322. About 2.0% of families and 3.1% of the population were below the poverty line, including 0.7% of those under age 18 and 1.3% of those age 65 or over.
References
- "ArcGIS REST Services Directory". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved September 20, 2022.
- "Geographic Identifiers: 2010 Demographic Profile Data (G001): Wading River CDP, New York". U.S. Census Bureau, American Factfinder. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020. Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- Newsday, written and edited by the staff of (1998). Long Island, our story : the celebrated series. Melville, N.Y.: Newsday. ISBN 9781885134141. OCLC 40145139.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help) - Ronald Steel. Walter Lippmann and the American Century. Boston, 1980.
- Wading River Historical Society (Official Site)
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. February 12, 2011. Retrieved April 23, 2011.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.