2004 United States presidential election in Maine
The 2004 United States presidential election in Maine took place on November 2, 2004, and was part of the 2004 United States presidential election. Starting which, Maine is one of two states in the U.S. that instead of all of the state's four electors of the Electoral College to vote based upon the statewide results of the voters, two of the individual electors vote based on their congressional district because Maine has two congressional districts. The other two electors vote based upon the statewide results.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elections in Maine |
|---|
 |
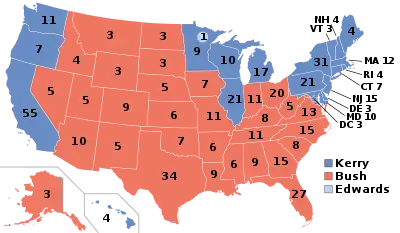
Maine was considered by some to be a swing state, because of the closeness of some polls.[1] However, the polls were consistently won by Kerry and neither campaign prioritized the state. On election day, Democrat John Kerry won the popular vote with 53.57% over George W. Bush with 44.58%. This is the most recent presidential election in which a losing Democrat won Maine's 2nd congressional district, and remained the last time until 2020 that the district voted for a losing candidate. This is the only election since 1968 in which a Republican won the popular vote without the state. Bush remains the only Republican to win two terms in the White House without carrying Maine at least once.
Campaign
There were 12 news organizations who made state-by-state predictions of the election. Here are their last predictions before election day.[2]
| Source | Ranking |
|---|---|
| D.C. Political Report | Lean D |
| Associated Press | Lean D |
| CNN | Likely D |
| Cook Political Report | Lean D |
| Newsweek | Lean D |
| New York Times | Lean D |
| Rasmussen Reports | Likely D |
| Research 2000 | Solid D |
| Washington Post | Toss-up |
| Washington Times | Lean D |
| Zogby International | Likely D |
| Washington Dispatch | Likely D |
Polling
Out of 15 pre-election polls, Kerry won thirteen of them. By the end of October, all polls showed Kerry over 50%. The final Real Clear Politics average showed Kerry leading 51% to 41.5% with a margin of 9.5%.[3] In three Survey USA polls taken in October, Kerry's numbers increased each time from 49% to 51% to 52%. Also, the final three polls averaged Kerry with 51% to Bush at 45%.[4]
Analysis
Once a typical Yankee Republican state, Maine has not been carried by a Republican presidential nominee since George H. W. Bush did so in 1988. While the younger Bush did make a play for the state in 2004, John Kerry ultimately won it by a fairly comfortable 9-point margin, including its two Congressional districts. Maine is one of two states, the other being Nebraska, which allocate their electoral votes by Congressional district. A candidate is awarded an electoral vote for each district won, even if the candidate loses statewide, while the statewide winner is awarded two additional electoral votes. In 2016 and 2020, Republican Donald Trump won Maine's 2nd district despite losing the state overall, and thus he received one electoral vote from the state both times. This makes George W. Bush the last Republican, and the last candidate of either party until Joe Biden in 2020, to win a presidential election without carrying Maine's 2nd district.
Bush became the first Republican to win the White House without carrying Lincoln or Waldo Counties since James A. Garfield in 1880.
Results
Statewide
| 2004 United States presidential election in Maine | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | Candidate | Votes | Percentage | Electoral votes | |
| Democratic | John Kerry | 396,842 | 53.57% | 4 | |
| Republican | George W. Bush (incumbent) | 330,201 | 44.58% | 0 | |
| Independent | Ralph Nader | 8,069 | 1.09% | 0 | |
| Green | David Cobb | 2,936 | 0.40% | 0 | |
| Libertarian | Michael Badnarik | 1,965 | 0.27% | 0 | |
| Others | - | 739 | 0.10% | 0 | |
| Totals | 740,752 | 100.00% | 4 | ||
| Voter turnout | 72.69% | — | |||
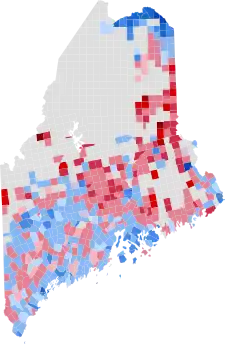
By county
| County | John Kerry Democratic |
George W. Bush Republican |
Various candidates Other parties |
Margin | Total votes cast | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # | % | # | % | # | % | # | % | ||
| Androscoggin | 30,503 | 54.40% | 24,519 | 43.73% | 1,045 | 1.86% | 5,984 | 10.67% | 56,067 |
| Aroostook | 19,569 | 51.86% | 17,564 | 46.55% | 600 | 1.59% | 2,005 | 5.31% | 37,733 |
| Cumberland | 94,846 | 58.20% | 65,384 | 40.12% | 2,732 | 1.68% | 29,462 | 18.08% | 162,962 |
| Franklin | 9,465 | 54.83% | 7,378 | 42.74% | 418 | 2.42% | 2,087 | 12.09% | 17,261 |
| Hancock | 18,048 | 54.49% | 14,405 | 43.49% | 669 | 2.02% | 3,643 | 11.00% | 33,122 |
| Kennebec | 35,616 | 53.34% | 29,761 | 44.57% | 1,395 | 2.09% | 5,855 | 8.77% | 66,772 |
| Knox | 12,690 | 54.59% | 10,103 | 43.46% | 454 | 1.95% | 2,587 | 11.13% | 23,247 |
| Lincoln | 11,351 | 51.26% | 10,370 | 46.83% | 421 | 1.90% | 981 | 4.43% | 22,142 |
| Oxford | 16,618 | 52.68% | 14,196 | 45.00% | 732 | 2.32% | 2,422 | 7.68% | 31,546 |
| Penobscot | 40,417 | 49.22% | 40,318 | 49.10% | 1,377 | 1.68% | 99 | 0.12% | 82,112 |
| Piscataquis | 4,409 | 44.36% | 5,299 | 53.31% | 232 | 2.33% | -890 | -8.95% | 9,940 |
| Sagadahoc | 11,107 | 52.69% | 9,497 | 45.05% | 475 | 2.25% | 1,610 | 7.64% | 21,079 |
| Somerset | 13,555 | 50.00% | 12,953 | 47.78% | 600 | 2.21% | 602 | 2.22% | 27,108 |
| Waldo | 11,555 | 51.77% | 10,309 | 46.19% | 454 | 2.03% | 1,246 | 5.58% | 22,318 |
| Washington | 8,391 | 48.47% | 8,619 | 49.79% | 300 | 1.73% | -228 | -1.32% | 17,310 |
| York | 58,702 | 53.35% | 49,526 | 45.01% | 1,805 | 1.64% | 9,176 | 8.34% | 110,033 |
| Total | 396,842 | 53.57% | 330,201 | 44.58% | 13,709 | 1.85% | 66,641 | 8.99% | 740,752 |
|
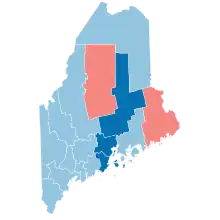
Democratic
Hold
Gain from Republican |
Republican
Hold
|
Counties that flipped from Republican to Democratic
Congressional district
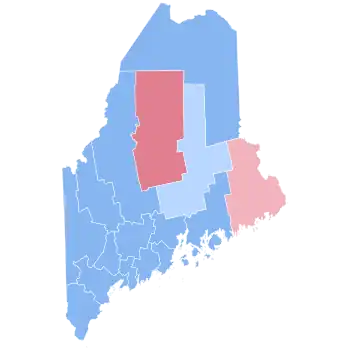
Kerry won both congressional districts.[9]
| District | Bush | Kerry | Representative |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st | 43% | 55% | Tom Allen |
| 2nd | 46% | 52% | Michael Michaud |
Electors
Technically the voters of Maine cast their ballots for electors: representatives to the Electoral College. Maine is allocated 4 electors because it has 2 congressional districts and 2 senators. All candidates who appear on the ballot or qualify to receive write-in votes must submit a list of 4 electors, who pledge to vote for their candidate and his or her running mate. Whoever wins the majority of votes in the state is awarded just 2 of the electoral votes. The other 2 electoral votes are based upon the congressional district results. Their chosen electors then vote for president and vice president. Although electors are pledged to their candidate and running mate, they are not obligated to vote for them.[10] An elector who votes for someone other than his or her candidate is known as a faithless elector.
The electors of each state and the District of Columbia met on December 13, 2004, to cast their votes for president and vice president. The Electoral College itself never meets as one body. Instead the electors from each state and the District of Columbia met in their respective capitols.
The following were the members of the Electoral College from the state. Since Kerry won both congressional districts, all 4 were pledged to Kerry/Edwards.
- Lu Bauer, elector for the 1st Congressional district.
- David Garrity, elector for the 2nd Congressional district.
- Jill Duson, at-large elector.
- Samuel Shapiro, at-large elector.
References
- "CNN.com Specials". CNN.
- "Archived copy". dcpoliticalreport.com. Archived from the original on November 21, 2010. Retrieved October 23, 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - "RealClear Politics - Polls".
- "Election 2004 Polls - Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". Archived from the original on June 2, 2006.
- "George W Bush - $374,659,453 raised, '04 election cycle, Republican Party, President".
- "John F Kerry - $345,826,176 raised, '04 election cycle, Democrat Party, President".
- "CNN.com Specials". CNN.
- "CNN.com Specials". CNN.
- "Presidential Results by Congressional District, 2000-2008 – Swing State Project".
- "Electoral College". California Secretary of State. Archived from the original on October 30, 2008. Retrieved November 1, 2008.