Townsend discharge
In electromagnetism, the Townsend discharge or Townsend avalanche is a ionisation process for gases where free electrons are accelerated by an electric field, collide with gas molecules, and consequently free additional electrons. Those electrons are in turn accelerated and free additional electrons. The result is an avalanche multiplication that permits electrical conduction through the gas. The discharge requires a source of free electrons and a significant electric field; without both, the phenomenon does not occur.
The Townsend discharge is named after John Sealy Townsend, who discovered the fundamental ionisation mechanism by his work circa 1897 at the Cavendish Laboratory, Cambridge.
General description
The avalanche occurs in a gaseous medium that can be ionised (such as air). The electric field and the mean free path of the electron must allow free electrons to acquire an energy level (velocity) that can cause impact ionisation. If the electric field is too small, then the electrons do not acquire enough energy. If the mean free path is too short, the electron gives up its acquired energy in a series of non-ionising collisions. If the mean free path is too long, then the electron reaches the anode before colliding with another molecule.
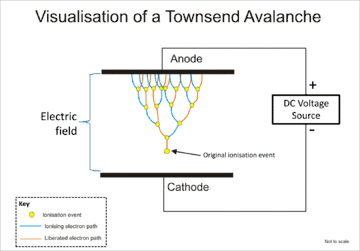
The avalanche mechanism is shown in the accompanying diagram. The electric field is applied across a gaseous medium; initial ions are created with ionising radiation (for example, cosmic rays). An original ionisation event produces an ion pair; the positive ion accelerates towards the cathode while the free electron accelerates towards the anode. If the electric field is strong enough, the free electron can gain sufficient velocity (energy) to liberate another electron when it next collides with a molecule. The two free electrons then travel towards the anode and gain sufficient energy from the electric field to cause further impact ionisations, and so on. This process is effectively a chain reaction that generates free electrons.[1] Initially, the number of collisions grows exponentially. The total number of electrons reaching the anode is equal to 2n with n the number of collisions, plus the single initiating free electron. Eventually, this relationship will break down - the limit to the multiplication in an electron avalanche is known as the Raether limit.
The Townsend avalanche can have a large range of current densities. In common gas-filled tubes, such as those used as gaseous ionisation detectors, magnitudes of currents flowing during this process can range from about 10−18 amperes to about 10−5 amperes.
Quantitative description
Townsend's early experimental apparatus consisted of planar parallel plates forming two sides of a chamber filled with a gas. A direct current high-voltage source was connected between the plates; the lower voltage plate being the cathode while the other was the anode. He forced the cathode to emit electrons using the photoelectric effect by irradiating it with X-rays, and he found that the current I flowing through the chamber depended on the electric field between the plates. However, this current showed an exponential increase as the plate gaps became small, leading to the conclusion that the gas ions were multiplying as they moved between the plates due to the high electric field.
Townsend observed currents varying exponentially over ten or more orders of magnitude with a constant applied voltage when the distance between the plates was varied. He also discovered that gas pressure influenced conduction: he was able to generate ions in gases at low pressure with a much lower voltage than that required to generate a spark. This observation overturned conventional thinking about the amount of current that an irradiated gas could conduct.[2]
The experimental data obtained from his experiments are described by the following formula
where
- I is the current flowing in the device,
- I0 is the photoelectric current generated at the cathode surface,
- e is Euler's number
- αn is the first Townsend ionisation coefficient, expressing the number of ion pairs generated per unit length (e.g. meter) by a negative ion (anion) moving from cathode to anode,
- d is the distance between the plates of the device.
The almost constant voltage between the plates is equal to the breakdown voltage needed to create a self-sustaining avalanche: it decreases when the current reaches the glow discharge regime. Subsequent experiments revealed that the current I rises faster than predicted by the above formula as the distance d increases: two different effects were considered in order to better model the discharge: positive ions and cathode emission.
Gas ionisation caused by motion of positive ions
Townsend put forward the hypothesis that positive ions also produce ion pairs, introducing a coefficient expressing the number of ion pairs generated per unit length by a positive ion (cation) moving from anode to cathode. The following formula was found
since , in very good agreement with experiments.
The first Townsend coefficient ( α ), also known as first Townsend avalanche coefficient is a term used where secondary ionisation occurs because the primary ionisation electrons gain sufficient energy from the accelerating electric field, or from the original ionising particle. The coefficient gives the number of secondary electrons produced by primary electron per unit path length.
Cathode emission caused by impact of ions
Townsend, Holst and Oosterhuis also put forward an alternative hypothesis, considering the augmented emission of electrons by the cathode caused by impact of positive ions. This introduced Townsend's second ionisation coefficient ; the average number of electrons released from a surface by an incident positive ion, according to the following formula:
These two formulas may be thought as describing limiting cases of the effective behavior of the process: either can be used to describe the same experimental results. Other formulas describing various intermediate behaviors are found in the literature, particularly in reference 1 and citations therein.
Conditions

A: random pulses by cosmic radiation
B: saturation current
C: avalanche Townsend discharge
D: self-sustained Townsend discharge
E: unstable region: corona discharge
F: sub-normal glow discharge
G: normal glow discharge
H: abnormal glow discharge
I: unstable region: glow-arc transition
J: electric arc
K: electric arc
A-D region: dark discharge; ionisation occurs, current below 10 microamps.
F-H region: glow discharge; the plasma emits a faint glow.
I-K region: arc discharge; large amounts of radiation produced.
A Townsend discharge can be sustained only over a limited range of gas pressure and electric field intensity. The accompanying plot shows the variation of voltage drop and the different operating regions for a gas-filled tube with a constant pressure, but a varying current between its electrodes. The Townsend avalanche phenomena occurs on the sloping plateau B-D. Beyond D the ionisation is sustained.
At higher pressures, discharges occur more rapidly than the calculated time for ions to traverse the gap between electrodes, and the streamer theory of spark discharge of Raether, Meek, and Loeb is applicable. In highly non-uniform electric fields, the corona discharge process is applicable. See Electron avalanche for further description of these mechanisms.
Discharges in vacuum require vaporization and ionisation of electrode atoms. An arc can be initiated without a preliminary Townsend discharge; for example when electrodes touch and are then separated.
Penning discharge
In the presence of a magnetic field, the likelihood of an avalanche discharge occurring under high vacuum conditions can be increased through a phenomenon known as Penning discharge. This occurs when electrons can become trapped within a potential minimum, thereby extending the mean free path of the electrons [Fränkle 2014].
Applications
Gas-discharge tubes
The starting of Townsend discharge sets the upper limit to the blocking voltage a glow discharge gas-filled tube can withstand. This limit is the Townsend discharge breakdown voltage, also called ignition voltage of the tube.
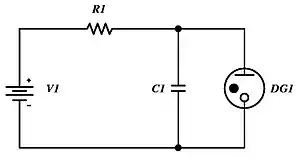
The occurrence of Townsend discharge, leading to glow discharge breakdown shapes the current–voltage characteristic of a gas-discharge tube such as a neon lamp in a way such that it has a negative differential resistance region of the S-type. The negative resistance can be used to generate electrical oscillations and waveforms, as in the relaxation oscillator whose schematic is shown in the picture on the right. The sawtooth shaped oscillation generated has frequency
- where
- is the glow discharge breakdown voltage,
- is the Townsend discharge breakdown voltage,
- , and are respectively the capacitance, the resistance and the supply voltage of the circuit.
- Since temperature and time stability of the characteristics of gas diodes and neon lamps is low, and also the statistical dispersion of breakdown voltages is high, the above formula can only give a qualitative indication of what the real frequency of oscillation is.
Gas phototubes
Avalanche multiplication during Townsend discharge is naturally used in gas phototubes, to amplify the photoelectric charge generated by incident radiation (visible light or not) on the cathode: achievable current is typically 10~20 times greater respect to that generated by vacuum phototubes.
Ionising radiation detectors
Townsend avalanche discharges are fundamental to the operation of gaseous ionisation detectors such as the Geiger–Müller tube and the proportional counter in either detecting ionising radiation or measuring its energy. The incident radiation will ionise atoms or molecules in the gaseous medium to produce ion pairs, but different use is made by each detector type of the resultant avalanche effects.
In the case of a GM tube the high electric field strength is sufficient to cause complete ionisation of the fill gas surrounding the anode from the initial creation of just one ion pair. The GM tube output carries information that the event has occurred, but no information about the energy of the incident radiation.[1]
In the case of proportional counters, multiple creation of ion pairs occurs in the "ion drift" region near the cathode. The electric field and chamber geometries are selected so that an "avalanche region" is created in the immediate proximity of the anode. A negative ion drifting towards the anode enters this region and creates a localised avalanche that is independent of those from other ion pairs, but which can still provide a multiplication effect. In this way spectroscopic information on the energy of the incident radiation is available by the magnitude of the output pulse from each initiating event.[1]
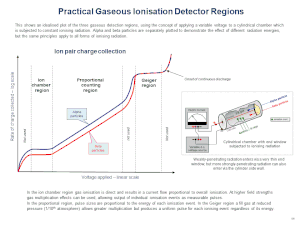
The accompanying plot shows the variation of ionisation current for a co-axial cylinder system. In the ion chamber region, there are no avalanches and the applied voltage only serves to move the ions towards the electrodes to prevent re-combination. In the proportional region, localised avalanches occur in the gas space immediately round the anode which are numerically proportional to the number of original ionising events. Increasing the voltage further increases the number of avalanches until the Geiger region is reached where the full volume of the fill gas around the anodes ionised, and all proportional energy information is lost.[1] Beyond the Geiger region the gas is in continuous discharge owing to the high electric field strength.
See also
Notes
- Glenn F Knoll. Radiation Detection and Measurement, third edition 2000. John Wiley and sons, ISBN 0-471-07338-5
- John Sealy Edward Townsend. 1868-1957 by A. von Engel. Biographical Memoirs of Fellows of the Royal Society. 1957 3, 256-272
References
- Little, P. F. (1956). "Secondary effects". In Flügge, Siegfried (ed.). Electron-emission • Gas discharges I. Handbuch der Physik (Encyclopedia of Physics). Vol. XXI. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York City: Springer-Verlag. pp. 574–663..
- Gewartowski, James W.; Watson, Hugh Alexander (1965). Principles of Electron Tubes: Including Grid-controlled Tubes, Microwave Tubes and Gas Tubes. D. Van Nostrand Co., Inc.
- Reich, Herbert J. (1944). Theory and applications of electron tubes (2nd ed.). McGraw-Hill Co., Inc. Chapter 11 "Electrical conduction in gases" and chapter 12 "Glow- and Arc-discharge tubes and circuits".
- Kuffel, E.; Zaengl, W. S.; Kuffel, J. (2004). High Voltage Engineering Fundamentals (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-7506-3634-6.
- Frankle, FM, et al. (2014). "Penning discharge in the KATRIN pre-spectrometer". Journal of Instrumentation. 9 (7): P07028. Bibcode:2014JInst...9P7028F. doi:10.1088/1748-0221/9/07/P07028. S2CID 123114495. Retrieved Dec 15, 2021.