Potassium thioacetate
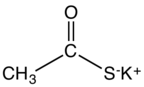
Potassium thioacetate is an organosulfur compound and a salt with the formula CH3COS−K+. This white, water-soluble solid is used as a reagent for preparing thioacetate esters and other derivatives.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.759 |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | C005732 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H3KOS | |
| Molar mass | 114.21 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| good | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Synthesis and reactions
Potassium thioacetate, which is commercially available, can be prepared by combining acetyl chloride and potassium hydrogen sulfide:
It arises also by the neutralization of thioacetic acid with potassium hydroxide.
Use in preparation of thiols
In a common application, potassium thioacetate is combined with alkylating agents to give thioacetate esters (X = halide):
Hydrolysis of these esters affords thiols:
The thioacetate esters can also be cleaved with methanethiol in the presence of stoichiometric base, as illustrated in the preparation of pent-4-yne-1-thiol:[2]
References
- Zongjun Qiao and Xuefeng Jiang "Potassium Thioacetate" e-EROS Encyclopedia Of Reagents For Organic Synthesis, 2014. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01737
- Matteo Minozzi; Daniele Nanni; Piero Spagnolo (2008). "4-Pentyne-1-thiol". EEROS. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00855. ISBN 978-0-471-93623-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.