Theories of taxation
Several theories of taxation exist in public economics. Governments at all levels (national, regional and local) need to raise revenue from a variety of sources to finance public-sector expenditures.
| Part of a series on |
| Taxation |
|---|
 |
| An aspect of fiscal policy |
Adam Smith in The Wealth of Nations (1776) wrote:
- "Such things as defending the country and maintaining the institutions of good government are of general benefit to the public. Thus, it is reasonable that the population as a whole should contribute to the tax costs. It is also reasonable to demand certain other things of a tax system – for example, that the amounts of tax individuals pay should bear some relationship to their abilities to pay… Good taxes meet four major criteria. They are (1) proportionate to incomes or abilities to pay (2) certain rather than arbitrary (3) payable at times and in ways convenient to the taxpayers and (4) cheap to administer and collect."[1]
In modern public-finance literature, a whole economy of the tax system has developed (tax system economics), which can be defined as "the overall management of public revenue of a state or integration grouping's public revenues and expenditures in order to shape smart economic policies that stimulates economic growth and development and safeguards against functional risks for present and future generations."[2] A narrower view of the theory of taxation reduces the system to two issues: who can pay and who can benefit (Benefit principle). Influential theories have been the ability theory presented by Arthur Cecil Pigou[3] and the benefit theory developed by Erik Lindahl.[4][5] There is a later version of the benefit theory known as the "voluntary exchange" theory.[6]
Under the benefit theory, tax levels are automatically determined, because taxpayers pay proportionately for the government benefits they receive. In other words, the individuals who benefit the most from public services pay the most taxes. Here, two models adopting the benefit approach are discussed: the Lindal model and the Bowen model.
Lindahl's model
Lindahl tries to solve three problems:
- Extent of state activity
- Allocation of the total expenditure among various goods and services
- Allocation of tax burden
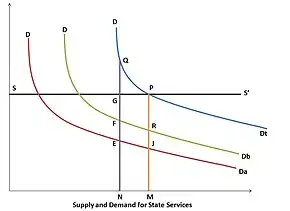
In the Lindahl model, if SS’ is the supply curve of state services it is assumed that production of social goods is linear and homogenous. DDa is the demand curve of taxpayer A, and DDb is the demand curve of taxpayer B. The Horizontal summation of the two demand curves results in the community’s total demand schedule for state services. A and B pay different proportions of the cost of the services which is vertically measured. When ON (O = graph origin, at axes intersection) is the amount of state services produced, A contributes NE and B contributes NF; the cost of supply is NG. Since the state is non-profit, it increases its supply to OM. At this level, A contributes MJ and B contributes MR (the total cost of supply). Equilibrium is reached at point P on a voluntary-exchange basis.
The Lindahl equilibrium proposes that individuals pay for the provision of a public good according to their marginal benefits in order to determine the efficient level of provision for public goods. In the equilibrium state, all individuals consume the same quantity of public goods but may face different prices because some people may value a particular good more than others. The Lindahl equilibrium price is the resulting amount paid by an individual for his or her share of the public goods.
Bowen's model
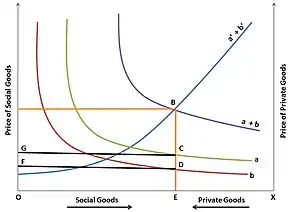
Bowen’s model has more operational significance, since it demonstrates that when social goods are produced under conditions of increasing costs, the opportunity cost of private goods is foregone. For example, if there is one social good and two taxpayers (A and B), their demand for social goods is represented by a and b; therefore, a+b is the total demand for social goods. The supply curve is shown by a'+b', indicating that goods are produced under conditions of increasing cost. The production cost of social goods is the value of foregone private goods; this means that a'+b' is also the demand curve of private goods. The intersection of the cost and demand curves at B determines how a given national income should (according to taxpayers' desires) be divided between social and private goods; hence, there should be OE social goods and EX private goods. Simultaneously, the tax shares of A and B are determined by their individual demand schedules. The total tax requirement is the area (ABEO) out of which A is willing to pay GCEO and B is willing to pay FDEO.
Advantages and limitations
The advantage of the benefit theory is the direct correlation between revenue and expenditure in a budget. It approximates market behaviour in the allocation procedures of the public sector. Although simple in its application, the benefit theory has difficulties:
- It limits the scope of government activities
- Government can neither support the poor nor take steps to stabilize the economy
- Applicable only when beneficiaries can be observed directly (impossible for most public services)
- Taxation in accord with the benefit principle would leave distribution of real incomes unchanged
Ability-to-pay approach
The ability-to-pay approach treats government revenue and expenditures separately. Taxes are based on taxpayers’ ability to pay; there is no quid pro quo. Taxes paid are seen as a sacrifice by taxpayers, which raises the issues of what the sacrifice of each taxpayer should be and how it should be measured:
- Equal sacrifice: The total loss of utility as a result of taxation should be equal for all taxpayers (the rich will be taxed more heavily than the poor)
- Equal proportional sacrifice: The proportional loss of utility as a result of taxation should be equal for all taxpayers
- Equal marginal sacrifice: The instantaneous loss of utility (as measured by the derivative of the utility function) as a result of taxation should be equal for all taxpayers. This therefore will entail the least aggregate sacrifice (the total sacrifice will be the least).
Mathematically, the conditions are as follows:
- Equal absolute sacrifice=U(Y)-U(Y-T), where y=income and t=tax amount
- Equal proportional sacrifice=(U(Y)-U(Y-T))/U(Y), where U(Y)=total utility from y
- Equal marginal sacrifice=(dU(Y-T))/(d(Y-T))[7]
References
- Adam Smith, The Wealth of Nations: A Translation into Modern English, ISR/Google Books, 2015. Book 5 (Government Finances: Public Expenditure, Taxation and Borrowing), pages 423, 429. Ebook ISBN 9780906321706
- Raczkowski, Konrad; Friedrich, Schneider; Węgrzyn, Joanna (2023). Tax System Economics. Warsaw: PWN Scientific Publishers. p. 14. ISBN 978-83-01-22663-3.
- Samuelson, Paul A. "Diagrammatic Exposition of a Theory of Public Extpenditure" (PDF). University of California, Santa Barbara. Retrieved August 27, 2012.
- "Erik Robert Lindahl". Encyclopædia Britannica. 1960-01-06. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- "Theories of Taxation – Benefit Theory – Cost of Service Theory – Ability to Pay Theory – Proportionate Principle". Economicsconcepts.com. Retrieved 2012-08-27.
- Giersch, Thorsten (August 2007). "From Lindahl's Garden to Global Warming: How Useful is the Lindahl Approach in the Context of Global Public Goods?" (PDF).
- Friedman, David D. (December 1999). Price Theory: an intermediate text. South-Western Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0538805643. Archived from the original on November 18, 2012. Retrieved November 23, 2012.