Tetracyclic
Tetracyclics are cyclic chemical compounds that contain four fused rings of atoms, for example, Tröger's base.
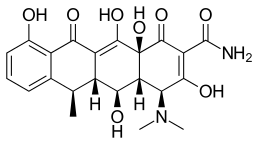
Doxycycline, a tetracyclic antibiotic.
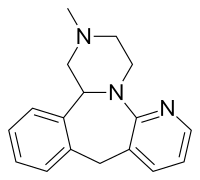
Mirtazapine, a tetracyclic antidepressant.
Some tricyclic compounds having three fused and one tethered ring (connected to main nucleus by a single bond) can also classified as tetracyclic, for example, ciclazindol.[1]
Tetracyclic compounds have various pharmaceutical uses, such as:
See also
References
- Wheatley, David (1982-05-01). "A new weight-reducing drug with novel properties". Postgraduate Medical Journal. 58 (679): 279–281. doi:10.1136/pgmj.58.679.279. ISSN 0032-5473. PMC 2426414. PMID 7050949.
- Jilani, Talha N.; Gibbons, Jonathan R.; Faizy, Rubina M.; Saadabadi, Abdolreza (2022). Mirtazapine. PMID 30085601. Retrieved 2023-01-03.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.