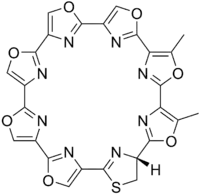
Telomestatin
Telomestatin is a macrocyclic chemical compound that acts by inhibiting the telomerase activity of in vitro cancer cells.[1] It was first isolated from the bacteria Streptomyces anulatus.[1] Telomestatin induces the formation of basket-type G-quadruplex (G4) structures from hybrid-type G-quadruplexes in the telomeric region. Upon formation of G4 structure there will be a decrease in the activity of the telomerase, which is involved in the replication of the telomeres and as a result the cell dies due to Hayflick type senescence.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(84R)-65,75-Dimethyl-84,85-dihydro-1(2,4),2,3,4,5,6,7(4,2)-heptakis([1,3]oxazolo)-8(2,4)-[1,3]thiazolocyclooctaphane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H14N8O7S | |
| Molar mass | 582.51 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- Shin-ya, Kazuo; Wierzba, Konstanty; Matsuo, Ken-ichi; Ohtani, Toshio; Yamada, Yuji; Furihata, Kazuo; Hayakawa, Yoichi; Seto, Haruo (2001). "Telomestatin, a novel telomerase inhibitor from Streptomyces anulatus". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 123 (6): 1262–1263. doi:10.1021/ja005780q. PMID 11456694.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.