Tan-Tan
Tan-Tan (Arabic: طانطان; Berber languages: ⵟⴰⵏⵟⴰⵏ) is a city in Tan-Tan Province in the region of Guelmim-Oued Noun in southwestern Morocco. It is a desert town with a population (2014 census) of 73,209.[1] It is the largest city in the province and second largest city in the region after the capital Guelmim.[2] It is located on the banks of the wadi Oued Ben khelil, which flows into the Draa River 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) north of the town. The Draa River at 1,100 kilometres (684 mi) is the longest in Morocco and flows into the Atlantic Ocean soon after the confluence with the wadi. The town also has an airport, Tan Tan Plage Blanche Airport.
Tan-Tan
| |
|---|---|
 Two camel statues mark the entrance to Tan-Tan, 2009 | |
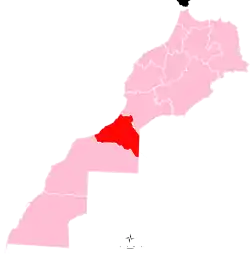
 Tan-Tan Location in Morocco  Tan-Tan Tan-Tan (Africa) | |
| Coordinates: 28°26′N 11°06′W | |
| Country | |
| Region | Guelmim-Oued Noun |
| Province | Tan-Tan |
| Elevation | 51 m (167 ft) |
| Population (2014) | |
| • Total | 73,209 |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
History
_%D0%B2_%D0%A2%D0%B0%D0%BD-%D0%A2%D0%B0%D0%BD%D0%B5_(%D0%9C%D0%B0%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%BA%D0%BA%D0%BE).jpg.webp)
The quartz figurine Venus of Tan-Tan was found in a river terrace deposit on the north bank of the Draa River. Dated between 200,000 and 500,000 BCE, it is considered one of the oldest human-form sculptures in the world, although its formation may actually be natural.[3]
Port
The nearby port, known as Tan-Tan Plage in French; Port of Tan-Tan in English; and El Ouatia, al-Watiyah or الوطية in Arabic is about 25 kilometres (16 mi) west of Tan-Tan on the Atlantic Ocean. With a population in 2004 of 6,294[2] it is the second-largest settlement in the province and ninth-largest in the region. Both Tan-Tan and Tan-Tan Plage are on Morocco's main highway, the N1.
Climate
Tan-Tan has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification BWh). While usually strongly moderated by the cold offshore Canary Current, occasional easterly winds from the Sahara Desert interior bring exceptionally hot temperatures to the maritime areas of southern Morocco. These winds being frequent in autumn and seasonal lag from warming sea temperatures cause October afternoons to average warmer than the July counterparts. The varying timing of the hot inland winds causes a vast difference between the individual monthly mean maxima and the many months in which brief temperatures above 40 °C (104 °F) may occur. Even the coldest winter nights remain well above freezing due to the Atlantic influence.
| Climate data for Tan-Tan (1991–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 30.4 (86.7) |
34.2 (93.6) |
38.5 (101.3) |
40.7 (105.3) |
44.0 (111.2) |
45.0 (113.0) |
47.6 (117.7) |
47.6 (117.7) |
42.8 (109.0) |
40.6 (105.1) |
35.6 (96.1) |
30.4 (86.7) |
47.6 (117.7) |
| Mean maximum °C (°F) | 26.5 (79.7) |
28.3 (82.9) |
32.9 (91.2) |
33.1 (91.6) |
33.4 (92.1) |
33.7 (92.7) |
34.3 (93.7) |
36.7 (98.1) |
34.1 (93.4) |
35.3 (95.5) |
32.5 (90.5) |
27.2 (81.0) |
41.4 (106.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 20.7 (69.3) |
21.4 (70.5) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.5 (72.5) |
23.3 (73.9) |
24.2 (75.6) |
25.6 (78.1) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.5 (79.7) |
24.1 (75.4) |
21.7 (71.1) |
23.9 (75.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 16.2 (61.2) |
17.0 (62.6) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
19.5 (67.1) |
20.8 (69.4) |
22.1 (71.8) |
23.1 (73.6) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.0 (71.6) |
19.5 (67.1) |
17.4 (63.3) |
19.8 (67.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 11.7 (53.1) |
12.5 (54.5) |
13.7 (56.7) |
14.5 (58.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
18.5 (65.3) |
19.2 (66.6) |
18.5 (65.3) |
17.5 (63.5) |
15.0 (59.0) |
12.9 (55.2) |
15.6 (60.1) |
| Mean minimum °C (°F) | 8.4 (47.1) |
9.4 (48.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
12.0 (53.6) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.2 (59.4) |
16.9 (62.4) |
17.3 (63.1) |
16.3 (61.3) |
14.2 (57.6) |
10.9 (51.6) |
9.8 (49.6) |
7.9 (46.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 4.9 (40.8) |
6.0 (42.8) |
7.7 (45.9) |
8.7 (47.7) |
11.4 (52.5) |
13.6 (56.5) |
15.5 (59.9) |
15.8 (60.4) |
14.5 (58.1) |
10.6 (51.1) |
7.7 (45.9) |
7.5 (45.5) |
4.9 (40.8) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 14.3 (0.56) |
17.0 (0.67) |
13.1 (0.52) |
3.8 (0.15) |
3.5 (0.14) |
1.4 (0.06) |
0.5 (0.02) |
5.0 (0.20) |
2.3 (0.09) |
11.8 (0.46) |
13.8 (0.54) |
14.1 (0.56) |
100.6 (3.96) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.4 | 1.0 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 1.7 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 17.8 |
| Source 1: NOAA[4] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat[5] | |||||||||||||
See also
- Tan-Tan Moussem
- Xlinks Morocco-UK Power Project – Proposed electricity interconnector between Morocco and Great Britain
References
- "Publications RGPH 2014 | Téléchargements | rgph2014". www.rgph2014.hcp.ma. Retrieved 1 April 2016.
- "Recensement général de la population et de l'habitat 2004". Hcp.ma. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- "The Tan-Tan Venus". Donsmaps.com. Retrieved 15 October 2013.
- "Tan-Tan Climate Normals 1991–2020". World Meteorological Organization Climatological Standard Normals (1991–2020). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Archived from the original on 10 September 2023. Retrieved 10 September 2023.
- "Climatologie de l'année à Tan-Tan" (in French). Infoclimat. Retrieved 9 October 2023.