T-vertices
T-vertices is a term used in computer graphics to describe a problem that can occur during mesh refinement or mesh simplification. The most common case occurs in naive implementations of continuous level of detail, where a finer-level mesh is "sewn" together with a coarser-level mesh by simply aligning the finer vertices on the edges of the coarse polygons. The result is a continuous mesh, however due to the nature of the z-buffer and certain lighting algorithms such as Gouraud shading, visual artifacts can often be detected.[1]

T-vertices after applying a subdivision modifier. The T-vertices result in cracks in the model because subdivision surfaces only work for meshes with correct topology.
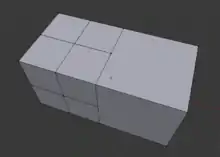
T-vertices created by joining a subdivided part with a non-subdivided part.
Some modeling algorithms such as subdivision surfaces will fail when a model contains T-vertices.
References
External links
 Media related to T-vertices at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to T-vertices at Wikimedia Commons
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.