Synageles venator
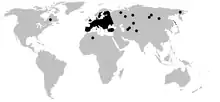
Synageles venator is a species of ant-like jumping spider. It occurs in the Palearctic region and Canada, and is also found in North Africa. In Central Europe it is the most common ant-like jumping spider.[1]
| Synageles venator | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Chelicerata |
| Class: | Arachnida |
| Order: | Araneae |
| Infraorder: | Araneomorphae |
| Family: | Salticidae |
| Subfamily: | Salticinae |
| Genus: | Synageles |
| Species: | S. venator |
| Binomial name | |
| Synageles venator (Lucas, 1836) | |
 | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Attus venator Lucas, 1836 | |
Description
Female are about four millimeters long, males slightly smaller. They are similar to the jumping spider Leptorchestes berolinensis, but feature a white line on the back of their heads.[1]
Effect of mimicry

These spiders are virtually indistinguishable from ants, even for humans looking at them rather closely. They move rapidly like an ant, and even raise their second pair of legs like an ant's antennae. Hand-raised tits that had never come in contact with ants ate spiders of this species readily. However, after their first encounters with real ants, and the nauseating effect of their formic acid, they refrained from eating S. venator.[1]

Footnotes
- Bellmann 1997: 238
References
- Bellmann, Heiko (1997): Kosmos-Atlas Spinnentiere Europas. Kosmos. ISBN 3-440-10746-9
External links
- Salticidae.org: Diagnostic drawings