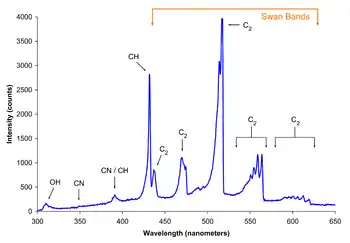
Swan band
Swan bands are a characteristic of the spectra of carbon stars, comets and of burning hydrocarbon fuels.[1][2] They are named for the Scottish physicist William Swan, who first studied the spectral analysis of radical diatomic carbon (C2) in 1856.[3]
Swan bands consist of several sequences of vibrational bands scattered throughout the visible spectrum.[4]
See also
References
- R.C. Johnson (1927). "The structure and origin of the Swan band spectrum of carbon". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A. 226 (636–646): 157–230. Bibcode:1927RSPTA.226..157J. doi:10.1098/rsta.1927.0005.
- W.E. Pretty (1927). "The Swan band spectrum of carbon". Proceedings of the Physical Society. 40 (1): 71–78. Bibcode:1927PPS....40...71P. doi:10.1088/0959-5309/40/1/313.
- W. Swan (1857). "On the prismatic spectra of the flames of compounds of carbon and hydrogen". Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 21 (3): 411–430. doi:10.1017/S0080456800032233. S2CID 98339461.
- Robert B. King (1948). "Relative Transition Probabilities of the Swan Bands of Carbon". Astrophysical Journal. 108: 429. Bibcode:1948ApJ...108..429K. doi:10.1086/145078.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.